Four HCoVs, NL63, 229E, HKU1, and OC43, are endemic worldwide, accounting for five to 30% of human respiratory illnesses. CoV infections primarily affect the gastrointestinal and upper respiratory tracts, resulting in mostly mild respiratory infections. However, CoVs can lead to life-threatening pneumonia and bronchiolitis in young children, newborns, old-aged, and immunocompromised people.
While sHCoVs are found globally and have a typical seasonality spanning December and April, the rate at which they are detected varies depending on the time and location. Furthermore, the evolution and epidemiology of these CoVs are underexplored relative to other seasonal respiratory viruses like influenza and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). This was due to their correlation with mild symptomatology. Moreover, there are no authorized vaccines or antiviral medicines for sHCoVs, and management consists of supportive measures.
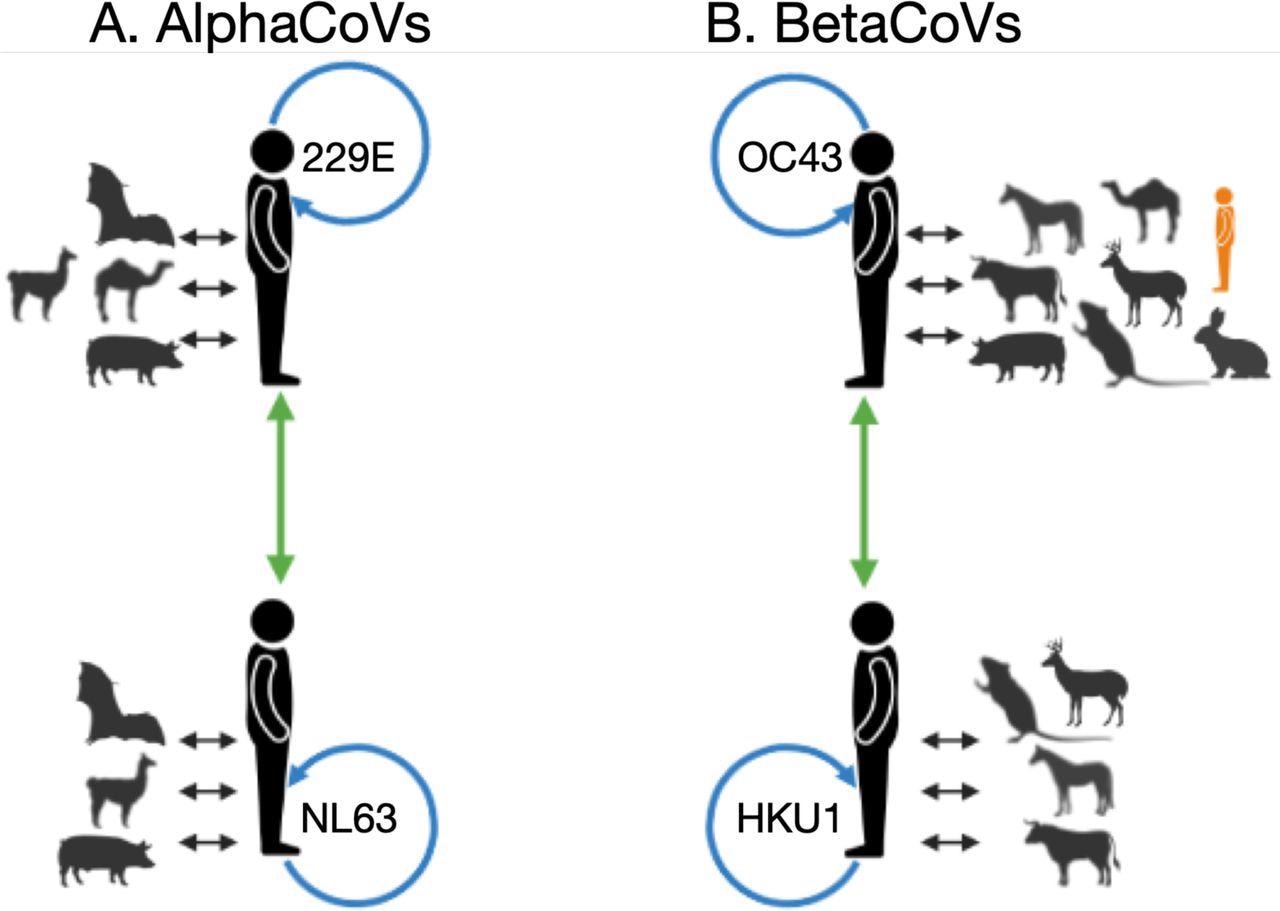
Summarized within and between host/species recombination patterns identified by RDP4, for alphaCoVs (A) and betaCoVs (B). For each sHCoV species, recombining CoVs are shown; non-human and sHCoV (black arrows), within sHCoV species (blue arrows), and between sHCoV species (green arrows). In orange is a lone human CoV (FJ415324) that clusters with ungulate and canine CoVs. Figure generated using Biorender.
