A recent study by researchers from Sweden and the United Kingdom shows that CRISPR/Cas9-based genomic engineering can prompt unwanted on-target effects, and highlights the complexity of human DNA repair mechanisms in the presence of the powerful prokaryotic Cas9 nuclease. The paper is currently available on the bioRxiv* preprint server.
In the recent decade, genome engineering endeavors were revolutionized with the increasingly pervasive use of the CRISPR/Cas9 system. As a result, a myriad of toolsets has been developed, allowing efficient and straightforward loss-of-function perturbations of functional genomic elements.
Consequently, both the functionality and applicability of these systems are astonishing. In the presence of a guide RNA (gRNA) complementary to the target site and alongside an adjacent protospacer motif (PAM), the expressed Cas9 endonuclease creates a double-strand break (DSB) at a particular genomic site.
In cases when an exogenous homologous template of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is supplied, such DSB is restored by the homology-directed repair in order to introduce specific mutations or insertions of selected sequences.
However, this is not only valid for single nucleotide or short sequence deletions; longer DNA regions can also be excised from the genome with the use of dual gRNAs that flank the targeted region and direct Cas9 to induce two DSBs.
Still, albeit a plethora of functional sequences were deleted from the genome very successfully, thus far, transfer RNA (tRNA) genes have not been targeted in human cells with the use of the dual gRNA system.
These issues were recently addressed by a research group led by Dr. Keyi Geng from the Karolinska Institute, Science for Life Laboratory in Sweden, with an end goal of characterizing Cas9-induced genotypic abnormalities in human cells.
CRISPR/Cas9 and two cell systems
In order to investigate the functionality of the tRNA gene, these researchers have deleted two tRNA genes from the genomes of human hyperploid hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) and haploid chronic myeloid leukemia (HAP1) cells by utilizing the CRISPR/Cas9 system with dual gRNAs.
More specifically, genomic on-target alterations in the aforementioned HepG2 and HAP1 cell clones were analyzed by applying Xdrop-based enrichment for the target region after long-read sequencing. In addition, to test how effective CRISPR/Cas9 is for deleting tRNA genes, the researchers have focused on a pair located on the human chromosome 17.
The underlying alterations that caused a re-arrangement of the CRISPR/Cas9-targeted region were appraised by a customized de novo sequence assembly approach. In addition, on-target insertion events in other confirmed HepG2 and HAP1 deletions were also actively sought.
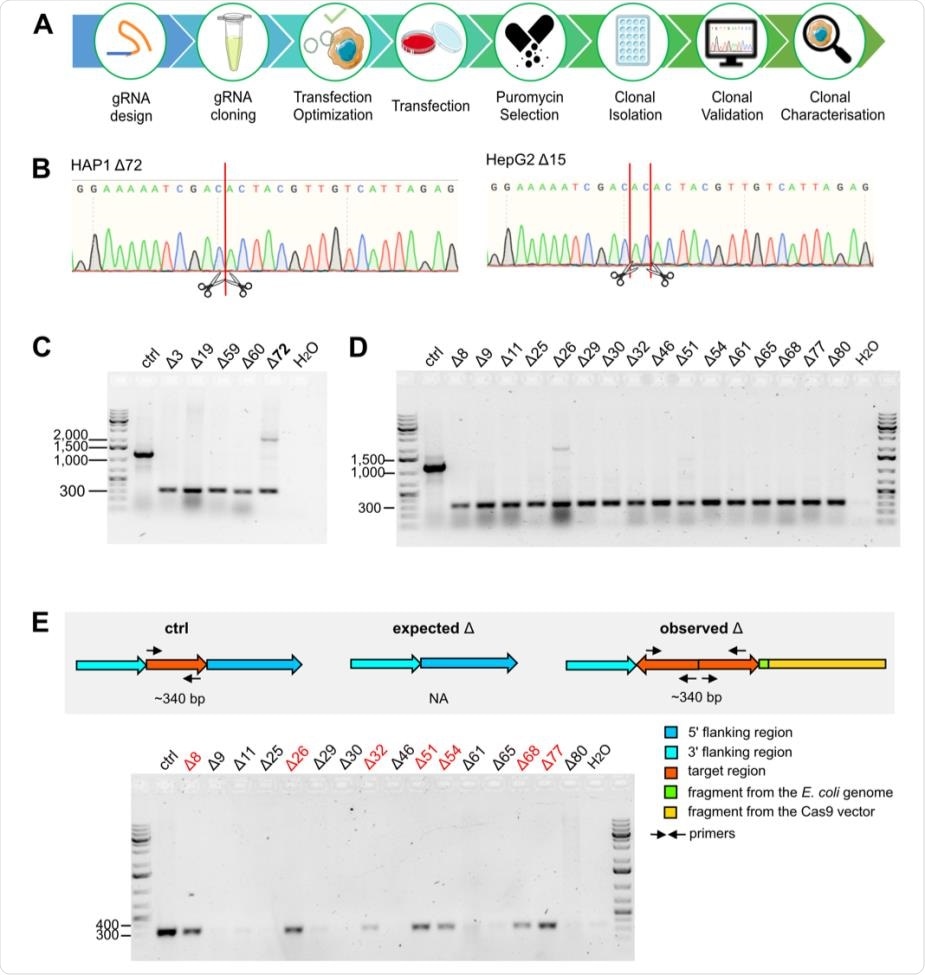
Validation of the deletion in HAP1 and HepG2. (A) Schematic illustration of the workflow to obtain single cell-derived deletion clones. (B) Chromatograms confirm deletions in the HAP1 Δ72 and HepG2 Δ15 clone. DSB sites induced by CRISPR/Cas9 are shown by red lines and scissors. (C-E) Agarose gels confirm the size of the obtained PCR products to validate deletion events (320bp) using primers annealing to the flanking regions of the target sites (Fig. 1B) in HAP1 (C) and HepG2 (D-E) clones. Additional primers to distinguish unmodified control, expected and observed deletion events are used (E). Marker bands specify DNA size in bp. In C, the HAP1 clone with duplicated target regions is bolded. In D, HepG2 Δ15 deletion clone is not shown here but in Fig. 1C. In E, deletion clones confirmed in D with a reinserted target region (340bp) are indicated in red.
