Sponsored Content by AutomataReviewed by Louis CastelSep 13 2024
While life science labs are at different stages of their automation journey, most now view it as a standard aspect of operations. However, for advanced labs, automation is essential for sustaining and achieving future success.
In the drug discovery sector, automation can speed up complicated processes end-to-end. This approach provides faster patient results, ultimately giving the business a competitive advantage.
Even though it has clear benefits, some platforms still do not possess one of the most important features necessary to compete in an ever-evolving sector like pharmaceuticals: flexibility.
The challenge
Flexibility in lab automation platforms can be challenging due to the varied requirements of lab environments. In life sciences, the variables that automation developers have to consider are complicated, including:
- Multiple vendors across consumables, instruments, databases, and software.
- Little standardization across suppliers and manufacturers.
- Labs focus on different scientific disciplines, using various assay types.
- Assays differ from lab to lab.
- Different benchmarks or KPIs for success, for example, turnaround time, accuracy rates, and equipment up/down time.
- A lack of lab space in the UK; however, this is not an issue in other markets.
- Location, as specific sectors and different countries have varying laws and regulations across multiple stages of the drug development pipeline.
These variables mean that flexibility becomes infinitely more important when designing lab automation solutions, but much more difficult to achieve.
Julie Huxley-Jones of GSK put it best when she said: “We need data, hardware, software, and algorithms that allow us to work in a flexible environment with different levels of digital literacy – digital innovation rather than a single standardized best-in-class.”
The need for new automation principles
Automata’s lab automation platform was developed on an ‘open, integrated automation’ principle, as the future of lab automation depends on flexibility. This cannot be achieved without developing open-access, vendor-agnostic solutions.
Flexibility can be attained with the right approach, but it requires understanding the obstacles in lab automation and how developers must respond to them.
How open, integrated automation will revolutionise your lab
Video Credit: Automata
Flexible automation and large organizations
When considering flexible automation within large organizations, several factors, including scale and responsiveness, must be considered.
Scale
The meaning of scaling up within pharmaceuticals differs depending on the stage of drug discovery and its development cycle. This could involve increased time or throughput, enhanced digital capabilities for data, or additional physical components like samples. Labs must be equipped to grow and adapt, regardless of these variables.
In response, automation must first analyze any relevant barriers and concerns. In labs, these can be:
- A lack of physical space
- Being locked into a specific vendor
- A lack of experience or knowledge
- The inability to replace legacy systems
- Cost or budgetary issues
- Quality of output and results
LINQ has been designed to neutralize these barriers by delivering an automation experience that is modular, reliable, and easy to use.
Users can begin with a small automated workcell system, adding more components as the opportunity to automate more actions arises, or there is a requirement to incorporate new processes. This system can be built and expanded over weeks.
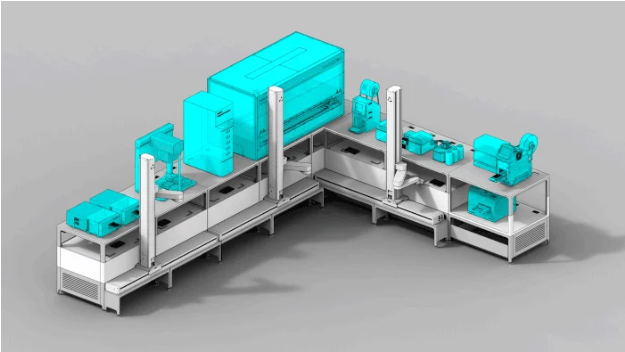
Image Credit: Automata
Responsiveness
Responsiveness involves scalability, but it fundamentally means having the flexibility to adapt and make changes quickly.
The COVID-19 exemplifies the importance of responsive capability and is one of the key reasons Automata began developing lab automation applications. It quickly became evident that a rapid response from the pharmaceutical sector was crucial in the fight to control the virus.
While a pandemic represents a worst-case scenario, changes in demand and needs are a constant in the pharmaceutical sector. Large-scale pharmaceutical labs can't be rebuilt for every shift, but LINQ offers adaptable automation that can adjust to any goal, allowing decisions about what to automate and when to be made without limitations.
Criteria for data collection can be altered, instruments can be switched out, and workflows can be designed and tested. LINQ can pull on resources from across a connected automation network, facilitating reallocation as the need arises.
Where more than one LINQ system is connected, users can utilize resources across the entire automation infrastructure, making it easier to innovate and respond to changing demands.
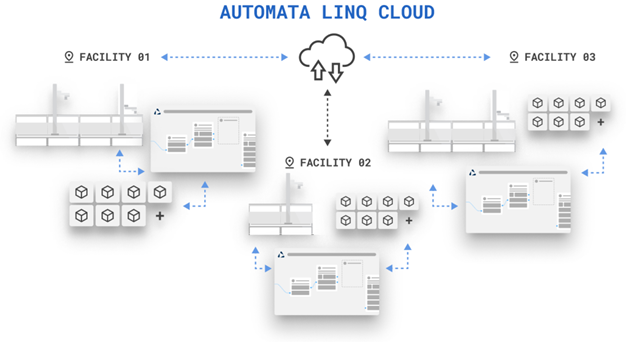
Image Credit: Automata
Facilitating innovation
These same flexibility issues also apply to automation in a research and development setting, but the consequences can be even more significant. There is a risk of creating an environment where technology restricts what can be achieved, hindering creativity and innovation.
Experimental design should be led by hypothesis or need, not the accessibility of data or the capabilities of an automation system.
