Diagnostic tests have played a crucial role during the global wave of COVID-19. The gold standard diagnostic for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection continues to remain molecular assays like reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) performed on nasopharyngeal (NP) swabs. Newer assays, for instance – chemiluminescent immunoassays (CLIA) and Single Molecular Arrays (Simoa), have also demonstrated a good correlation with RT-PCR on NP swabs, at least for cycle thresholds.
 Study: Serum SARS-CoV-2 Antigens for the Determination of COVID-19 Severity. Image Credit: anyaivanova / Shutterstock
Study: Serum SARS-CoV-2 Antigens for the Determination of COVID-19 Severity. Image Credit: anyaivanova / Shutterstock

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Despite the high sensitivity of RT-PCR, the correlation between RT-PCR results from NP swabs and disease severity has been challenged. Moreover, variability in cycle threshold (Ct) values dependent on sample procedure, as well as the likelihood of false negatives, are some of the drawbacks associated with RT-PCR results from NP swabs collected before symptom onset. As a result, there is scope for improvement in the diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2 infection. The ideal diagnostic test should be capable of detecting the viral presence with similar or higher sensitivity than RT-PCR performed on NP swabs, with a superior estimation of the prognostic value, in addition to requiring easily accessible biological specimens.
Routinely, blood samples are employed to determine the antibody concentration. Still, this technique is seldom used in cases with acute infection or due to the possibility of pre-existing circulating antibodies. Another alternative is examining the antigen in non-respiratory fluids like the bloodstream—which is backed by evidence that SARS-CoV-2 migrates from the lungs into the bloodstream.
In this perspective, a new study published on the medRxiv* preprint server analyzed the clinical efficacy of two serum antigen tests to identify SARS CoV-2 infection and evaluate the kinetics of serum nucleocapsid (N) antigen in severe and non-severe patients for disease severity prediction.
Here, the serum N antigen was evaluated using a CLIA and the Simoa, and severity thresholds were established. This study involved 90 patients and 243 blood samples collected at various times following symptom onset. The severity of the disease was assessed using the World Health Organization (WHO) clinical progression scale. The study (in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration) flow diagram has been illustrated below:
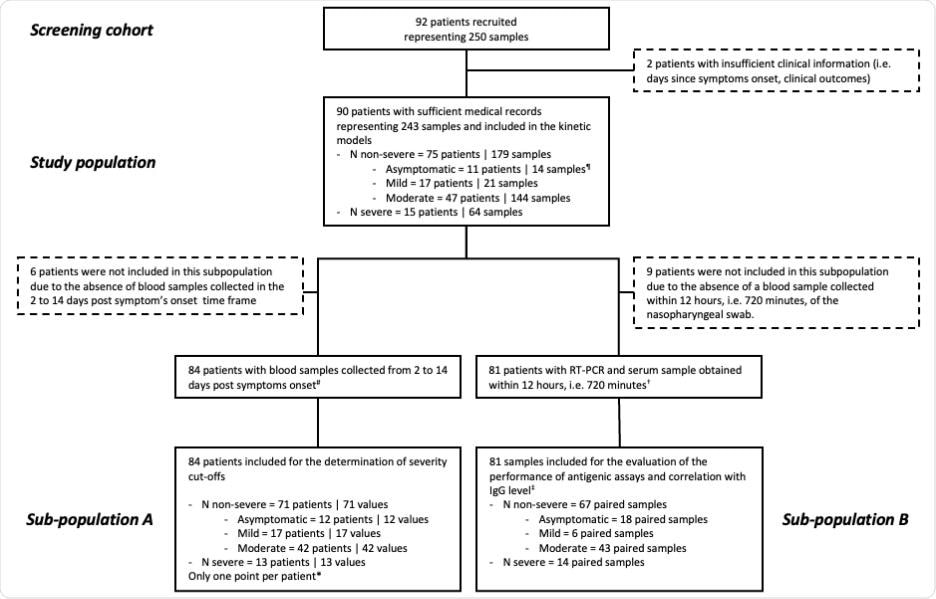
Study flow diagram
The commercial SARS-CoV-2 N-Protein Advantage kit, a paramagnetic microbead-based sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), was used to examine the samples. CLIA detected the SARS-CoV-2 N antigen in patient sera. RT PCR for SARS-CoV-2 detection in NP swab samples was performed targeting the N2 and E genes. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics. All longitudinal samples from the research population were utilized to estimate the time kinetics curves using smoothing splines with four knots.
