
 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
In August 2021, a large outbreak of the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant occurred in Israel's heavily vaccinated population. The outbreak resulted in an unusually high number of BTIs, which drew international attention. This led to scientists concluding that either the vaccine-induced immunity was dramatically reduced, or the Delta variant has immunity-escape skills.
About the study
The following data sources received from the Israel Ministry of Health and the World Health Organization were used to build this modeling study:
- March 21, 2020 - November 6, 2021: Weekly reported polymerase-chain-reaction (PCR)-confirmed cases stratified by age.
- March 11, 2020 - November 6, 2021: Daily hospitalization conditions, including patients' average age, gender, and disease severity.
- December 20, 2020 - November 6, 2021: Daily immunization with three doses stratified by age.
- July 29, 2021 - November 6, 2021: Daily identified severe cases classified by age, including patients' vaccination status.
- March 1, 2020 - November 6, 2021: Daily verified cases and deaths for all ages.
The proportions of the various types of variants of concerns were also confirmed throughout the course of the study.
The S, E, I, R, and V(k) variables refer to the number of individuals in the Susceptible, Exposed, Infectious, Recovered, and Vaccinated groups, respectively, in the standard SEIRV epidemic population model. Individuals who are susceptible move through the compartments in the following order: S→E→I→R.
The vaccinated class V(k) is divided into five stages (k = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5) to mimic the diminishing of immunity. The model includes age classes with i = 0,1 signifying 60 years and above 60 years.
The duration of individuals surviving in each compartment is exponentially distributed in the classic SEIR model. However, the time spent in the V compartment by vaccinated people is unlikely to be exponentially distributed.
As a result, vaccinated people were moved through a chain of five serial compartments in the model, with the duration in the V classes following a fairly flexible gamma distribution with appropriate parameters.
Study findings
The researchers presented a mathematical model that accounts for a variety of characteristics, including age, vaccination efficiency over time, transmission rate over time, BTIs, lower susceptibility and infectivity of vaccinated individuals, vaccine-induced immune protection duration, and vaccine distribution. To address these issues, the researchers fitted the model to cases among the vaccinated and unvaccinated for those younger than 60 years of age and above 60 years age groups.
Multiple factors, including the invasion of the Delta variant and mitigation actions, were shown to drive the transmission rate. The highest transmission rate of the Delta variant was 1.96 times higher than the prior Alpha variant, according to a model reconstruction of the reproductive number R0.
Vaccine efficiency declined considerably from 90% to 40% over six months according to the model, with the immune protection duration found to exhibit a peaked Gamma distribution, rather than exponential. The researchers also ran model simulations to determine the role of the third immunization booster dose in lowering the number of BTIs. This allowed them to investigate "what if" scenarios in the event that the booster dose had not been approved.
