Introduction
Blood clotting or coagulation is a complex process. Researchers at the Maastricht University and Synapse spin-off are conducting fundamental studies and developing practical detection techniques for bleeding and thrombosis. A complete picture of the clotting process will enable scientists to gain a better insight into this unique phenomenon.
Synapse is using the Phenom benchtop scanning electron microscope (SEM) for this purpose. With the help of sophisticated software, the microscope expedites blood sample analysis from three days to a matter of just three minutes.
Thrombin
The clotting may be too weak (spontaneous bleeding) or too strong (thrombosis) if the interaction of coagulation factors in the blood function inappropriately. The thrombin enzyme plays a major role in the conversion of fibrinogen clotting factor, also known as blood plasma protein, into fibrin. This phenomenon was first discovered at Maastricht University.
When a blood vessel is damaged, protein fibres from fibrinogen create a network, which is capable of capturing platelets, and this in turn creates a clot that closes the wound.

Figure 1. Phenom SEM image of a clot at 5500x magnification: platelets trapped in a fibrin network.
Measuring Thrombin Activity
According to Bas de Laat, Managing Director at Synapse, the company continues to study innovative methods to detect and predict bleeding and thrombosis.
Synapse covers everything from fundamental research to prototype. Earlier, in 2009, the company was acquired by STAGO, a leading company in blood coagulation tests.
Thanks to STAGO’s significant investment, Synapse received a number of grants and now has 35 employees and five laboratories. The company also collaborates with other companies such as Maastricht Instruments.
De Laat added that once a prototype has been developed, it is transferred to the parent company or to another firm for production. This way, Synapse generates revenues by licensing its patents.
The company also developed a measuring device for the thrombin activity in blood plasma. Blood plasma is the liquid blood that lacks blood cells.
Fiber Measurements
Synapse continues to study blood clotting. Key parameters include the thickness of the fibres and the number of fibres within a fibrin network (Figure 1).
There is risk of thrombosis if the network is fine and strong, and if the network has large gaps in between, then there is risk of bleeding.
The Phenom tabletop SEM was developed by PhenomWorld Eindhoven, which was established five years ago as a spin-off company of FEI, a leading manufacturer of large electron microscopes.
Following an extensive build-up, Phenom-World sold around 300 SEMs to educational institutions and research and analysis laboratories in 2013.
Phenom’s mechatronic construction together with smart image processing software makes the SEM fast and efficient. De Laat added that the Phenom features a nice algorithm for fibres. The Fibermetric software not only determines the pore size between the fibrin threads, but also measures the fibre thickness in the order of 100nm (Figure 2).
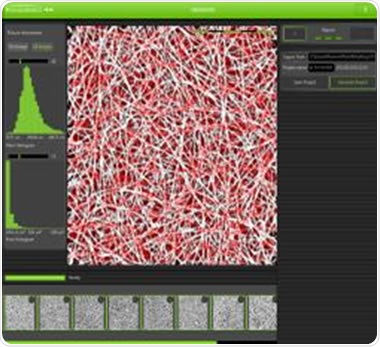
Figure 2. Analysis of fibres using the Phenom FiberMetric software.
Simple Operation and Automatic Analysis
Synapse have saved considerable labour costs thanks to the automatic analysis and simple operation of the Phenom SEM.
Users can simply place the sample and operate through the touchscreen, making the instrument simple and easy to use. This unique technology has also enabled Synapse to reduce the expansion of its workforce and focus more on smarter thinking.
In addition, a second generation of Phenom now exists that comes with higher magnification. This SEM proves useful when more detail is required in certain analyses. At present, Synapse is going to the Maastricht University to view its samples under the large SEM.
Conclusion
The Phenom SEM has become a huge demand in hospitals. So far, the measurements obtained from this instrument appear to be clinically relevant. The use of Phenom SEM in the detection and prediction of thrombosis is set to redefine the medical industry.
About Phenom-World

Phenom-World believe breakthroughs happen when complex nanotechnology is made intuitive, easier to use and brought within reach. As the leading global supplier of desktop scanning electron microscopes, their aim is to make imaging and analysis at the nanoscale available to every scientist in every lab.
That’s why Phenom-World invest their time and effort into developing high-quality electron microscope solutions that are functionally rich, yet simple to use. Because their mission is to create technology that has a real impact on how people work.
This takes innovative thinking, collaborative working and an entrepreneurial attitude. At their home in the high-tech region of Eindhoven in The Netherlands, Phenom-World have a group of passionate people who are given the freedom they need to innovate. Plus a highly skilled team of specialists in more than 40 countries who can provide support on a global scale.
Cooperation and co-creation are key to Phenom-World's success. They work closely with their partners to ensure they have the latest technologies, state-of-the-art equipment and applications for imaging and analysis. So they can get fast and accurate results and achieve more in nanotechnology.
Phenom-World is globally the yearly number 1 manufacturer of desktop scanning electron microscopes and imaging and analysis packages.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.