It was found that in individuals with severe symptoms, the maximal antigen reaction was detected on day-7 using both assays. Following that, a decline was recorded in the antigen reaction until day-20. The antigen-response in non-severe individuals corresponded to a plateau phase that gradually reduced with time. Using the Simoa assay, the difference in kinetics between severe and non-severe individuals was more discernible.
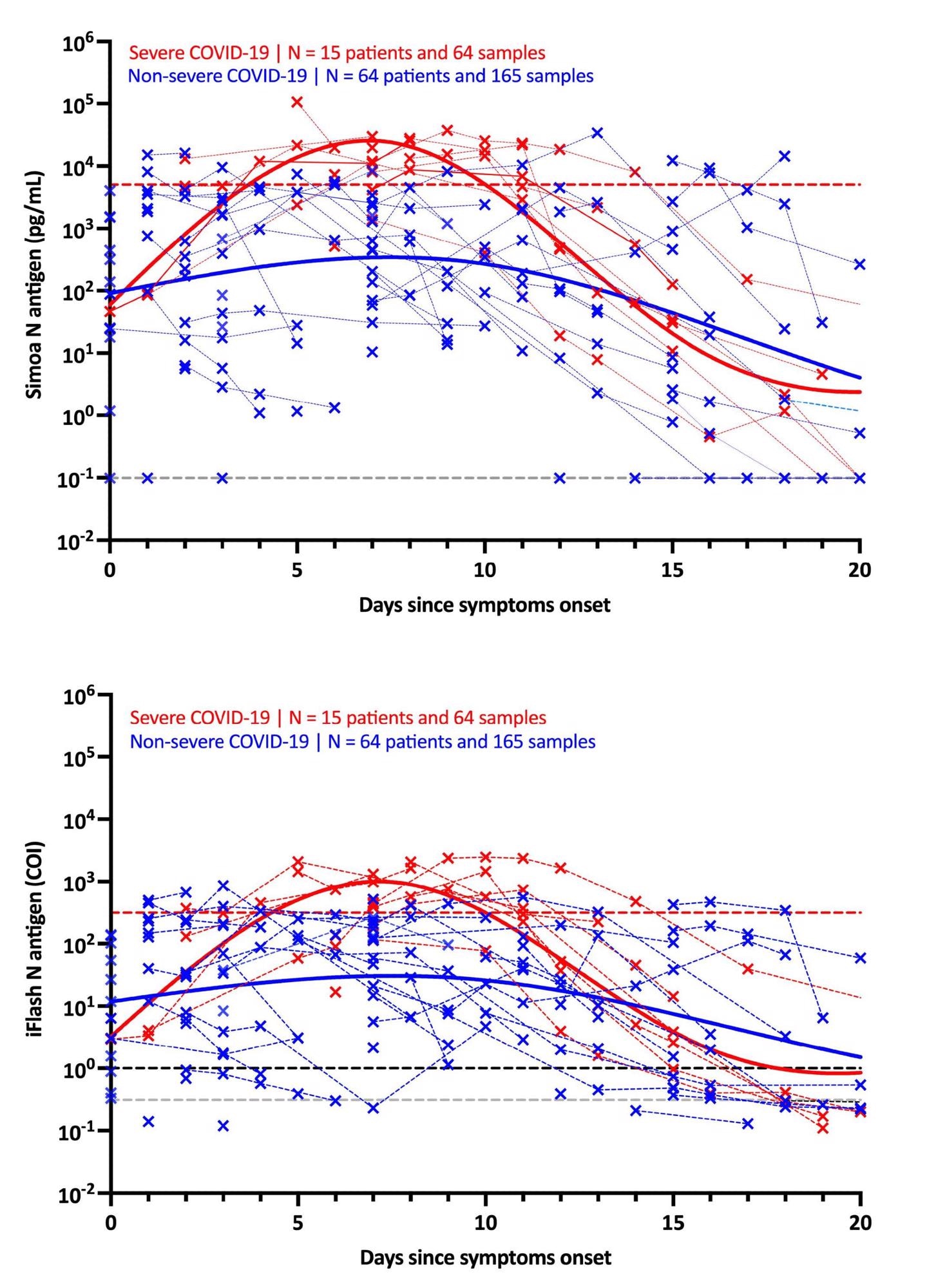 Kinetics of antigenemia since the onset of symptoms in non-severe and severe patients. The grey dotted lines correspond to the positivity cut-off of each antigen assay, as found by ROC curves analyses. The black dotted line corresponds to the positivity cut-off of the iFlash assay, as declared the manufacturer. The red dotted lines correspond to the severity cut-off of each antigen assay, as found by ROC curve analyses for the day 2 – day 14 window. Only patients with symptoms and negative for SARS-CoV-2 Spike IgG directed against the spike protein were included in this kinetics representation.
