Saffron and its by-products are considered a valuable source of several bioactive compounds that are known to play preventive and therapeutic roles in a range of diseases, including degenerative maculopathy, depression and anxiety, neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic syndrome, cancer, and chronic kidney disease.
The authors of this review article have searched various scientific databases to identify studies that investigated the preventive and therapeutic potencies of saffron and its by-products. This review includes studies published in English between 1990 and 2024.
Bioactive compounds in saffron
The main bioactive compounds found in saffron include crocins, safranal, and picrocrocin. Crocins are hydrophilic carotenoids. Approximately 15 crocin esters have been identified in saffron stigmas.
Picrocrocin is a degradation product of zeaxanthin. It loses glucose and is transformed into safranal during the enzymatic process. Apart from the most abundant safranal, 60 volatile compounds have been identified in saffron stigmas.
Various flavonoids have also been identified in saffron stigmas, including kaempferol-3-sophoroside, kaempferol-3-sophoroside-7-glucoside, kaempferol-3,7,4′-triglucoside, kaempferol tetrahexoside, kaempferol-3-dihexoside, quercetin, rutin, and naringin.
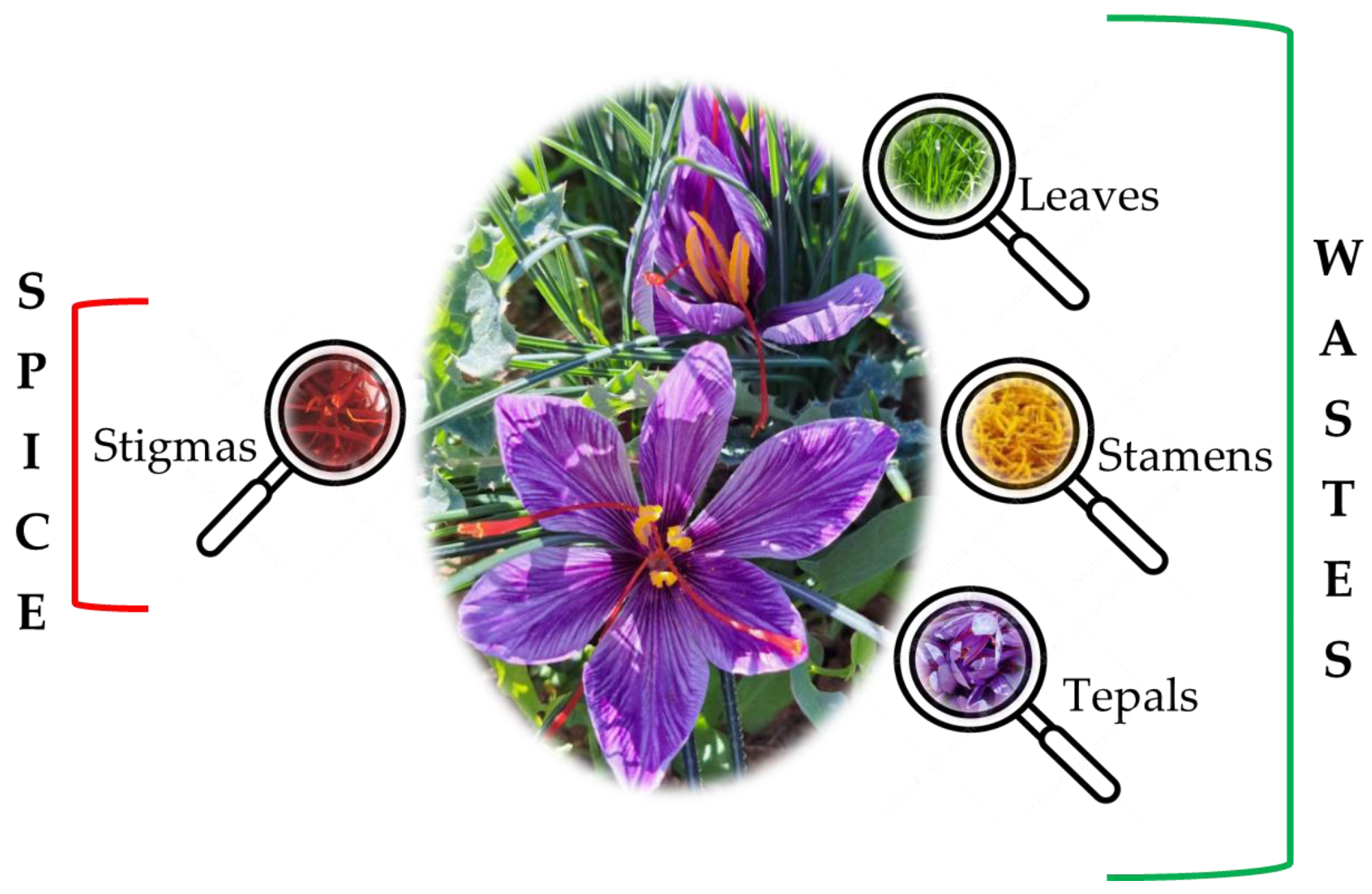 Parts of C. sativus L.
