Blood separation is the dividing of whole blood into its various components. Whole blood is often isolated for therapeutic and diagnostic reasons, including research.
For this to be achieved, researchers use various blood separation methods. The most famous of which include blood separation machines that have the potential to spin at high speed, exerting a centripetal force and isolating the blood into its several components.
CAPPRondo blood separation centrifuges obtained from CAPP help researchers achieve improved clinical results for patients and trustworthy blood separation for their research.
What are the components of blood?
Whole blood is tissue with various cellular and non-cellular components. The significant components of blood are plasma, cells, and platelets (cellular fragments included in clotting). Blood comprises two types of cells—white blood cells (leukocytes) and red blood cells (erythrocytes).
Erythrocytes are the blood cells that distribute oxygen from the lungs to all parts of the living organism. Leukocytes, as part of the immune system, are responsible for attacking infectious cells, keeping the organism healthy.
Leukocytes can be classified into monocytes, lymphocytes, eosinophils, neutrophils (granulocytes), and basophils. The components of whole blood could be isolated utilizing blood separation methods such as centrifugation. Blood separation enables researchers to offer treatments and study disease markers with the help of various components of blood.
What are the components of blood plasma?
In a yellowish substance known as plasma, blood cells are suspended. Plasma comprises water and various dissolved molecules. Collectively, the components of blood plasma consider its large volume in the blood (±55%).
A few components of blood plasma include glucose, salts, proteins, clotting factors, immunoglobulins, hormones, and carbon dioxide from metabolic processes. Researchers could isolate the components of blood plasma and utilize them to treat medical conditions such as disease and injury. Since plasma comprises several valuable components, suitable blood separation methods help clinicians treat patients more effectively.
Separation of blood into its components
Diagnostic laboratories perform blood separation assays to test for disease markers or prepare for transfusions. Every blood component has a special function, and isolating it from the other components could be essential for precise diagnoses or effective therapeutic applications. Researchers frequently use the special densities of blood components to develop blood separation methods.
Such blood separation techniques enable diagnostic laboratories to assay every blood component with great precision, and this translates to improved results for patients. Separating blood into its components is a vital first step that is the foundation for several significant diagnostic and research procedures.
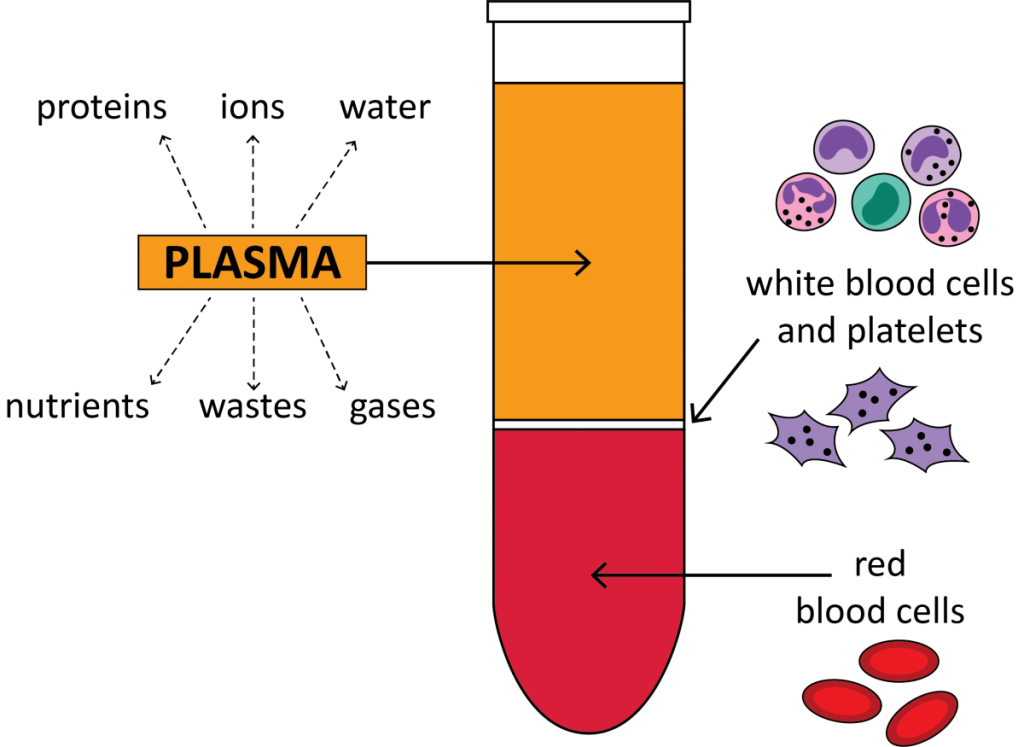
Image Credit: AHN Biotechnologie GmbH
Blood separation techniques
Several blood separation techniques rely on centrifugation to obtain the utmost separation of blood present in collection tubes. The collection tube’s size should be suitable for the blood separation centrifuge that will be utilized. At CAPP, centrifuges are ideally suited for blood cell separation, blood plasma separation, and several other applications (PRP, PPP, Stem-Cell, etc.).