Kinetics of antigenemia since the onset of symptoms in non-severe and severe patients. The grey dotted lines correspond to the positivity cut-off of each antigen assay, as found by ROC curves analyses. The black dotted line corresponds to the positivity cut-off of the iFlash assay, as declared the manufacturer. The red dotted lines correspond to the severity cut-off of each antigen assay, as found by ROC curve analyses for the day 2 – day 14 window. Only patients with symptoms and negative for SARS-CoV-2 Spike IgG directed against the spike protein were included in this kinetics representation.
The use of these severity cut-offs on kinetic models determined the optimal time since symptom-onset in severe patients (i.e., 4 to 10 days). For both antigen assays, the clinical sensitivity was 100% and the clinical specificity was 92.3%.
Further, when NP RT-PCR was used, the mean Ct value of asymptomatic patients was substantially greater than that of severe patients. At the same time, no significant difference was found between mild, moderate and severe patients. Serum-antigen assays revealed that severe patients had higher antigen levels. The distinction between severe and non-severe patients was most apparent between days 4 and 10.
On the Simoa and iFlash assays, cut-offs for identifying patients at higher risk for severe disease were predicted to be 5,043 pg/mL and 313.8 cut-off index (COI). The likelihood ratios for these cut-offs were 30.0 and 10.9, respectively, indicating their ability to differentiate severe from non-severe patients from day-2 to day-14.
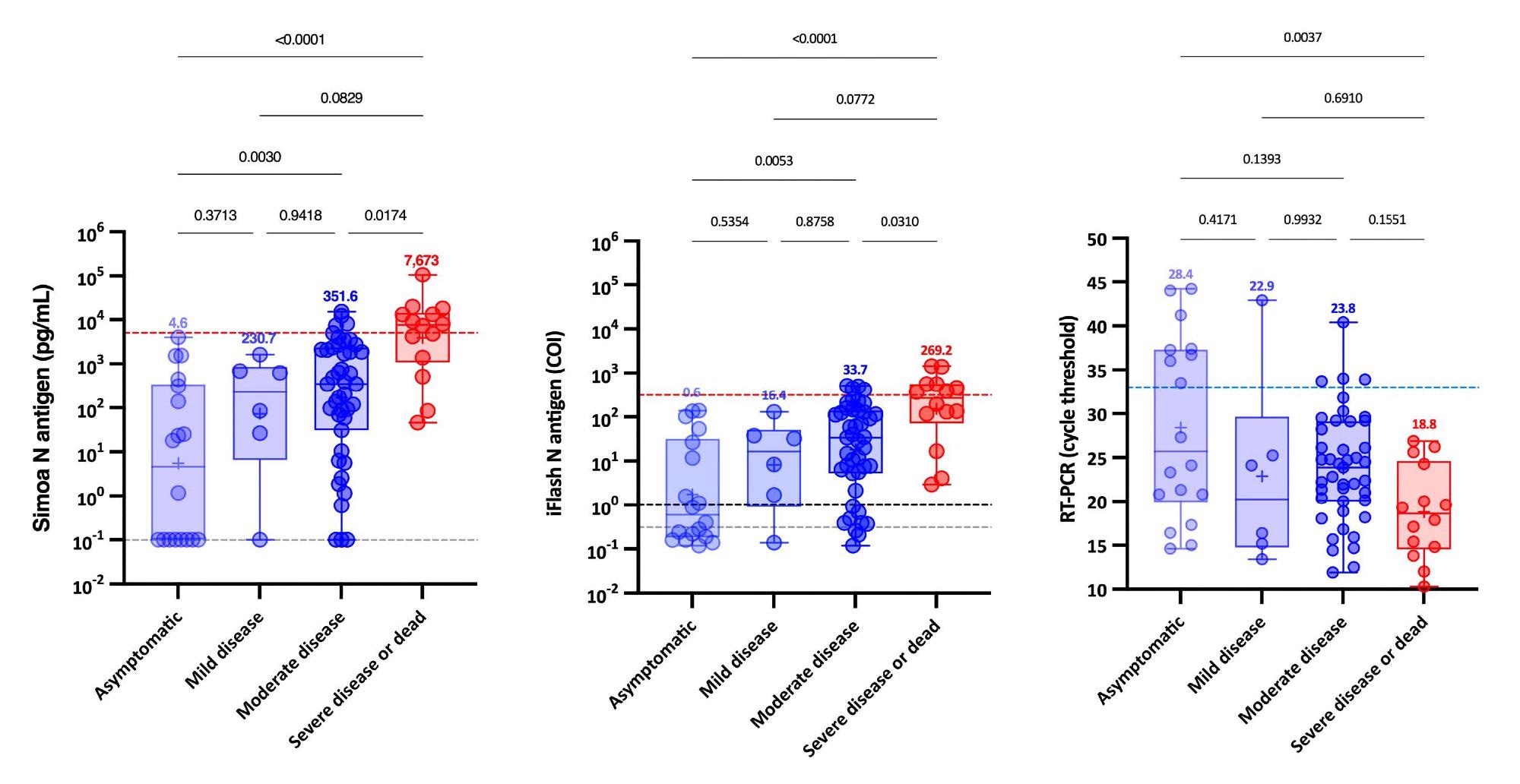 Antigenemia and RT-PCR results according to the WHO clinical progression scale on samples obtained on the day of diagnosis, i.e. within 12 hours since the RT-PCR. The blue dotted lines correspond to a cycle threshold of 33. The red dotted line corresponds to the severity cut-off, as determined by the ROC curve analyze. The grey dotted lines correspond to the positivity cut-off of each antigen assay, as found by ROC curves analyses. The black dotted line corresponds to the positivity cut-off of the iFlash assay, as declared the manufacturer. Medians are represented on top of each whisker box.