Appraising undesired on-target effects
Although a genomic region of interest was cleaved by Cas9 in this study, the researchers have shown that the genomic fragment from the target region was not eliminated from the cell nucleus. Instead, the cleaved fragment has been duplicated, inverted and locally inserted into the genomes of HepG2 and HAP1 cells.
The study has also demonstrated the successful integration of exogenous DNA fragments in HepG2 cells. In addition, aberrant, target-derived DNA fragments were shown to be still functional, marked by active histones (i.e., proteins that enable structural support to a chromosome) and bound by RNA polymerase III.
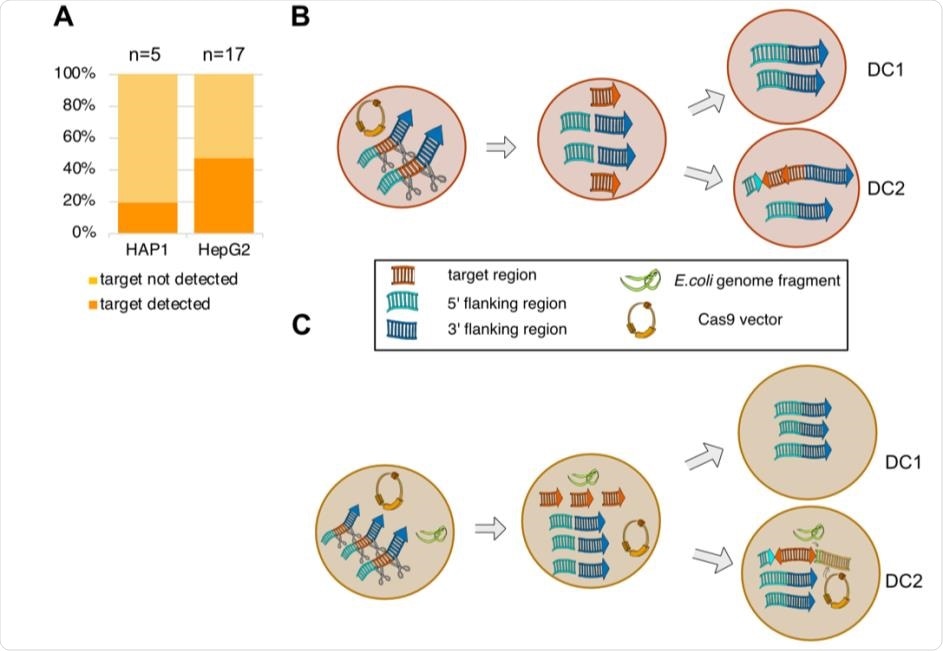
The frequency of on-target genomic alterations and a proposed model. (A) Stacked bar plot indicates the frequency of on-target genomic alterations in the validated HAP1 (n=5) and HepG2 (n=17) deletion clones. (B-C) Hypothetical model of on-target genomic alterations in HAP1 (B) and HepG2 (C). Cas9 caused DSBs cleaving the target region from the genome. Fragments were inverted and reinserted in one daughter cell (DC). In HepG2, additional exogenous DNA sequences from the E. coli genome and the Cas9 vector carrying gRNA-1 were integrated into the HepG2 genome downstream of the reinserted target-derived fragments.
Despite the initial attempt of researchers to delete tRNA genes in order to hinder their expression, the aberrant genomic modifications found at the original locus gave rise to active transcription of tRNA genes in both cell types used in this study.
This emphasizes the fact that CRISPR/Cas9-based genomic engineering can result in undesired on-target effects, and that inversion and duplication events (together with an integration of exogenous DNA fragments) can happen at the same time.
The consequential spectrum of the Cas9 deletion system
In conclusion, Xdrop technology in combination with de novo long-read sequence assembly surprisingly reveals complex genomic alterations that go along with CRISPR/Cas9 deletions. These genomic rearrangements are not amenable for study only with the use of approaches such as Sanger sequencing, PCR genotyping or standard alignments to the reference genome.
“Our findings broaden the consequential spectrum of the Cas9 deletion system, reinforce the necessity of meticulous genomic validations and rationalize extra caution when interpreting results from a deletion event”, underscore study authors in this bioRxiv paper.
These findings definitely represent a novel example of unintended CRISPR/Cas9 editing events that can be overlooked but that can significantly affect conclusions drawn from experimental read-outs. Hence, such serious concerns should always be addressed when studying the functionality of modified genomes.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Geng, K. et al. (2021). CRISPR/Cas9 deletions induce adverse on-target genomic effects leading to functional DNA in human cells. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.01.450727, https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.07.01.450727v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Geng, Keyi, Lara G. Merino, Linda Wedemann, Aniek Martens, Małgorzata Sobota, Yerma P. Sanchez, Jonas Nørskov Søndergaard, Robert J. White, and Claudia Kutter. 2022. “Target-Enriched Nanopore Sequencing and de Novo Assembly Reveals Co-Occurrences of Complex On-Target Genomic Rearrangements Induced by CRISPR-Cas9 in Human Cells.” Genome Research 32 (10): 1876–91. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.276901.122. https://genome.cshlp.org/content/32/10/1876.