About the study
In the current work, the researchers used a multigene and whole-genome analysis technique to evaluate the evolutionary background of sHCoVs (NL63, 229E, HKU1, and OC43).
Using a pool of 855 sequences obtained from GenBank, the team explored the sHCoVs evolutionary history. They investigated zoonotic origins, emergence time, genetic diversity, recombination rates and patterns, and adaptive protein modifications. The scientists employed a multigene analytic strategy to learn about the evolutionary background of these CoVs' nucleocapsid, spike, envelope, and membrane open reading frames (ORFs).
The investigators created maximum clade credibility (MCC) trees using the whole-genome sequences (WGS) and the envelope, spike, nucleocapsid, and membrane ORFs to study the zoonotic origins of the four sHCoV species. They calculated the apparent recombination frequencies between CoVs and throughout the genome using the ClonalFrameML software.
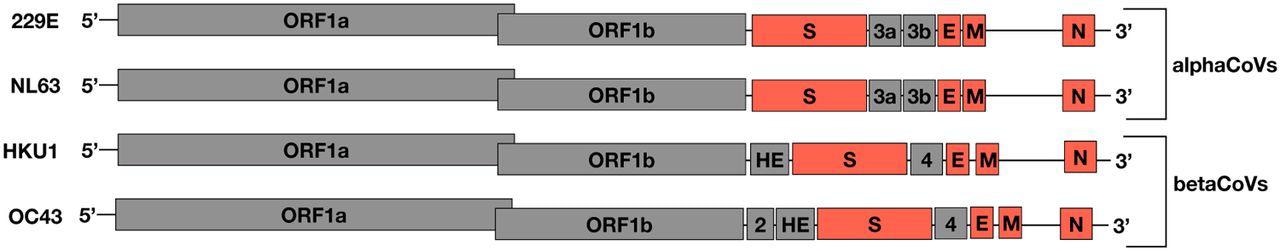
An illustration of the sHCoV genomes, not drawn to scale. In orange are the ORFs analyzed in this study.
Results and discussions
The team discovered that the evolutionary timelines of sHCoVs were more complex than priorly thought because of the common recombination of CoVs, consisting of between and within sHCoVs occurring at various rates. OC43 and 229E had the highest recombination rates within sHCoV, and β-CoVs had the highest recombination rate within the genus. Further, in HKU1, NL63, and the α-CoVs, substitutions for each recombination incident were conversely greatest.
The authors mentioned that the sHCoVs OC43 and 229E origins might rely on the gene assessed. OC43 could have canine, ungulate, or rabbit CoV ancestors, whereas 229E could have come from a camel, bat, or an unknown intermediate host, depending on the gene examined.