Antigenemia and RT-PCR results according to the WHO clinical progression scale on samples obtained on the day of diagnosis, i.e. within 12 hours since the RT-PCR. The blue dotted lines correspond to a cycle threshold of 33. The red dotted line corresponds to the severity cut-off, as determined by the ROC curve analyze. The grey dotted lines correspond to the positivity cut-off of each antigen assay, as found by ROC curves analyses. The black dotted line corresponds to the positivity cut-off of the iFlash assay, as declared the manufacturer. Medians are represented on top of each whisker box.
Remarkably, patients with SARS-CoV-2 Spike IgG levels above the positive cut-off had statistically significant higher Ct values and decreased serum-antigen levels. Whereas the majority of patients (96.6%) with negative SARS-CoV-2 Spike IgG were positive for antigen in serum with both assays.
The analysis leads to the following conclusions.
- Sensitive N antigen detection in serum offers an important novel marker for COVID-19 diagnosis that is accessible in all clinical laboratories and just demands a blood draw.
- It enables prospective new improvements to create rapid antigen blood tests or integrated ELISA assays that detect both antigens and antibodies.
- Significantly, evaluating antigenemia in the first two weeks post symptom onset may aid in identifying people at risk of developing severe COVID-19.
- These assays are more convenient as testing procedures for patients and may eventually improve clinical triage in order to optimize intensive care utilization.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Favresse, J., Bayart, J., David, C., et al. (2021), “Serum SARS-CoV-2 Antigens for the Determination of COVID-19 Severity”, doi: 10.1101/2021.11.18.21266478, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.11.18.21266478v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Favresse, Julien, Jean-Louis Bayart, Clara David, Constant Gillot, Grégoire Wieërs, Gatien Roussel, Guillaume Sondag, et al. 2022. “Serum SARS-CoV-2 Antigens for the Determination of COVID-19 Severity.” Viruses 14 (8): 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081653. https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/14/8/1653.