Antibody assays are widely used in clinical diagnostics and also in the process of drug development. Gold standard assay techniques include the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), western blotting, and radioimmunoassay techniques.
Most immunoassay techniques rely on immunorecognition of specific antigens. Despite the usefulness of these assay strategies, their inability to run several analyses of multiple analytes limits its large-scale utility.
Multiplexing with multiplex bead array assays, however, offer the ability to independently and simultaneously assay numerous analytes in small or very minute material volumes. Compared with gold standard singleplex assay techniques, the concurrent quantification of several analytes may confer both cost- and time-saving benefits.
© sruilk / Shutterstock.com
Gold Standard Assay Techniques: Advantages and Disadvantages
ELISA
The singleplex Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA), the most utilized assay method performed in 96- or 384-well plates, has played a prominent role in the quantitative and qualitative identification of analytes. There are direct and indirect ELISA detection methods, each of which offer their own advantages and disadvantages.
One of the benefits of direct ELISA is its ability to accurately measure specific analytes found within a crude solution. Since ELISA detection only requires one antibody and few steps are used, it’s generally a fast test. Indirect ELISA detection is also more versatile in that primary antibodies can often be produced in one species and the identical labeled secondary antibody can potentially be utilized for subsequent detection.
In comparison with multiplexing, the use of ELISA for measuring multiple analytes is time-consuming due to the large number of workflows occurring simultaneously. In indirect ELISA, there is an extra incubation step that’s required, further reducing efficient time spent in the laboratory.
Western Blotting
The western blot is a sensitive immunological protein detection strategy which examines a tissue sample and calculates specificity via band positioning.
The western blot can potentially detect proteins as little as 0.1ng, detecting only the protein of interest to the researcher. This selectivity may help provide analysis of the desired protein in a complex solution. Specificity of western blotting is also important—gel electrophoresis will sort a sample into the different proteins contained within the solution, providing somewhat straightforward detection.
Although western blotting is specific, if large proteins are not given enough transfer time to the membrane a false-negative can result. Blotting itself can lead to faded or multiple bands, producing unfavorable and hard-to-interpret results. Also, the western blot is difficult to automate, and transferring large proteins can be challenging.
© phloxii / Shutterstock.com
Radioimmunoassay
Another gold standard assay technique is the radioimmunoassay, an in vitro process whereby a radioisotope-labeled antigen (usually radiolabeled with gamma-radioactive iodine isotopes) is introduced and the radioactivity of the antibody is measured.
Similar to western blotting, the radioimmunoassay is highly sensitive and specific. This method is also not restricted to merely serum antigens; any biological molecule can theoretically be used in a radioimmunoassay.
Due to the use of radiolabeled reagents, there are potential radiation hazards with this technique. This often means only specially trained individuals can handle this assay. Laboratories usually need licensure to handle this radioactive material as well as special protocols for storing and disposing this material.
Multiplex Assays: Advantages and Disadvantages
Newer technological advancements have allowed for more robust multiplex assays in the detection of complex diseases. Multiplex assays can detect, identify, and monitor dozens of proteins at once, thereby optimizing clinical research and aiding in the discovery of new therapeutic options.
There are two basic types of multiplex assays: bead- and planar-based. Specific types of multiplex assay techniques include protein microarray, antibody microarray, DNA microarray, and fluorescent bead microarray.
_research%2c_scientifically_accurate-Alila_Medical_Media.jpg)
© Alila Medical Media / Shutterstock.com
Advantages
In multiplex assays, researchers are able to receive more data from a sample than they would if using a singleplex assay such as with the ELISA or western blot. More simultaneous evaluation of analytes also translates into a faster procedure, resulting in both time and cost savings.
Multiplexing can also be customizable and automated, further reducing the time needed in the lab. Additionally, a multiplex immunoassay will combine assays for a multitude of analytes of different types in one reaction volume, resulting in a more time- and cost-efficient procedure.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages to using multiplex assay technology is that it often requires specialized equipment and a validated antibody pair. The initial investment in a multiplex system may also be higher than singleplex devices.
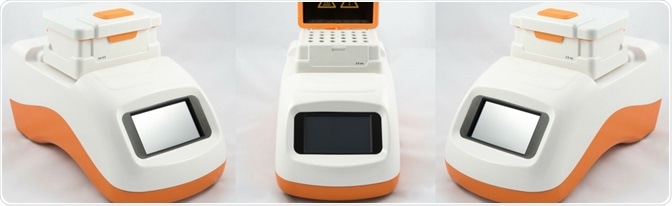
Ther-Mix for Immunoassays
Most immunoassay techniques require incubation on a shaker. Techniques also involve heating and mixing at different temperatures and at varying amounts of time. Incubators, stopwatches, mixers and shakers, and a variety of other tools can be cumbersome and time-consuming. The Ther-Mix by Vitl is a heated mixer that allows the operator to program and store their custom mixing programs.
Once programmed, the Ther-Mix can automatically run through the numerous incubation and mixing steps without requiring constant attention. When the protocol has been completed, the Ther-Mix alerts the operator. Interchangeable Heated Modules allows an operator to use a variety of sample tubes and plates.
Dr Helen Bennett reviews the Vitl Ther-Mix
References:
- Tighe PJ, Ryder RR, Todd I, Fairclough LC. ELISA in the multiplex era: potentials and pitfalls. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2015;9(3-4):406-422.
- Immunoassays: Protein Arrays vs. ELISA and Westerns. Grace Bio-Labs. https://gracebio.com/immunoassays-protein-arrays-vs-elisa-and-westerns/.
- Five Ways That Multiplex Technology Accelerates Cancer Research. Luminex White Paper. http://cdn2.hubspot.net/hub/128032/file-1242255217-pdf/WP885.xMAP.Cancer.0714.WR.pdf?t=1410627766815.
- The Role of Multiplexed Assays in Vaccine Development. Luminex White Paper. http://www.nature.com/app_notes/nmeth/2015/151011/pdf/an9676.pdf?spMailingID=50203593&spUserID=ODkwMTM2NjMzOQS2&spJobID=821232547&spReportId=ODIxMjMyNTQ3S0&foxtrotcallback=true.
- The power of multiplexing. ThermoFisher Scientific White Paper. https://www.thermofisher.com/content/dam/LifeTech/global/technical-reference-library/s2s/dbourdon/The%20power%20of%20multiplexing.pdf.
- Multiplex immunoassay techniques: a review of current methods. Abcam. https://www.abcam.com/.
- Multiplexed Protein Assays. Biocompare. http://www.biocompare.com/Editorial-Articles/41806-Multiplexed-Protein-Assays/.
- Elshal MF, McCoy JP. Multiplex bead array assays: performance evaluation and comparison of sensitivity to ELISA. Methods. 2006;38(4):317-323.
About Vitl Life Science Solutions
Vitl designs, manufactures and sells high quality laboratory instruments to compete with market leaders at an affordable price with unrivalled functionality, usability and style.
The growing Vitl laboratory products range includes the world’s best-selling microplate heat sealer- the VTS and its compact counterpart the MicroTS. Vitl also sell a range of foil and film heat seals as well as microtube pickers and programmable mixers and vortexers.
Vitl products was established in 2006 by the medical, diagnostic and analytical device design and manufacturing company Integrated Technologies Ltd.
As a member of the ITL group, Vitl benefits from the experience and expertise of a parent company that works with globally successful medical devices and laboratory instrumentation.
Vitl products are sold through a global network of distributors and OEM (private label) partners, managed by their main sales offices in the UK, USA and China.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.