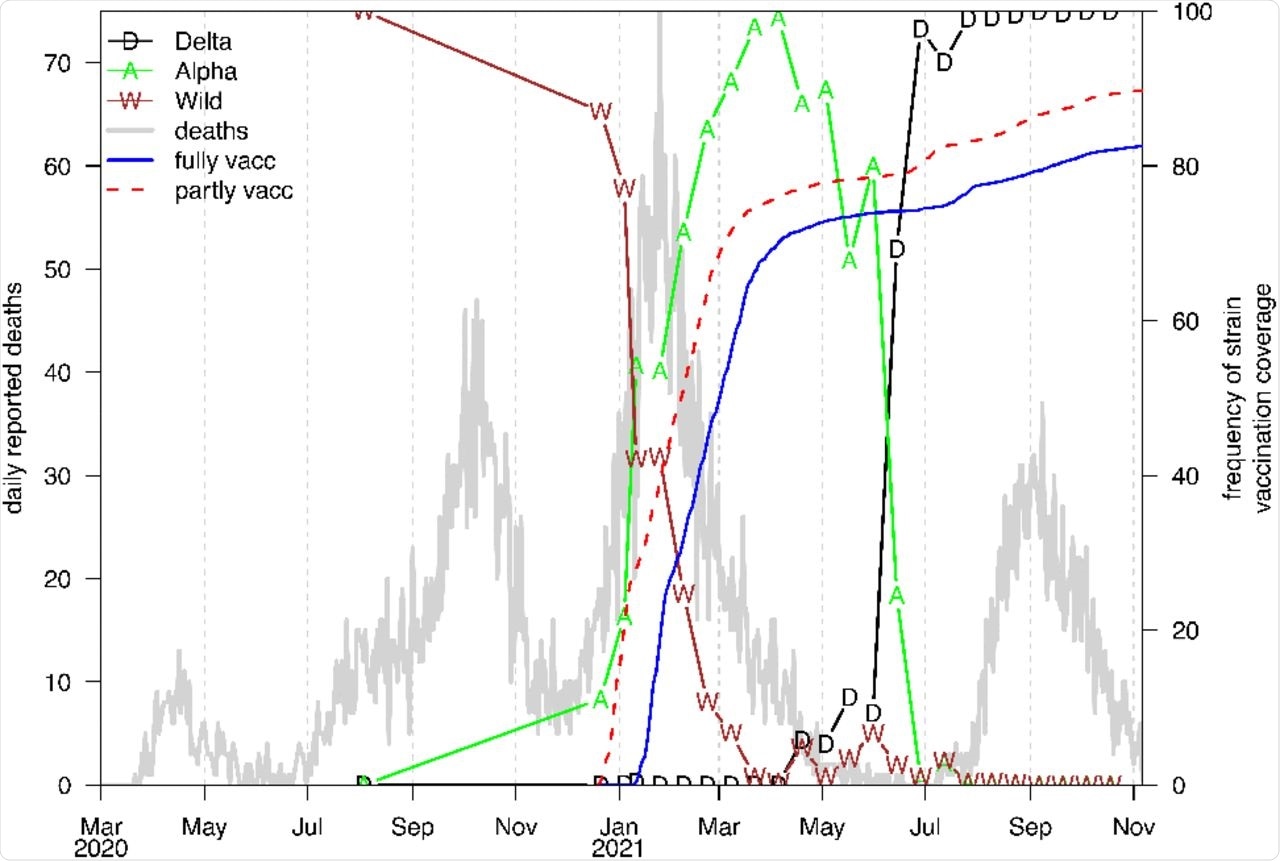
Daily reported COVID-19 deaths (grey) over the pandemic period. Colored symbols show the frequency of individual strains (as a percentage) of all strains sequenced (mostly biweekly) in Israel.
Conclusions
The study findings were applicable to Israel, which has a highly vaccinated population, well-functioning healthcare system, and data collection mechanism that is both efficient and open to the public. This nation was therefore the ideal case study, especially considering its early desire to disseminate the booster dose as quickly as possible. As a result, the lessons learned from SARS-CoV-2 dynamics in Israel may be used to improve preparedness in other areas that are experiencing invasions of variants of concerns.
As the COVID-19 pandemic or other outbreaks unfold, the suggested approach can be simply applied to new data on emerging variants to compare and assess different possibilities.
“The significance of the booster in mitigating the Israeli COVID-19 epidemic cannot be overstated.”

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Feng, A., Obolski, U., Stone, L., & He, D. (2022). Modeling COVID-19 Vaccine Breakthrough Infections in Highly Vaccinated Israel - the effects of waning immunity and third vaccination dose. medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2022.01.08.22268950. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.08.22268950v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Feng, Anyin, Uri Obolski, Lewi Stone, and Daihai He. 2022. “Modelling COVID-19 Vaccine Breakthrough Infections in Highly Vaccinated Israel—the Effects of Waning Immunity and Third Vaccination Dose.” Edited by Meru Sheel. PLOS Global Public Health 2 (11): e0001211. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgph.0001211. https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0001211.