Both the messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) and adenoviral vaccines have proven to be quite effective in reducing the spread of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and severity of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in fully vaccinated people. In fact, individuals vaccinated against COVID-19 have a ten times lower risk of experiencing severe COVID-19. However, following a quick-paced vaccination in early 2021, vaccination rates have slowed down in many countries during the summer months, despite the proven benefits of the vaccine.
Additionally, with the emergence of the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant, an increased viral transmission was observed, even with high vaccination rates. As a result, several non-pharmaceutical interventions had to be re-introduced including wearing masks and staying indoors.
 Study: COVID-19 Vaccination Mandates and Vaccine Uptake. Image Credit: Michael Vi / Shutterstock.com
Study: COVID-19 Vaccination Mandates and Vaccine Uptake. Image Credit: Michael Vi / Shutterstock.com

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Therefore, a higher vaccination rate would be required in some places to minimize the health and economic impacts of the virus. For example, several governments have introduced proof of vaccination mandates to increase the vaccination rates and reduce the transmissibility of the virus.
A new study published in the preprint server medRxiv* aimed to evaluate and quantify the effect of proof of vaccination mandates on first-dose vaccine uptake in nine Canadian provinces and three European countries including France, Italy, and Germany between July and September 2021.
About the study
The current study included data on COVID-19 vaccination numbers, cases, and deaths for all Canadian provinces, as well as France, Italy, and Germany. Announcement dates and implementation dates for the proof of vaccination mandates were collected from major newspapers and government websites.
The study also assessed the magnitude of changing weekly first doses after the announcement of the vaccination mandate. A behavioral model was also used to estimate where the decision to receive the first dose of the vaccine was affected by the announcement of the vaccination mandate, as well as to assess the current COVID-19 epidemiological and public health conditions.
The current study assumed that no lag was present between the mandate announcement and a person’s ability to receive a first vaccine dose, as well as that information on current public health conditions, is taken into account.
Study findings
The panel data analysis results indicated that Canadian provinces that announced vaccination mandates might have different trends in first dose vaccinations as compared to provinces that did not. The impact of the mandate was found to be relatively quick, at around one week after the announcement, with a significant effect on the pace of first-dose vaccinations. However, this effect gradually decreased with time and dissipated seven weeks after the announcement.
