There have been increased demands by consumers for natural compounds capable of enhancing food quality and safety. As a result, many have proposed the substitution of synthetic antioxidants with plant extracts.
Bioactive tea tree oil (TTO) and hemp seed oil (HSO) are of particular interest due to their antioxidant and antimicrobial properties.

Study: The Biological Activity of Tea Tree Oil and Hemp Seed Oil. Image Credit: ronstik / Shutterstock.com
Background
TTO is obtained from the Melaleuca alternifolia plant of the Myrtle family and is well known for its antimicrobial properties.
A tea tree is a tree or shrub that constitutes a papery bark and can grow up to 14 meters in height. This plant originated from Australia and can thrive in mostly warm temperatures. Steam distillation is commonly used for the extraction of active components of the tea tree plant, most of which are terpenes.
Following harvest, cold pressing of hemp seeds allows for the extraction of HSO. Cannabidiol (CBD) content in HSO can be either low or high; however, no comparison regarding the bioactivity of HSOs with different CBD contents with that of TTO has been made.
Along with the antibacterial properties associated with many plant oils, these extracts are also associated with anti-fungal properties. In fact, some plant oils can resist the adverse impact of harsh chemicals used to sanitize food-processing areas.
This has led to an increased demand for improved antimicrobials used in the food industry. Therefore, discovering natural antimicrobials that are not associated with toxic effects is important.
Antioxidants are synthetic or natural substances that aid in the neutralization of harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS). These agents help to avoid oxidative stress that arises due to an imbalance between oxidants and antioxidants.
Oxidative stress can be caused by external factors such as smoking, exposure to the sun without protection, or alcohol consumption. High levels of ROS for long periods can also lead to aging and many chronic diseases. Two plant extracts that are known for their antioxidant properties include sesame oil and vetiver oil.
