Contact tracing has been pivotal in assessing the general population’s health responses to SARS-CoV-2 and involves the identification of contacts of SARS-CoV-2-positive individuals and giving them advice on self-isolation to decrease SARS-CoV-2 transmission.
In September 2020, 15,861 COVID-19 case records of the second generation laboratory surveillance system (SGSS) failed to be uploaded to the contact tracing advisory service (CTAS) data tool and subsequently delayed the tracing of COVID-19 case contacts.
SGSS records contain demographic and diagnostic information from laboratory test reports for patients who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, whereas CTAS records represent SARS-CoV-2 case episodes, including information on the movements of cases in their infectious period, their contacts, and demographic and clinical characteristics.
About the study
In the present observational study, researchers from the UK Health Security Agency, the University of Bristol, and the University of Cambridge evaluated the effect of delay in contact tracing of COVID-19 cases on SARS-CoV-2 transmission and hospitalizations and deaths in England.
The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) provided the SGSS records which were matched with the CTAS records to validate the cases affected by the event, and successive contacts and cases were identified. The study utilized CTAS data of SARS-CoV-2-positive individuals and their contacts for the analysis.
Matching was performed in several rounds on the basis of combinations of identifiers such as the national health service (NHS) number. SGSS unique identifier, date of birth (DOB). first name, last name, and postal code.
CTAS dataset comprised the primary cases which were affected by the event and these cases have been referred to as the ‘delay group’, whereas the primary cases belonging to the same timeframe (between September 30 and October 5, 2020) were not affected by the event comprised the ‘control group.
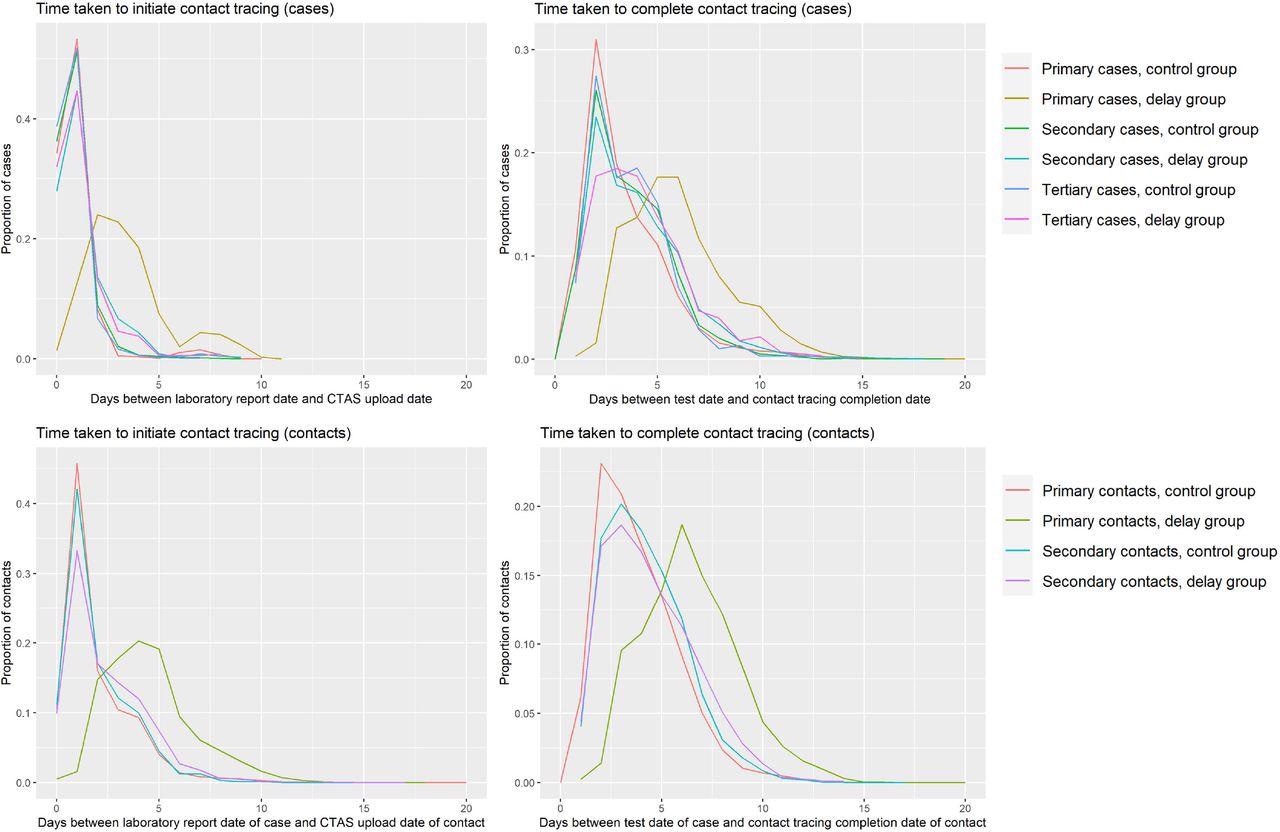
Graphs describing the time taken to initiate and complete contact tracing of cases and contacts in the delay and control groups
Secondary cases were described as those individuals who reported contact with a primary case individual and individuals who had contact with a primary case between day 2 and day 14 after symptom onset or the test date among the secondary case individuals.
In addition, the contact datasets were linked to the UKHSA hospital-onset COVID-19 dataset, which was extracted on November 22, 2021, and retrieves daily data from two national datasets namely the Secondary Uses Services (SUS) dataset and the Emergency Care Data Set (ECDS) that describe patient hospitalizations and, usage of emergency care services, respectively.
The primary outcome measures included secondary attack rates (SARs), hospitalizations, and deaths among primary contacts and secondary contacts compared to concurrent and unaffected cases.
Results
A total of 15,861 SGSS records were detected as affected by the event, of which 98% (15,467) matched the CTAS records. After data cleaning, 96% (15,285) of primary cases affected by the delay were eligible for the analysis. The control group comprised 43,742 primary contact concurrent cases, comprising all CTAS records within the aforementioned timeframe unaffected by the event.
Contact tracing initiation was delayed by three days in the primary contact cases among the delay group in comparison to controls, associated with the incomplete tracing of contacts of primary cases among the delay group individuals (80%) and controls (83%).
The delay increased viral transmission to non-household contacts. The SARs among non-household contacts were higher among the secondary contacts (7.9%) of the delay group compared to the controls (5.9%). Among secondary contacts, there were no statistically significant differences between the delay group individuals and controls with regard to hospitalization (crude odds ratio 1) and death (crude odds ratio 0.7).
Overall, the study findings revealed that the delay in tracing contacts for the COVID-19 cases marginally affected their health.

 *Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
*Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
Journal reference:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Evaluating the impact on health outcomes of an event that resulted in a delay in contact tracing of COVID-19 cases, Lucy Findlater, Livia Pierotti, Charlie Turner, Adrian Wensley, Cong Chen, Shaun Seaman, Pantelis Samartsidis, Andre Charlett, Charlotte Anderson, Gareth Hughes, Matt Hickman, Obaghe Edeghere, Isabel Oliver, medRxiv preprint 2022, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.19.22275053 https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.05.19.22275053v1