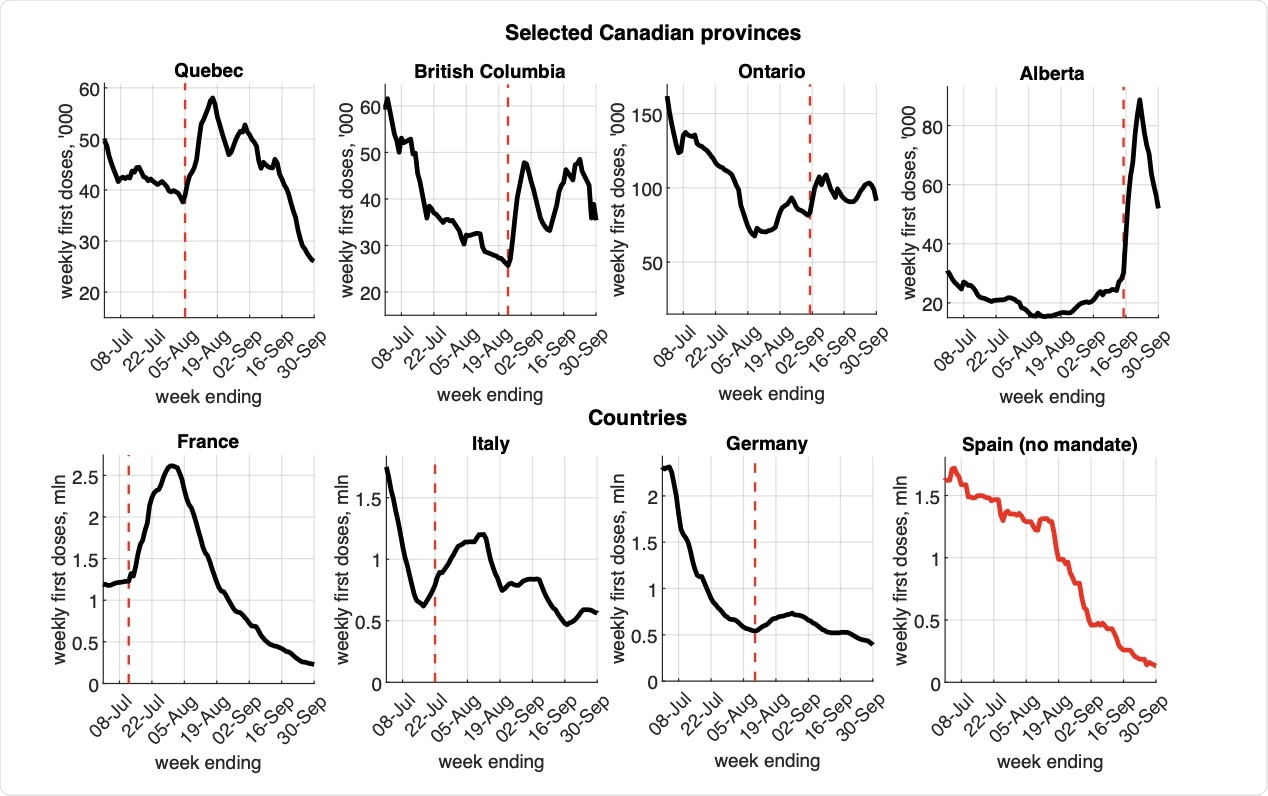 Vaccination mandates and first dose uptake as of Sep. 30, 2021
Vaccination mandates and first dose uptake as of Sep. 30, 2021
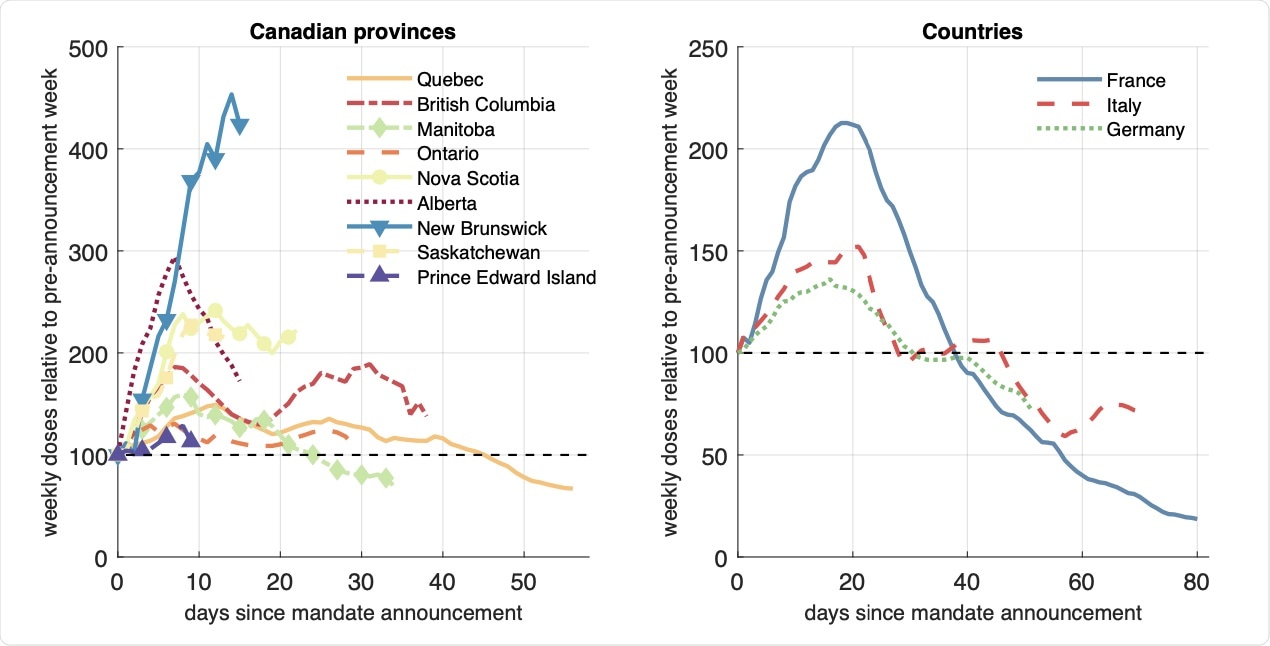 First doses after mandate announcement.
First doses after mandate announcement.
The robustness analysis indicated that the results were not affected by any assumptions, particular provinces, choice of weekly doses, and asymptotic inference approximations. The current study was also found to be consistent with the ‘ceiling effect’ idea that suggests that provinces with more eligible people at the time of the announcement will have more room for vaccination boost.
Assessment of second doses indicated that there was an increase in second dose uptake in the second week from the announcement; however, this trend was short-lived and did not persist in the following weeks. A structural break test following the announcement of a mandate was associated with a trend break in first-dose vaccine uptake in most or all locations.
The counterfactual analysis helped to get an idea about location-specific mandate effects and thus potentially gain precision. The counterfactual analysis for the Canadian provinces suggested that the announcement of the vaccination mandate led to 289,000 additional first doses in Canada.
The largest gains in vaccination were observed in Alberta, Ontario, and British Columbia. For countries, the additional first doses after the announcement were found to be large in France and Italy, whereas its impact was rather small in Germany.
Conclusion
The increase in the speed of vaccination is important, as it can accelerate the progress toward achieving herd immunity against SARS-CoV-2.
The results of the current study indicate that the proof of vaccination mandate imposed by the Canadian provinces and France, Germany, and Italy were quite effective in increasing first dose vaccinations. However, vaccination mandates are controversial, as some people consider them to be restrictions on personal freedom. Additionally, the costs of imposing and enforcing these mandates are quite high. Therefore, governments must devise cost-benefit methods to increase vaccination rates in order to reduce COVID-19 cases.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Karaivanov, A., Kim, D., Lu, S. E., & Shigeoka, H. (2021). COVID-19 Vaccination Mandates and Vaccine Uptake. medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2021.10.21.21265355. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.10.21.21265355v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Karaivanov, Alexander, Dongwoo Kim, Shih En Lu, and Hitoshi Shigeoka. 2022. “COVID-19 Vaccination Mandates and Vaccine Uptake.” Nature Human Behaviour, June, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-022-01363-1. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41562-022-01363-1.