Pharmaceutical research includes developing new drugs or constantly improving existing drugs. This versatile research topic is an extensive field of study handling an increasing number of challenges, due to new pathogens emerging continuously and known pathogens becoming more and more resistant to existing drugs.
As more information is required, the use of sophisticated tools, such as scanning electron microscopes (SEMs), has been proven to be very powerful in different applications in the pharmaceutical field. In pharmaceutical research, SEMs are used to acquire insights into cellular interactions with new drugs, for applications in the most complex cancer treatments, and for powder imaging and analysis.
This article discusses some examples to demonstrate the successful application of SEMs in research facilities all over the world to develop novel and more powerful drugs to treat diseases.
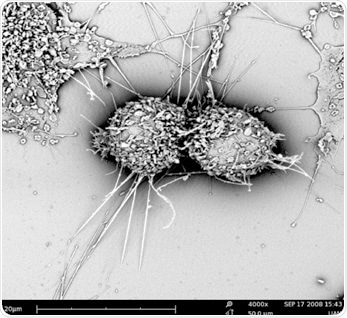
Figure 1. An example of mammalian cells observed with SEM.
Superporous Hydrogels
Researchers at AIMST University in Malaysia are engaged in developing a new class of superporous hydrogel beads. Hydrogels are made up of a network structure of cross-linked hydrophilic polymers that has the ability to absorb water in large amounts without dissolving.
These beads are used as carriers in pharmaceuticals for controlled drug delivery depending on their swelling abilities and biodegradation. Superporous hydrogel beads help in realizing easier and faster regeneration because a targeted drug delivery eliminates side effects on other cells or tissues.
Thanks to developments in research, and the rising need to develop highly performing and improved drugs, the researchers have developed a new class of hydrogels with rapid swelling capacities and hence the name “Superporous Hydrogels”. Here, the researchers examined the porosity and surface structure of the dried beads using a SEM.
Cancer Drug Research
A new kind of approach was employed in cancer drug research. It was found that an enzyme called aromatase, which is responsible for determining the final sex phenotype of fish, was also playing a vital role in the development of breast cancer. As a result, in a study, researchers used aromatase inhibitors for treating breast cancer.
In fish, aromatase enzymes irreversibly convert androgens into estrogens, thereby establishing the embryo’s gender to female. Researchers are more interested in studying male fish than female fish of this species since male fish generate anti-aromatase in large amounts.
Similar to Nile tilapia which attracted considerable attention as a source of food globally, aromatase obtained from this fish was the subject of interest for researchers in search of aromatase inhibitors.
Nile tilapia microsomes were employed to study the enzyme activity of aromatase inhibitors. Microsomes are vesicle-like fractions of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) present in healthy living cells. In this study, hepatic microsomes were prepared from Nile tilapia and their morphology was investigated using a SEM.
The proliferation of cancer cells was explored using MCF-7 human breast cancer cells and HepG2 human hepatoma cells. The study results showed that a specific anti-aromatase present in microsomes efficiently inhibited the growth of both cancer cell lines.
The morphology of tissues should be analyzed and understood for a successful cancer research. Currently, this can be realized using the correlated light and electron microscopy technique.
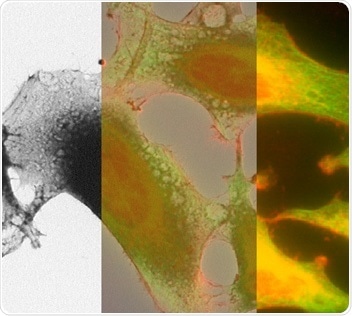
Figure 2. Correlated light and electron microscopy image of HeLa cells.
Development of Antibacterial Powders
The numbers of antibiotic resistant bacteria are continuously increasing due to the excessive use of antibiotics. Hence, researchers are exploring new ways to find the presence of bacteria on medical devices to prevent hospital-acquired infections or nosocomial infections to a feasible extent. Extensive research is being performed to develop new antibacterial powders.
A study showed that the addition of ZnO and Ag-ZnO crystals to antibiotics can effectively destroy the pathogens present on polymer medical appliances. Here, an SEM was employed to analyze the morphology and elemental composition of the crystals prior to using them for further experiments.

Figure 3. Pharmaceutical crystals observed with SEM.
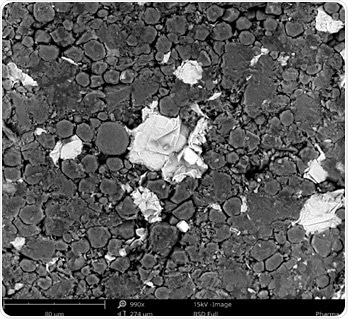
Figure 4. Pharmaceutical components including crystals observed with SEM.
Conclusion
In brief, the scanning electron microscope is a highly versatile tool that can be used for diverse research activities in the pharmaceutical field. It aids in understanding the morphology of the component of interest and emphasizes the effect of interactions with its environment.
References
- Development and in vitro Evaluation of New Generation Superporous Hydrogel Beads (SPHBs) Containing Fluconazol. Kumar et al. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences & Research; Vol. 5 Issue 12, p259 (2013)
- Investigation of anti-aromatase activity using hepatic microsomes of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Pikulkaew et al., Drug Discoveries and Therapeutics (2017)
- Antibacterial Powders for Medical Application Prepared by Microwave Hydrothermal Assisted Synthesis. Kunitka et al,. Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 6(1A): 88-91 (2016)

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Phenom-World BV.
For more information on this source, please visit Phenom-World BV.