Sponsored Content by NuAireApr 18 2018
Biosafety cabinets, an integral part of hospital, research, and industry laboratories across the globe, create a clean and/or ventilated workspace for drug preparation, diagnosis, research, and development. In order to ensure the best protection for personnel, samples, and products, individuals must be confident that their biosafety cabinets align with regulatory authority and industry-approved standards.
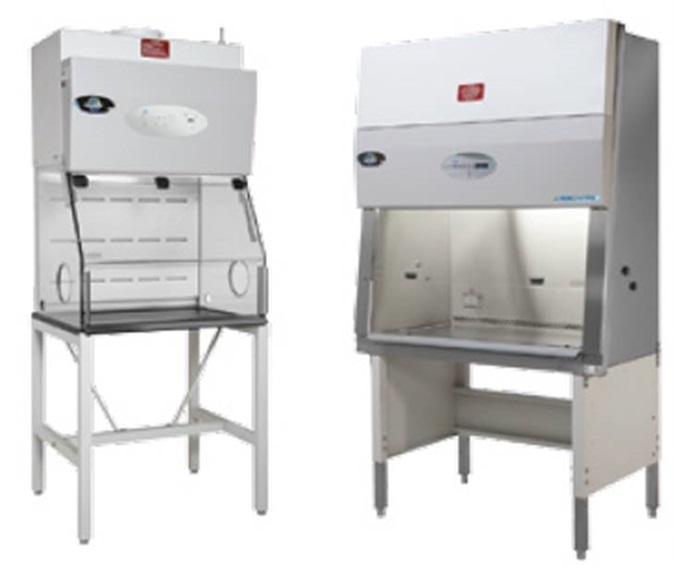

Image credit: NuAire
An introduction to biosafety cabinets
Biosafety cabinets, also referred to as microbiological safety cabinets or biological safety cabinets, provide a ventilated but enclosed workspace. These cabinets are used for three main purposes:
- to protect personnel from potentially infectious or toxic materials
- to protect products and samples from laboratory contamination
- to protect the environment from infectious or toxic materials
The initial versions of biosafety cabinets had basic on/off switches but they are now equipped with a range of safety features which can all be monitored using software. These features can include sensors that monitor motor function and window position, as well as airflow monitoring and control using airflow sensors.
Biological safety cabinet classes
Based on their design and use, biosafety cabinets are grouped into three classes: 1
Class I
- Protects the environment and personnel from aerosols when exhausted through a facility hvac system and when using biological agents, but cannot protect products from contamination
- Air exhausted externally or room recirculated into the lab
- HEPA filter in the air exhaust

Image credit: NuAire
Class II
- Protects products, workers, and the environment when handling handling biological agents and Hazardous Drugs (HD’s) such as chemotherapeutic agents when properly vented through a facility exhaust system.
- Air exhausted externally or room recirculated
- HEPA filter in the supply and exhaust

Image credit: NuAire
Class III
- Gas-tight; protects products, workers, and the environment when handling risk 4 biological agents
- Total containment cabinets
- Usually a double exhaust HEPA filter configuration
- HEPA filter placed in the air supply

