Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) and its management has posed a challenge for the medical community around the world. Identifying biomarkers correlated to PASC is necessary to optimize the classification of patients suffering from PASC and develop appropriate treatment approaches.
 Study: Persistent circulating SARS-CoV-2 spike is associated with post-acute COVID-19 sequelae. Image Credit: Dmitry Demidovich / Shutterstock
Study: Persistent circulating SARS-CoV-2 spike is associated with post-acute COVID-19 sequelae. Image Credit: Dmitry Demidovich / Shutterstock

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
About the study
In the present study, researchers analyzed plasma samples obtained from PASC as well as COVID-19 patients to evaluate the proportion of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) antigens and cytokines.
The team tested plasma samples from a group of 63 persons with a history of SARS‑CoV‑2 infection, among which 37 persons were diagnosed with PASC. Blood samples were obtained two or three times for up to 12 months after the first positive SARS‑CoV‑2 diagnosis with either an anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody test or a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test. Moreover, blood samples were collected from persons with a history of SARS-CoV-2 but reported no PASC diagnosis for up to five months after diagnosis.
The team also estimated the proportion of SARS-CoV-2 antigens such as spike (S)-1 subunit, full-length spike, as well as nucleocapsid (N) using ultra-sensitive single-molecule array (Simoa) assays. Furthermore, blood samples were collected from a subset of COVID-19 patients and a number of PASC patients at different time points.
Results
The study results showed that most PASC patients were women, indicating that females exhibited comparatively more persistent symptoms after COVID-19 infection. Among the individuals who had no PASC diagnosis, ten were hospitalized in the intensive care unit (ICU), and seven needed intubation.
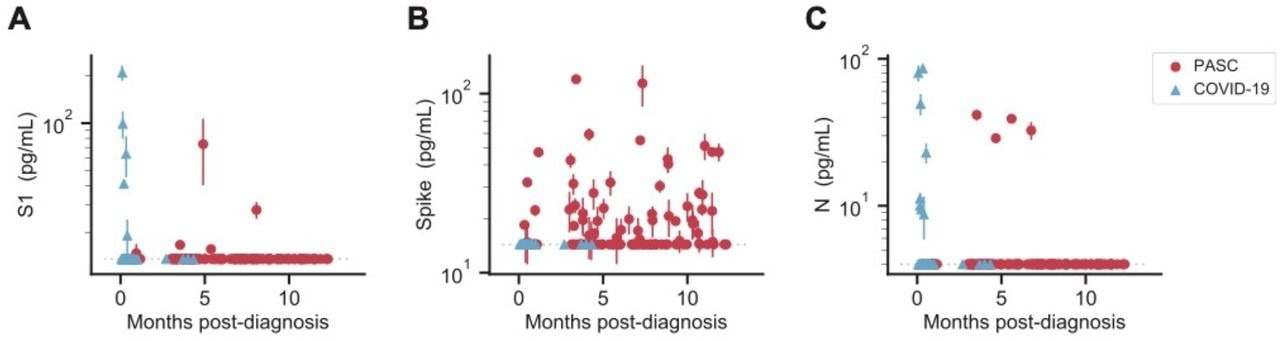
SARS-CoV-2 antigen levels versus time. The concentration of S1 (A), spike (B), and N (C) measured in the plasma of individuals over time after diagnosis with PASC or COVID-19 following SARS-CoV-2 infection. Multiple data points may correspond to the same individual, where repeat sampling was available. Data points represent mean values ± SD (n = 2). Dashed lines indicate the LOD for each assay.
The team also detected S, S1, or N in almost 65% of PASC patients at any given point, even several months after a positive SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis. The S antigens were found in 60% of the individuals experiencing PASC, while no S antigens were detectable in the COVID-19 patients. S1 antigen was found to a comparatively lesser extent among one-fifth of the PASC-diagnosed individuals, while N was found in only one patient at different time points. The team also detected N and S1 in COVID-19 patients within the first week after diagnosis among patients hospitalized due to severe COVID-19. Moreover, the full spike protein was not detected in any of the severe COVID-19 patients.