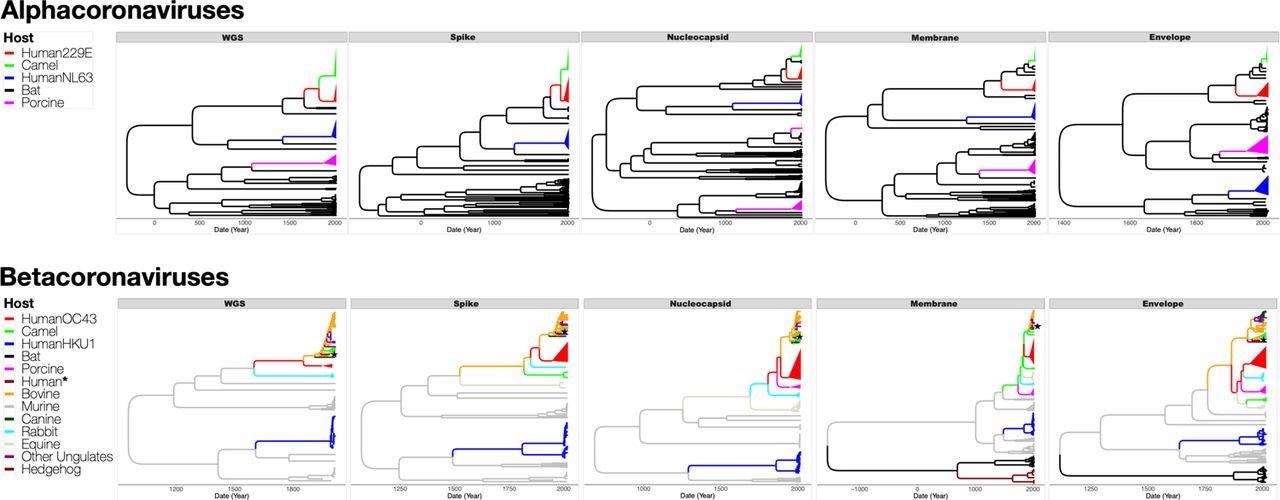
Maximum clade credibility (MCC) trees inferred from dataset D5 for full genomes (WGS), and the spike, nucleocapsid, membrane and envelope proteins, with the branches color-coded by the inferred coronavirus host. The upper panel shows MCC trees from alphacoronaviruses while the lower panel shows MCC trees from betacoronaviruses. Human, camel and porcine coronavirus clades have been collapsed to increase readability. Human* is a lone human CoV (FJ415324) that clusters with ungulate and canine CoVs.
The present analysis did not substantially support the origin of 229E from camelids. On the contrary, autonomous transmissions of CoVs from bats to humans and camelids seemed to be more probable. The current observations widen the list of putative OC43 origin or intermediate hosts to incorporate other rabbits, ungulates, and canines, either wild or domesticated yet always close to humans.
The scientists hypothesized that two autonomous non-human to human transmission incidents could occur in HKU1. HKU1 harbored the oldest, most latest shared ancestor, made up of two genetically dissimilar genotypes (B and A), presumably indicating two separate transmission episodes from murine CoVs. Besides, genotype B had a greater genetic diversity than the other sHCoVs.
The team discovered that the sHCoVs were non-human CoVs recombinants, implying that either the sHCoVs that appeared in humans were already recombinants of various non-human CoVs or that the current sHCoVs are the result of persistent viral to and fro transmission among human and non-human hosts. The authors described previously unknown recombination between the sHCoV species among the same genera and recombination within 229E. The present results show that recombination often happens outside the spike protein, which was frequently the subject of recombination studies.
Finally, even though the non-human to sHCoV host-jump branches did not always seem to be among the positive selection, the authors discovered common amino acid (AA) changes in several proteins in these branches.
Conclusions
To summarize, the authors discovered that the origins of sHCoVs were far more complicated and ambiguous than thought earlier, showing evolutionary reconstructions indicating that various ORFs within a single sHCoV may have unique souces. In addition, they noted that recombination and undersampling, especially among non-human hosts, may play a role in the unknown and intricate evolutionary trajectories of sHCoVs. Additional sequence data and re-analysis will also help to have a better grasp of sHCoV's evolutionary history.
According to the researchers, persistent monitoring of CoVs throughout non-human hosts might help assess the intricate evolution of CoVs and their regular host shifts. Tracing the evolution of sHCoVs has ramifications for the vaccine, diagnostics, therapeutics development, a better knowledge of their evolutionary past, and pathways for the possible emergence of new human CoVs.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Origins and Evolution of Seasonal Human Coronaviruses; James R. Otieno, Joshua L. Cherry, David J. Spiro, Martha I. Nelson, Nídia S. Trovão. bioRxiv preprint 2022, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.02.494567, https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.06.02.494567v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Otieno, James R., Joshua L. Cherry, David J. Spiro, Martha I. Nelson, and Nídia S. Trovão. 2022. “Origins and Evolution of Seasonal Human Coronaviruses.” Viruses 14 (7): 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14071551. https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/14/7/1551.