To tackle these numerous applications, CAPP has come up with two kinds of blood separation centrifuges. Such blood separation centrifuges tend to make use of either a fixed-angle rotor or a swing-out rotor. The rotors of CAPP blood separation centrifuges have the potential to handle tubes of numerous capacities (that is, 1.5 mL, 2 mL, 5 mL, 7 mL, 10 mL, or 15 mL).
Expell secure micro tubes. Image Credit: AHN Biotechnologie GmbH

BluCapp centrifuge tubes 15 ml. Image Credit: AHN Biotechnologie GmbH

CAPPRondo blood mixer roller. Image Credit: AHN Biotechnologie GmbH
Blood separation with a swing-out rotor
Blood separation centrifuges and a swing-out rotor enables particles to deposit uniformly at the tube’s bottom. One benefit of this blood separation method is simply separating blood components following centrifugation.
Another benefit of this blood separation technique comes under the use of smaller centrifugal forces, decreasing energy consumption. Generally, swing-out rotors are utilized for blood separation in research and medical laboratories.
CAPP does the work of manufacturing and supplying the CAPPRondo Advanced Clinical Centrifuge CRC-416X with an elective swing-out rotor (6 ×10 mL tubes) for blood separation. This main blood separation machine has the potential to provide centrifugal forces of up to 2270 g at variable speeds ranging up to 4000 RPM.

Image Credit: AHN Biotechnologie GmbH
Blood separation with a fixed-angle rotor
Being an alternative to blood separation machines along with a swing-out rotor, a few blood separation centrifuges consist of a fixed-angle rotor. The fixed-angle rotor blood separation machines tend to spin blood components to the opposite side of the tube, from which they further slide down to the bottom.
This blood separation technique, linked to the higher centrifugal forces of fixed-angle blood separation centrifuges, leads to quicker blood separation. The speed benefit of such blood separation machines seems to be considerable, and research laboratories preferably use blood separation centrifuges with fixed-angle rotors for their analyses.
With the help of fixed-angle rotors, CAPP provides two blood separation centrifuges, including the CAPPRondo Basic Clinical Centrifuge CRC-658 and the CAPPRondo Advanced Clinical Centrifuge CRC-416X.
The CAPPRondo Basic Clinical Centrifuge houses around eight tubes of varying capacities, making it one of the most highly flexible blood separations centrifuges commercially available. The rotor has been developed to tackle most common tube sizes with ranging capacities that include 1.5 mL, 2 mL, 5 mL, 7 mL, 10 mL, and 15 mL.
This blood separation machine can spin blood samples at speeds ranging up to 6500 RPM, equivalent to a centrifugal force of 3873 g.
On the higher end of the spectrum is the CAPPRondo Advanced Clinical Centrifuge CRC-416X, which features two fixed-angle rotors of 8x15 mL and 16x10 mL. However, both blood separation machines are ideally suited for high-efficiency blood separation with repeatable precision.

Image Credit: AHN Biotechnologie GmbH
Recommended centrifuge speed for blood
The suggested centrifuge speed for blood separation relies on the application for which the blood will be used. For the majority of the diagnostic assays and few research applications, a centrifuge speed of ±4000 RPM would be adequate while a centrifuge speed of ±6500 RPM would be ideally suited for the majority of the research applications.