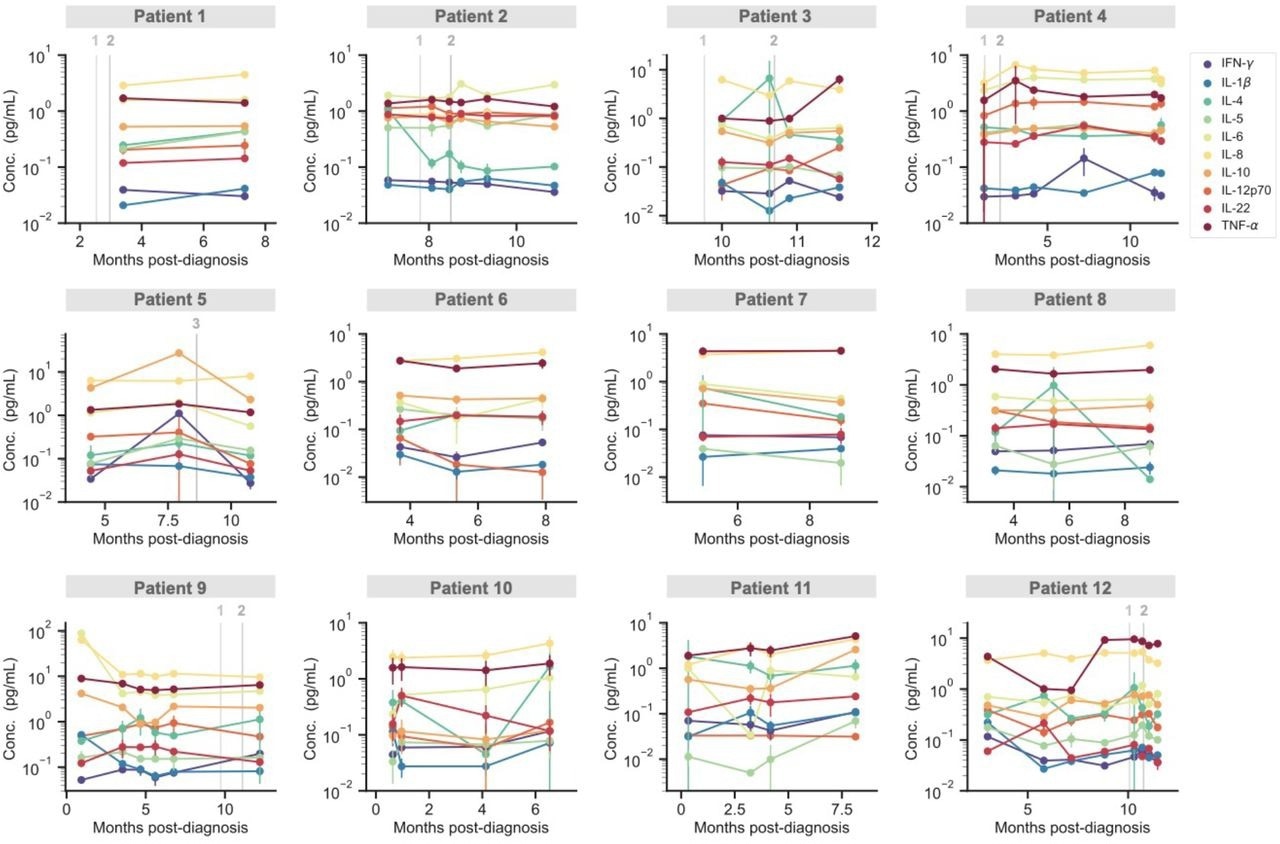
Temporal profiling of cytokines for individual PASC patients. The concentration of 10 cytokines measured over time for 12 individual PASC patients. Grey vertical lines correspond to the times when each patient received either the first, second or third dose of a COVID-19 vaccine. Data points represent mean values ± SD (n = 2).
Among the PASC patients, the team found antigens more than once in 12 patients, which suggested the presence of circulating antigens. Also, patterns of consistent levels of the full spike antigen over several months were noted in many of the patients. In other cases, the team also noted variations between the antigen being detectable and non-detectable, which suggested that the time of blood sampling was crucial. On the other hand, the temporal antigen profiles displayed by six COVID-19 patients showed high levels of antigens soon after the COVID-19 diagnosis, which quickly reduced to undetectable levels.
Overall, the study findings showed the persistent presence of SARS-CoV-2 viral reservoirs in the body up to 12 months after COVID-19 diagnosis. In addition, the detection of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in most of the PASC patients also indicated that the spike protein was an efficient biomarker for PASC.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Persistent circulating SARS-CoV-2 spike is associated with post-acute COVID-19 sequelae, Zoe Swank, Yasmeen Senussi, Galit Alter, David R. Walt medRxiv 2022.06.14.22276401, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.14.22276401, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.06.14.22276401v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Swank, Zoe, Yasmeen Senussi, Zachary Manickas-Hill, Xu G Yu, Jonathan Z Li, Galit Alter, and David R Walt. 2022. “Persistent Circulating SARS-CoV-2 Spike Is Associated with Post-Acute COVID-19 Sequelae.” Clinical Infectious Diseases, September. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciac722. https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/76/3/e487/6686531.