Parts of C. sativus L.
Saffron by-products
Different classes of flavonoids have been found in saffron tepals, including flavonols and anthocyanins. The most abundant flavonols are kaempferol, quercetin, isorhamnetin derivatives, and kaempferol 3-O-sophoroside. The most abundant anthocyanins are delphinidin and its derivatives, petunidin and its derivatives, and malvidin derivatives.
Bioactive compounds found in saffron leaves include kaempferol and its derivatives, quercetin and its derivatives, luteolin and its derivatives, organic acids, and phenolic compounds.
Saffron in internal medicine
Saffron and its by-products exhibit numerous beneficial effects in internal medicine.
 Potential beneficial effects of C. sativus L. in internal medicine. Abbreviations: ↑, increase or improvement; ↓, decrease; 5-HT, serotonin; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Potential beneficial effects of C. sativus L. in internal medicine. Abbreviations: ↑, increase or improvement; ↓, decrease; 5-HT, serotonin; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Degenerative maculopathy
It is a retinal neurodegenerative disease caused by genetic and environmental factors. The major hallmarks are oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. The disease is characterized by hyper or hypopigmentation of the retinal pigment epithelium, which can lead to visual impairment.
Crocetin, the main compound in saffron, inhibits the expression of caspases to prevent retinal damage and counteract retinal cell death.
A clinical trial involving patients with early degenerative maculopathy showed that daily saffron intake can improve visual acuity and slow disease progression. Carotenoids have also been reported to have a positive effect on retinal flicker sensitivity.
Depression and anxiety
Saffron's antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and serotonergic properties have made it a strong, natural antidepressant. Daily use of different forms of saffron has been found to reduce oxidative stress in patients with depression by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes.
Safranal, crocin, and crocetin have been found to act synergistically to reduce neuroinflammation, which is a major hallmark of depression.
Depression is characterized by a reduction in serotonin levels. Saffron has been found to increase serotonin bioavailability, probably by exerting an antagonistic effect on the serotonin receptor present on neurons.
A clinical trial involving patients with anxiety and depression has highlighted that intake of saffron stigmas for 12 weeks is associated with an improvement in disease conditions.
Neurodegenerative diseases
The main bioactive compounds of saffron, including safranal, crocin, and crocetin, have been found to counteract neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease) by synergistically preventing neuroinflammation, modulating the metabolic pathways of autophagy and apoptosis, and reducing oxidative stress.
Crocin and crocetin have been found to inhibit amyloid-beta peptide aggression and delay synaptic loss, leading to neuroprotection against Alzheimer's disease-related cognitive deterioration.
An improvement in cognitive functions has been observed in Alzheimer's disease patients who consumed saffron in any form.
Metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a group of conditions defined by the presence of obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and impaired blood lipid profile.
Saffron and its components have been found to increase total antioxidant capacity, improve fasting blood glucose, reduce serum insulin, and inhibit the production of advanced glycation end products in animal models of diabetes.
Saffron intake for 12 weeks has been found to improve serum oxidant-antioxidant balance in patients with metabolic syndrome. Saffron intake, together with resistance training, has been found to reduce inflammation and cardiovascular disease risk factors in elderly hypertensive patients.
Cancer
Saffron stigma extracts have been found to inhibit prostate cancer cell proliferation by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. The anticancer effects of saffron stigma extracts have also been found in human non-small lung, breast, and cervical cancers.
Safranal and topotecan have been found to act synergistically to induce DNA double-strand breaks and reduce the expression of DNA repair enzymes in lung cancer and colon cancer cell lines.
A saffron petal extract has been found to exert radical scavenging activity and cytotoxic activity in liver cancer cells. Saffron stigma extracts and flower extracts have been found to reduce the viability of kidney and bladder cancer cells.
Chronic kidney disease
Crocetins and safranal have been found to reduce oxidative stress through increased serum nitric oxide, malondialdehyde, and glutathione S-transferase activity in animal models of chronic kidney disease.
Saffron intake has been found to reduce serum creatinine levels, increase renal blood flow, and induce a diuretic action on distal convoluted tubules.