A new Applied Microbiology study compares the antimicrobial activity of HSO and TTO products against pathogenic bacteria such as Salmonella enteritidis (S. enteritidis), Escherichia coli (E. coli), and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). The researchers also assessed the antioxidant properties of these agents, as well as the existence of any interrelationship between their antimicrobial and antioxidant properties.
About the study
The current study utilized antimicrobial and antioxidant assays. The antimicrobial assays included time-kill studies, minimum inhibition concentration (MIC) evaluation, and the Kirby–Bauer disk diffusion method for evaluation of antimicrobial properties of the samples.
Comparatively, the antioxidant assay was used to determine the concentration of antioxidants in the sample. This assay was done using the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl-hydrate (DPPH) radical-scavenging activity method.
The antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of seven oils, including tea tree, sesame, rosehip, vetiver, pure hemp, organic hemp, and 5% CBD oil, were assessed.
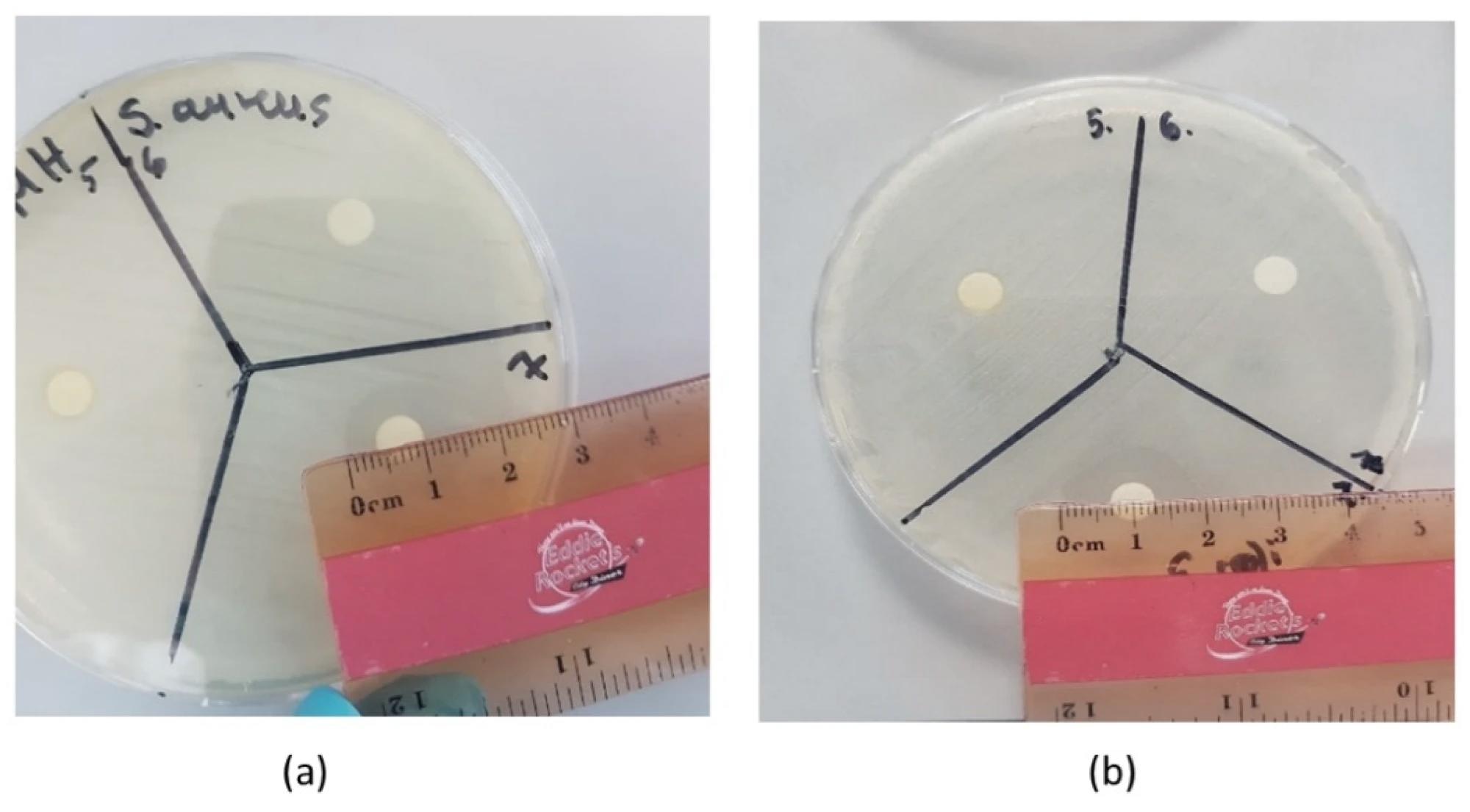 The measurement of the inhibition zone of tea tree oil on different bacteria: (a) S. aureus and (b) E. coli.
The measurement of the inhibition zone of tea tree oil on different bacteria: (a) S. aureus and (b) E. coli.
Study findings
The onset of bacteria was reported to be six hours, while the highest concentration was observed at 24 hours. The number of bacteria in the TTO group was lower than in the HSO groups.
The MIC and disk diffusion method results indicated that out of all oils, TTO exhibited significant antimicrobial activity against all three pathogens. The MIC range for TTO was reported to be 8, 2, and 8 mg/mL for S. aureus, S. enteritidis, and E.coli, respectively. The inhibition zones were reported to be 2.19, 1.87, and 2.02 cm against S. enteritidis, S. aureus, and E.coli, respectively.
Conversely, 5% CBD oil was found to produce the highest antioxidant activity that was 5.7 times more potent as compared to that of TTO. Pure hemp and organic hemp also showed promising antioxidant properties.