Having a top speed of 4000 RPM, the CAPPRondo Advanced Clinical Centrifuge CRC-416X, with a swing-out rotor, has been recommended as the best blood separation centrifuge for clinical applications.
CAPP also recommends the CAPPRondo Basic Clinical Centrifuge CRC-658 and the CAPPRondo Advanced Clinical Centrifuge CRC-416X with fixed-angle rotors for research applications.
How long does it take to centrifuge blood?
Blood separation performed by centrifugation is a quick process that generally takes less than 15 minutes. Before blood separation has started, it is essential to gather the blood sample in the right tube for blood separation work.
Once this is done, it is necessary to let the sample sit on the bench for around 30 minutes to an hour for the blood to get coagulated in the collection tube. To obtain the best outcomes, it would not be advisable to allow the collection tube to sit unrefrigerated for longer than an hour before centrifuging the blood.
As far as clinical applications are concerned, blood separation centrifuges with lower centrifugal force, such as the CAPPRondo Advanced Clinical Centrifuge CRC-416X, are chosen. Research applications that need rapid turnover might make use of the CAPPRondo Basic Clinical Centrifuge with a greater centrifugal force for briefer blood separation times.
Why are white blood cells separated from red blood cells before being analyzed?
White blood cells are isolated from red blood cells prior to analysis to make it simpler for scientists and clinicians to examine them. There are less white blood cells in whole blood than the red blood cells.
It would be hard for researchers to access the white blood cells for regular clinical assays and research in the absence of an initial blood separation step. The blood separation methods that are utilized generally make a diverse layer of white blood cells that researchers can further eliminate for additional analysis.
When researchers make use of blood separation centrifuges to isolate white blood cells from red blood cells, the white blood cells are situated in a layer called the Buffy coat.
Centrifuged blood
Centrifuged blood consists of a multi-layered appearance along with three horizontal stacks of various colors. When users eliminate a specimen tube from the blood separation centrifuge, the three colored layers are simple to be distinguished.
The straw-colored top layer comprises the liquid portion of blood—plasma—and it considers 55% of the total blood volume. The layer present below the plasma could have a gray or whitish coloration. White blood cells and platelets tend to occupy this layer of centrifuged blood, and it is specified as the Buffy coat.
The lowest layer consists of the red blood cells, and these consider 45% of the total blood volume. The lowest layer of centrifuged blood’s color might seem bright red or dark red based on the oxygen content of the cells.
It is simple and rapid to get outstanding separation of centrifuged blood with the help of a high-quality blood separation centrifuge such as the CAPPRondo Advanced Clinical Centrifuge CRC-416X.
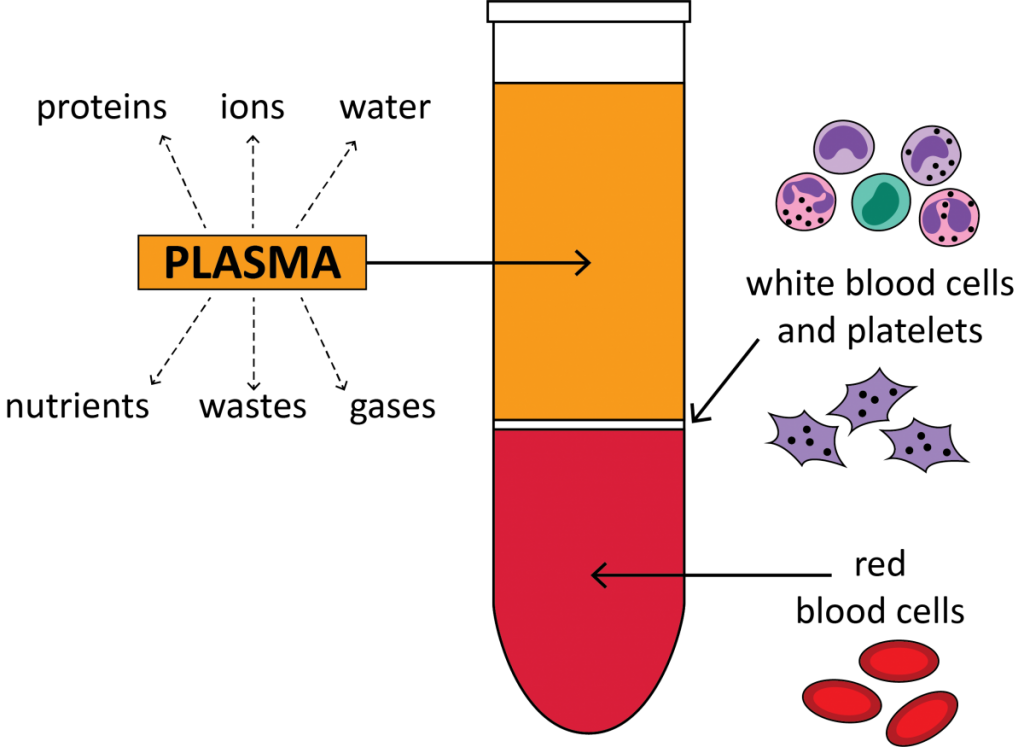
Image Credit: AHN Biotechnologie GmbH
How a centrifuge separates blood
The functioning of blood separation centrifuges is done by spinning blood samples (in collection tubes) at high speeds. The high rotation speeds tend to apply a rotational force on the blood collection tubes that are known as the centrifugal force.
