Introduction
Blood is an essential component of the body, supplying necessary oxygen to all organs and tissues and eliminating unwanted metabolites from cells. However, in addition to transporting oxygen, blood protects the body from a variety of diseases using the immune cells and platelets present in it. These blood cells also play a role in bleeding disorders.
Researchers across the world are showing interest in understanding ing the nature of blood cell interactions, such as clotting and binding to different fibers in particular. This article discusses the effective role that integrated correlative light-electron microscopy (CLEM) and scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) can play, in laboratories involved in blood research.
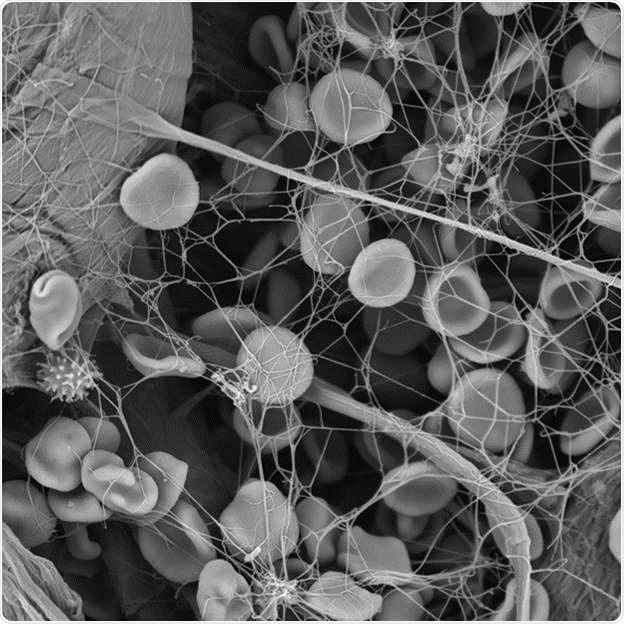
Figure 1: Each wounding causes a reaction by the body- This is the example of a fibrin network with blood cells images with scanning electron microscopy.
Blood contains various types of cells in a solution known as plasma. Water is the main component of plasma, which also contains: hormones, proteins, such as clotting factors, ions and roughly 45% of blood cells.
The human plasma consists of three types of blood cells: Red blood cells (RBCs) or erythrocytes; white blood cells (WBCs) or leukocytes; and platelets or thrombocytes. RBCs are the most abundant blood cells transporting oxygen between lungs and the organs by attaching it to an iron-containing protein called hemoglobin.
WBCs are available in five different types and form the body’s immune system to fight all types of pathogens. Platelets are tiny cell fragments that play a vital role in blood clotting.
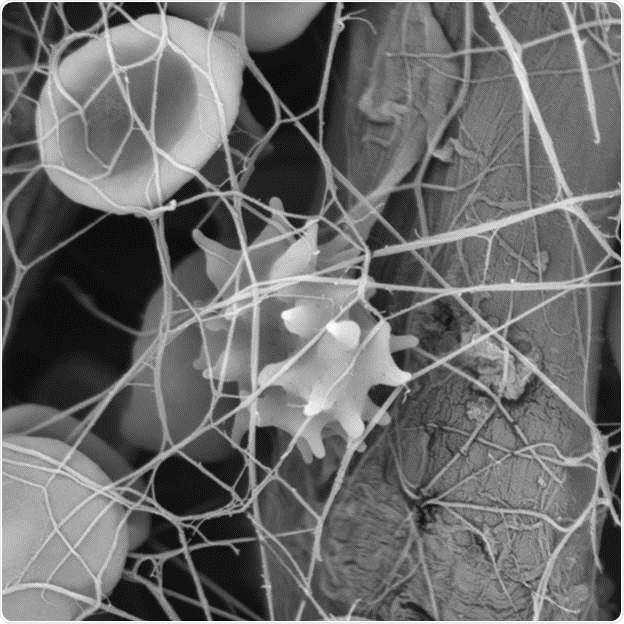
Figure 2: High resolution scanning electron microscopy imaging of blood cells.
What makes blood diseases dangerous?
Skin injuries, bacterial infections, and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) expose blood to all types of pathogens. The body’s immune system combats these diseases by activating a specific type of WBCs, depending on the kind of pathogen the blood is exposed to.
Blood disorders are a different class of blood diseases that occur due to insufficient blood clotting caused by lack of thrombocytes or other components involved in the blood clotting process. In case of an injury, in normal conditions, clotting factors and fibrin present in the blood allow binding of thrombocytes with each other to form a plug at the affected site to avoid further hemorrhage and facilitate healing of the injured tissue.
On the other hand, persons with a clotting disorder can suffer excessive bleeding. This condition not only causes damage to tissues, but can also be potentially fatal. The presence of excess number of clotting factors and thrombocytes is equally detrimental as their absence. This condition can cause several kinds of strokes such as cardiac arrest or brain strokes.
New approaches to better understand blood disorders
Blood research has turned out to be an increasingly popular research field to gain insights into the interactions taking place during clot formation. For this purpose, the SEM has been shown to be very useful, enabling scientists to easily observe the 3D structures of blood clots and the interactions taking place between the blood cells and different fibers.