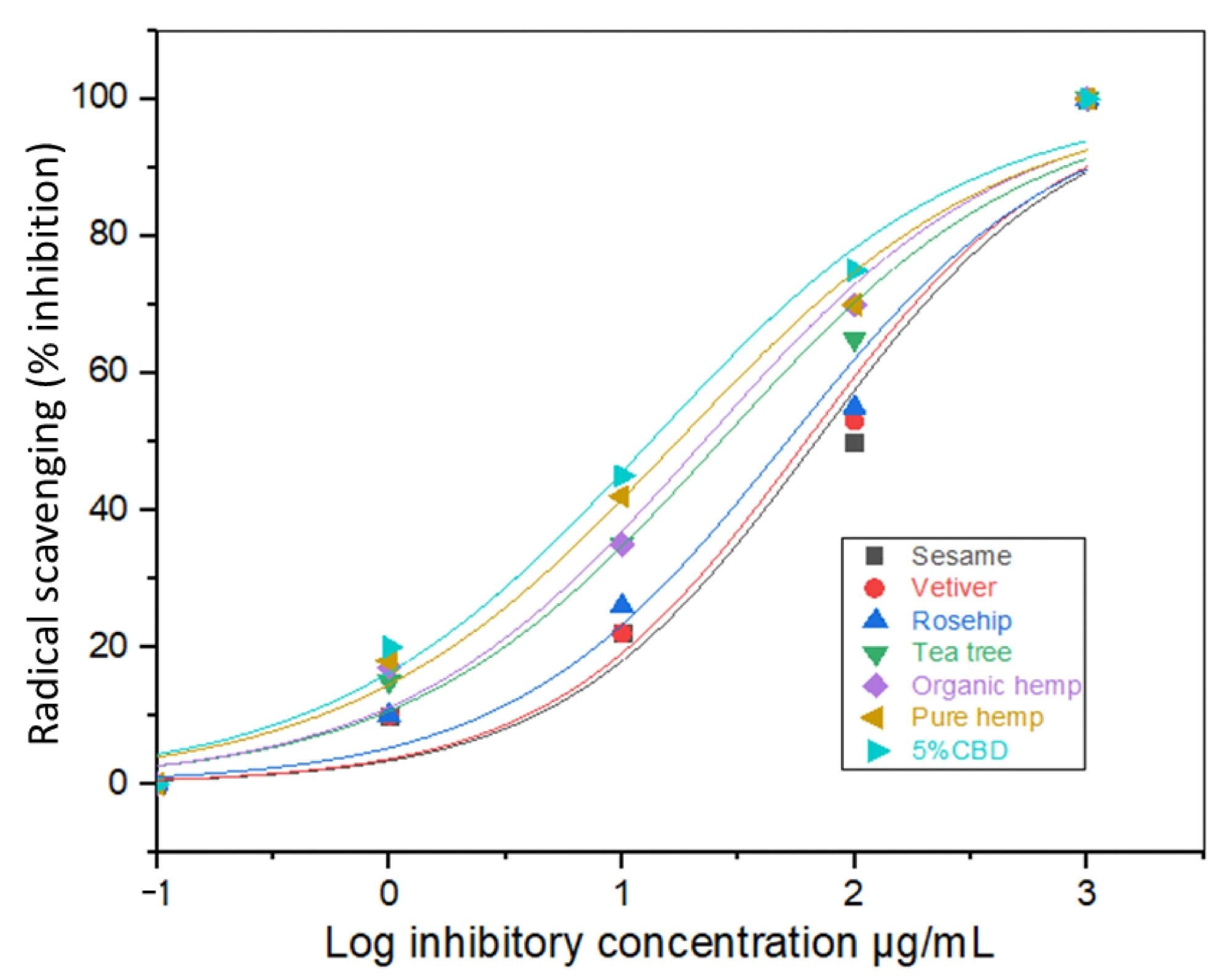 IC50 values of the antioxidant activities of the different oils.
IC50 values of the antioxidant activities of the different oils.
Conclusions
The current study determined TTO to be the most effective antimicrobial agent against E.coli, S. aureus, and S. enteritidis. Furthermore, the CBD content of HSOs was found to play an important role in their antioxidant properties. Substances with higher CBD exhibited better antioxidant properties.
Therefore, both TTO and CBD plants can be useful in food science studies to make food products safe for consumers. Further research is needed to optimize the antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of these oils for their use in the food and medical industries.
Journal reference:
- Lakatos, M., Apori, S. O., Dunne, J., & Tian, F. (2022). The Biological Activity of Tea Tree Oil and Hemp Seed Oil. Applied Microbiology. doi:10.3390/applmicrobiol2030041.