Image credit: NuAire
In chemical, medical, biological research, and biopharma R&D, biosafety cabinets make sure that research experiments are performed in a sterile consistent setting. Similarly, in medical diagnostics, these cabinets protect both operators and samples from contamination (for example viruses and bacteria).
To prepare combination HD drug regimens, for example cancer chemotherapy, when used with aseptic technique or good manufacturing practices, biosafety cabinets offer injection and infusion solutions are free from contamination and protect operators from drugs that are often toxic.
The Biosafety Standards
Biosafety cabinet standards have been published for four decades or more, and they offer the minimum construction and performance requirements to ensure a safe working environment. Cabinets that conform to international standards will increase customers’ confidence that they are working with biosafety cabinets that adhere to industry guidelines.
EN 12469 and NSF/ANSI 49 are the main standards used. NSF International, a non-profit and accredited independent organization, designs standards and certification programs for the American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
In the United States, the NSF/ANSI 49 standard is considered the “gold standard” for biosafety cabinets. Technischer Überwachungsverein (TÜV) Nord, one of the leading independent testing agencies in Europe, tests to the EN 12469, biosafety cabinet standard. TÜV Nord tests most of the biological safety cabinets that were earlier tested to EN standard. The documentation prepared for these standards shows how biosafety cabinets are evaluated (refer Table 1).
Table One - Biosafety Standards 2
|
|
NSF/ANSI 49
|
EN 12469
|
|
Classes
|
Covers Class II cabinets; broken down into subtypes
|
Covers Classes I-III Cabinets
Class II requirements are virtually identical to NSF/ANSI 49
|
|
Microbiological Challenge
Testing for Operator, Cross and Product Contamination.
|
Yes
|
Requirements adopted from NSF/ANSI 49 Include optional
test to validate containment in the field (KI-Discus text)
|
|
Airflow Velocity – Downflow
|
Includes downflow velocity but no specific requirements; requires larger number of test points
Specifies thermoanenometer
|
Recommended downflow velocity range of 0.25-0.50 m/s
Does not specify instrument accuracy and type
|
|
Airflow Velocity – Inflow
|
Uses direct inflow measurement (DIM)
Minimum inflow velocity of 100 fpm (0.51 m/s)
|
Recommends airflow measurement above exhaust and calculates inflow
Minimum inflow velocity of 0.4 m/s
|
|
Performance Envelope
|
Function within +/-0.025 m/s of the inflow and downflow set points, using the airspeed parameters
|
No specification
TUV Nord requires low alarm point to be tested
|
|
Pressurization Testing
|
Soap bubble pressure leak test as routine test
|
Soap bubble pressure leak test as a test type
|
|
Filter Leak Test
|
Generated Aerosol Challenge
|
Generated Aerosol Challenge
|
|
Airflow Smoke Pattern Tests
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Room Airflow Patterns in Situ
|
Not Required
|
Optional – uses potassium iodide
|
|
Worker Comfort
|
Noise – 67 dBA at operator head position
Vibration Test – Yes
Light level – 650 lux
|
Noise – 65 dBA 1m away from center of access opening
Vibration Test – Yes
Light level – 650 lux
|
|
Other
|
Measure ‘cleanability’ of contaminated surfaces
No noise insulation inside contaminated areas
Chemical/abrasion resistance of paintwork Motor/Blower Test
|
Airflow alarms
Audio and visual alerts for malfunctions
|
One of the most significant parts of European and US standards is the biological testing aspect which employs a biological aerosol challenge. The main difference between European and US standards is that the former checks for bacterial challenge at minimal set point velocities (that is calibrated downflow and inflow air speed), while the latter also tests above and below those levels that enables variability in the testing protocols.
Some countries across the globe publish their own standards. Most of these standards are based on European and US guidelines, but they also have their own differences. For instance, biological tests are not included in the Australian standards, which require testing on site together with potassium iodide or dioctylphthalate (DOP) testing for containment performance.
If the biosafety cabinet is room recirculated, British standards specify two exhaust HEPA filters and the Chinese standards specify a coved work zone insert, i.e., dual side wall construction.
Conversely, users and purchasers should remember that these standards are only the minimum expectations for construction, safety, and performance quality. The standards do not cover how the cabinet is manufactured, but only how it performs.
Look beyond the standards
Clients should look beyond these standards. For instance, is the cabinet merely fastened along with rivets or screws, or tightly and smoothly built, welded, and polished? Is the biosafety cabinet service friendly (front access)? Quality of materials utilized – painted steel versus stainless steel?
Cabinets that surpass the minimum standards, instead of meeting them, will increase the confidence of users about the highest containment performance with some level of safety. For instance, a vivarium setting may create more airflow movements and currents. A biosafety cabinet subjected to dynamic testing can help detect its limitations when placed in a turbulent setting.
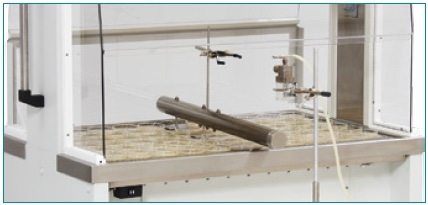
Biological Testing, Generated Aerosol Challenge. Image credit: NuAire
Testing to meet the standards
When purchasing EN and NSF-certified cabinets, customers should know what to anticipate from a safety and containment standpoint. Biosafety cabinet manufacturers submit their base unit models to the testing center, which then checks the unit to see if it satisfies the standards requirements, but this process is very costly; for instance, NSF testing can cost as much as $50,000 for one model.
The approved model lines bear the suitable labels and are listed on the website of the organization. still, a degree of “buyer beware” remains for the client. Through third-party testing, a few companies submit just one or two models and then provide similar models for sale, but these units may not be the ones listed under the EN or NSF standards.
After a cabinet passes, the standards will apply if no significant changes are made. Yet, many cabinets are custom-made to suit the needs of customers. While mild construction or cosmetic changes will not impact the listing, cabinets with profound customization changes cannot carry the TÜV or NSF labels.
Major changes include:
- Providing customized access (e.g., side access)
- Creating non-stock size cabinets
- Developing the cabinet to fit a specific instrument and space
- Including robotics
When searching for a custom-made biosafety cabinet, it is recommended to locate a manufacturer who can address this challenge by developing tailored solutions as if they were going to be TÜV or NSF tested. It is possible to validate these changes because most cabinet manufacturers will have on-site testing centers that imitate third-party testing.
Future standards
With emerging technological advancements and rigorous research and industry requirements, standards also have to evolve to address these changes. At NSF International, the Joint Committee on Biosafety Cabinetry continuously updates the guidelines depending on user submissions.
The updated version of the European standard and the updated guidelines were published in 2000 and 2014, respectively. However, it is difficult to update these standards because the EN standards have to be agreed upon across all the European countries.
Laboratory equipment supply from NuAire
NuAire develops scientific laboratory equipment that is ergonomically designed and engineered and provides product, personnel and/or environmental protection in important research settings. The company offers the following range of laboratory equipment:



Biological Safety Cabinets, Animal Research Products, CO2 Incubators. Image credit: NuAire



Laminar Airflow Products, Polypropylene Fume Hoods & Casework, Centrifuges. Image credit: NuAire
References
- University of Minnesota. Biosafety: Types (Classes) of BiologicalSafety Cabinets. Created: 2010. Last updated: 14 June 2010; Accessed: 21 October 2015
- Qian, L.X. Biological safety cabinets: Comparison betweenEuropean and US standards. Clean Air and Containmnent Review, 2011. (5).

About NuAire
Quality and Service
For more than 40 years, NuAire has been committed to bringing you the highest-quality, most dependable laboratory products on the market.
We are universally recognized as one of the world's leading providers of reliable equipment for the most demanding environments, including Biological Safety Cabinets, CO2 Incubators,Laminar Air Flow workstations, Ultra Low Temperature Freezers, Centrifuges,Animal Transfer Stations, Pharmacy Compounding Isolators, Polypropylene Fume Hoods, Polypropylene Casework, and a variety of complementary products and systems.
You can depend on our products to feature brilliant but practical design, and we pay keen attention to every step of the production process, from fabrication to assembly to thorough testing. As a NuAire customer, you can also rely on us for outstanding value and dependable service - the cornerstones of our reputation as the leading provider of laboratory products internationally.
Committed to Your Success
At NuAire, we create our high-quality products with your success in mind. This means that if you purchase a piece of laboratory equipment from us, we want you to be completely happy while using it.
NuAire will work hand-in-hand with you in order to ensure that your experience using our product meets your standards, and if you encounter any issues or difficulties along the way, we'll help you work through them until you are 100% satisfied. Our philosophy is that we succeed only when you succeed - and we are committed to working hard to ensure you achieve your goals.
Made in America
At NuAire, you can depend on us for being a company that is "Made in America." Our Airflow Products, CO2 Incubators, and Polypropylene Products are manufactured at three locations in Minnesota.
With over 300,000 square feet of manufacturing space, including a state-of-the-art robotic sheet metal facility, NuAire is able to provide employment to 300 Minnesota families and 60 North American sales representatives, and our manufacturing labor is 100% American.
We also purchase our materials from over 500 American vendors, each operating principally in the United States. More than 60% of the raw materials, parts, and supplies for our products originates in the U.S., and an average of 20-30% of the stainless steel flats we use are made from recycled metal.
International Leader
While NuAire is an American company, we also have several international business partnerships, which allow us to better serve you, the global laboratory community. NuAire recently started manufacturing a line of Biological Safety Cabinets in China in order to supply products to the Asian markets via Techcomp, Ltd., a publicly traded Chinese company.
In 2014, NuAire founded an international partnership with Hitachi Koki in order to supply high performance centrifuges to the North American market. NuAire can now provide customers with the sales and service of Hitachi High Speed, Ultra, and Micro Ultracentrifuges.
With several other partnerships with a variety of European and Asian companies, we have sold over 100,000 biological safety cabinets to customers in 150 countries and have equipment located on all 7 continents.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.