In the coming years, many blood clotting disorders, such as the Von Willebrand disease will be explored. For instance, the latest advancements in the integrated CLEM will allow fluorescent-marked components to be observed using light microscopy and the cell environment’s 3D structure using the integrated SEM. The combined image provides a clear picture of the interactions, thereby yielding readily available and reliable results.
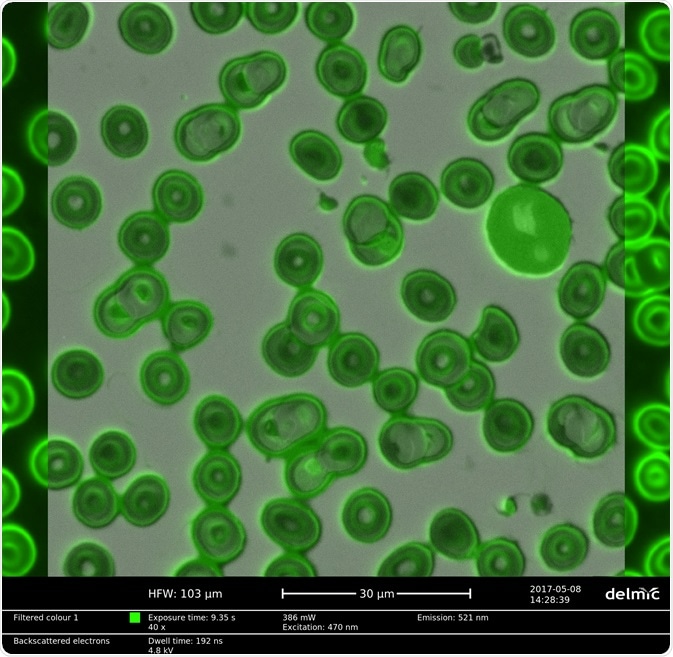
Figure 3 Correlative light and electron microscopy image of red blood cells stained with a hydrophilic fluorescent dye.
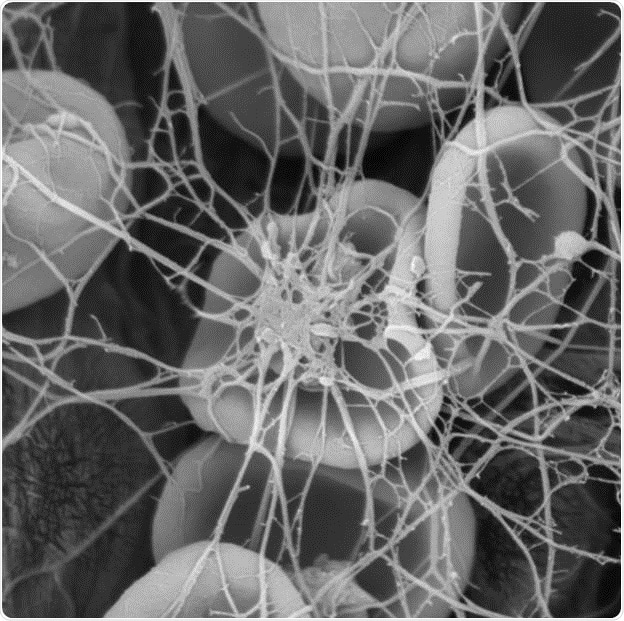
Figure 4: Insights into blood clot formation using a scanning electron microscope
The significance of fast research results
Addressing malaria, an infectious disease caused by mosquitoes, is another objective of blood research. Parasitic protozoans, a kind of Plasmodium, causes this disease, which has an equal effect on both humans and animals.
Generally, symptoms of malaria can be observed in patients only after 10 to 15 days of infection. Improper treatment of malaria leads to the recurrence of the disease. Around 214 million malaria-affected cases were reported across the globe in 2015, of which 438,000 cases were fatal; 90% reported in Africa.
To create potential vaccines or medications, significant studies have been carried out. The combination of Phenom scanning electron microscope and an integrated correlative solution, such as the Delphi, will be very useful, as it allows scientists to easily examine the direct interactions between the parasite and the surrounding cells and tissues.
If you want to know more about CLEM and SEM systems for blood research, visit Phenom-World at the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH) in Berlin from July 8-13.
About Phenom-World

Phenom-World believe breakthroughs happen when complex nanotechnology is made intuitive, easier to use and brought within reach. As the leading global supplier of desktop scanning electron microscopes, their aim is to make imaging and analysis at the nanoscale available to every scientist in every lab.
That’s why Phenom-World invest their time and effort into developing high-quality electron microscope solutions that are functionally rich, yet simple to use. Because their mission is to create technology that has a real impact on how people work.
This takes innovative thinking, collaborative working and an entrepreneurial attitude. At their home in the high-tech region of Eindhoven in The Netherlands, Phenom-World have a group of passionate people who are given the freedom they need to innovate. Plus a highly skilled team of specialists in more than 40 countries who can provide support on a global scale.
Cooperation and co-creation are key to Phenom-World's success. They work closely with their partners to ensure they have the latest technologies, state-of-the-art equipment and applications for imaging and analysis. So they can get fast and accurate results and achieve more in nanotechnology.
Phenom-World is globally the yearly number 1 manufacturer of desktop scanning electron microscopes and imaging and analysis packages.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.