This applies at software and hardware levels: as software needs to cope with new modalities and remove data silos, hardware needs to be interchangeable and capable of handling any selection of consumables, chemistries, and sample types.
Data
The labs of the future will have heterogeneous data ecosystems, so rigid automation with unchangeable data handling parameters will not suffice. Automation platforms must accommodate multiple data points and integrate seamlessly with any data lake.
LINQ Cloud, the software component of the LINQ automation platform, can do this. It can integrate with any LMS, deliver data to any repository, adapt to multiple client data formats, and transfer data in real time for full multipoint and viability analysis.
With LINQ, there are no data restrictions on input or output, so it allows flexibility within a known system. It can also transfer new data types from AI resources when they become scientifically suitable.
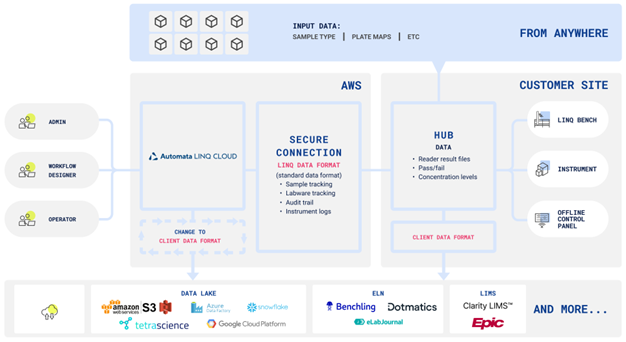
Image Credit: Automata
Collaboration
Multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company GSK issued a document detailing its position on pandemic preparedness in March 2022. This document pinpointed collaboration as one of its underlying principles:
“…the world’s ability to identify, contain, and respond to pandemic threats requires coordinated disease surveillance, unfettered access to pathogen identification, expedited access to clinical trial networks, and joint working on procurement and manufacturing readiness to enable global and domestic responses.”
Facilitating access to required information in a secure, measurable, and traceable manner allows for greater collaboration opportunities, now and in the future.
LINQ has 21 CFR-approved user management capabilities to promote confidence through secure access rules, facilitating internal collaboration. Permissions can be set at admin, creator, and operator levels, allowing users to view required data.
Information, such as audit logs, is tracked on LINQ. This data is easily accessible and exportable, making it readily available whenever needed.
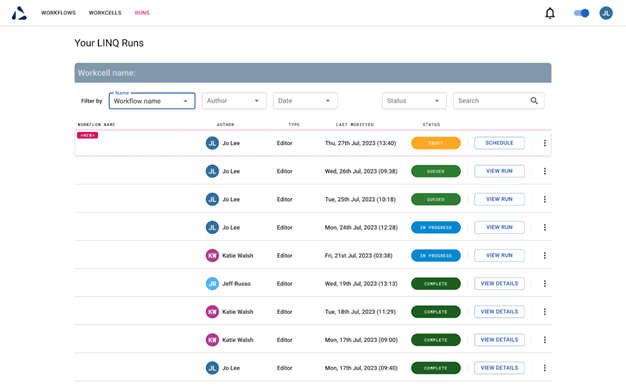
Image Credit: Automata
Connectivity
The life science sector requires greater connectivity to enable this kind of collaboration. Here, connectivity means:
- The ability to easily view equipment status.
- Cloud connectivity that supports centralized knowledge sharing and remote error handling.
- The capability to connect instrument data flows to data lakes.
- At the network level, multiple automated workcells need to communicate with a central platform and each other for real flexibility in data collection and resourcing.
- Systems that allow interventions both physically and digitally from robot technology and software like schedulers and orchestrators. Without these systems, end-to-end workflow automation is not possible.
Everything integrated on the LINQ platform, from instruments to data to users, is connected.
- LINQ Cloud communicates run instructions to integrated instruments and platforms, and it also pulls information back from those elements and sends it to the appropriate data lake.
- Anyone possessing the appropriate user permissions can access LINQ Cloud online, meaning global teams can utilize one source of truth.
- A magnetic transport superhighway and Scara robot arms connect samples and instruments. A scheduling engine drives actions, creating bridges between the physical and digital worlds.
The challenges to flexibility in automation will intensify as populations become more diverse, AI generates more data, and new lab technologies emerge.
Automation can meet these challenges by actively responding to scientists' needs and removing current limitations. This can be achieved by embracing solutions built on open, integrated automation principles like those offered by Automata.
Acknowledgments
Produced from materials originally authored by Automata Technologies Ltd.
 About Automata
About Automata
Born from a world-leading research lab, Automata is making total workflow automation accessible to labs frustrated by the limitations of their own environment.
Accelerating the innovation evolution
When two architects from Zaha Hadid’s research lab first approached robotics, their idea was to explore applications specific to architectural engineering.
But they soon discovered that modern automation wasn’t just unnecessarily complex – it was actively restricting innovation. And not just within their industry – within many others too. It was clear that robotic automation was a field where their combined experience in computational research and design could make a real difference. Assembling a team of industry experts, Automata was founded, with a clear aim: to enable new opportunities for innovation with automation.
A clearer path to progress
Automata’s focus narrowed on an industry where they felt their expertise could have the most impact – life sciences, and particularly within biolab environments.
Since then, the team has been working closely with leading pathology labs to pioneer protocols that enable labs to scale with precision
Automata Labs is the product of that philosophy – simplifying lab environments and empowering the people working tirelessly in the pursuit of progress.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.