When blood collection tubes have been spun in a blood separation centrifuge, the centrifugal force isolates the several components of blood as a function of their quantity and density present in the sample.
Therefore, the several components of blood could be isolated into various layers for simple separation by just running the blood samples in a high-quality blood separation centrifuge such as the CAPPRondo Basic Clinical Centrifuge.
Medical procedures involving the separation of plasma from blood cells in whole blood
Plasmapheresis is known as a procedure that finds its application in clinical facilities to isolate plasma (the liquid portion of the entire blood) from blood cells. Even though the majority of the blood separation techniques such as centrifugation are performed in a laboratory environment, it is possible to conduct plasmapheresis in a clinical facility.
Blood separation by plasmapheresis might be utilized to exchange unhealthy plasma present in patients for healthy plasma from a donor. The plasmapheresis process includes a two-way blood separation process. Since plasma exits the body, the individual gets saline to safeguard them from dehydration.
Blood separation centrifuges
If users are looking for a blood separation centrifuge with outstanding value and trustworthy precision, CAPP supplies a few of the best commercially available blood separation machines. The CAPPRondo line of blood separation centrifuges consists of both swing-out rotor and fixed-angle options.
These include the CAPPRondo Advanced Clinical Centrifuge CRC-416X and the CAPPRondo Basic Clinical Centrifuge CRC-658. However, both blood separation machines provide inventive features that have been developed to help users get the most out of every blood separation.
Image Credit: AHN Biotechnologie GmbH
About AHN Biotechnologie GmbH
AHN Biotechnologie GmbH, based in Nordhausen, Germany, is a manufacturer of plastic injection molded products, life science products and laboratory consumables for worldwide laboratory use.
With over 20 years’ manufacturing experience in serving German and global leaders in the Laboratory Automation Industry, we have been acting as a global OEM manufacturer of consumables for many outstanding life science brands and distributors. Our state-of-the-art manufacturing facility meets and exceeds the rigorous standards and quality requirements of the best-known brands we supply.
At the same time, we are strengthening our three associated brands: CAPP, AHN and Maxxline by producing and supplying a comprehensive range of consumables, liquid handling devices and laboratory equipment. Our unique combination of flexibility, innovation and high-quality production automation ensures that our laboratory products meet the needs of customers worldwide and meet their high-quality requirements.
With our expertise in manufacturing laboratory consumables and the state-of-the-art electric injection molding technology that offers faster production turnaround time and sustainable quality products, we achieve the best value for money that meets the strict standards of the modern laboratory industry.
Sustainability is built into every part of our production flow and is reflected in all our products, such as the plastic-saving pipette tip refill systems, the cardboard racks for pipette tips or cryovials.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.