Sponsored Content by AutomataReviewed by Louis CastelSep 13 2024
Automation has long been regarded as a cost-effective way to ‘deliver more, better,’ enabling large-scale experimentation and rapid data production.
There is now an almost overwhelming amount of data in certain areas, some of which cannot be easily contextualized in a manner that makes it truly usable in a scientific setting.
Without standardization and traceability, in particular, data reproducibility and relatability will be compromised.
Data and life sciences
Technology, connectivity, consumerism, and a shift in social attitudes have given life scientists unparalleled access to biophysical, behavioral, and biomedical data on a global scale.
This data has led to a much better understanding of public health problems and has uncovered many potential means of responding to these issues. While these developing treatments have complex strings of data to rationalize, much of that data was not obtained with scientific applications in mind.
Due to disparities in collection techniques, for example, commonalities can be hard to find, and crucial elements can often be absent from auxiliary metadata or supporting information.
Numerous manual processes are also involved in experiments and data collection stages, meaning that ensuring the quality of data can be time-consuming.
The development of non-networked lab systems has not been helpful, nor has locking drivers or data files. A lack of flexibility in lab automation solutions exacerbates this issue by generating this inoperable data at a rapid pace.
Adopting a new approach to lab automation can help address some of these challenges.
Rethinking how data from lab automation can work harder for scientists
To fully leverage this vast pool of information, automation must deliver data that is high-quality, timely, and usable, while also being secure, traceable, and connected.
Higher-quality data with automation
Although there is an abundance of data, this does not mean less is needed. Occasionally, more data must be collected to contextualize findings correctly and achieve the required quality. Relying on manual activities for this data collection compromises the reliability of the data and increases the risk of transcription errors.
More data points
Where lab automation connects and transfers data across integrated workflows or workcells, many more data points can be introduced to support analysis and promote further experimentation.
LINQ, Automata’s complete lab automation platform, transfers data from all integrated instruments. It can do this directly into a LIMS or via any third-party data tool.
LINQ can also remove manual transcription tasks and collect more data directly from the experiment.
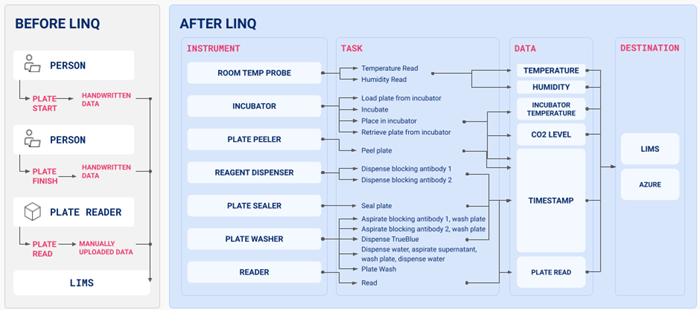
Image Credit: Automata
Optimal lab automation software will assist in standardizing and transferring data as much as possible. Systems that do not possess advanced data management options are adding to the problem.
For example, one clinical genomics laboratory went from three data points per plate to 39 after automating with LINQ, highlighting how rapidly the volume of data can become overwhelming without automated data management.
| 3 |
39 |
| data points per plate before LINQ |
data points per plate after LINQ |
Automated data transfer
Lab automation focuses on removing errors and improving the quality and reliability of results, but this should also extend to data.
Automation that facilitates the two-way sharing of information between databases and instruments, and even better, automation that standardizes that data, is essential for high-throughput labs.
LINQ has been architecturally designed to work with most data repositories and can connect the instruments and data generated from automated workflows to any ELN/LIMS, and the user dictates what data is collected.
Such direct integration can help contextualize information by giving the user access to metadata files and eliminating the necessity for manual data entry, which can generate errors.
Timely information sharing with automation
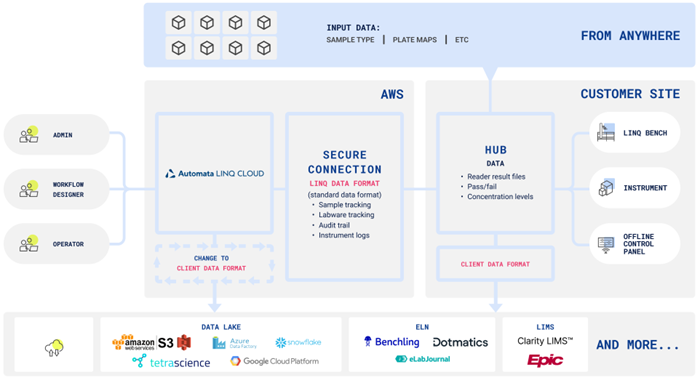
Image Credit: Automata
Data can quickly become outdated, and it can be difficult to maintain an accurate record of the most up-to-date information available.
This difficulty becomes more significant when running advanced workflow automation that can test thousands of compounds over a period of days.
A high-throughput screening assay automated by Automata could test 10,000 compounds across five cell lines in just one and a half days. In contrast, performing this assay with comparable semi-automated solutions would take one and a half weeks.

Image Credit: Automata
| 10,000 compounds |
5 cell lines |
1.5 days |
With as many as 100 plates per day running through this system per set-up, the volume of data generated would be enormous. If this data was not delivered to a LIMS in real time, it could become obsolete, even by the end of that day.
LINQ is a complete automation platform, meaning each action is tracked without intervention and securely recorded by LINQ Cloud software. Any data that the system is instructed to collect from workflow components will be transferred to the relevant data lake in real time, making it immediately available for use.
Improving data traceability with automation
Data will lose its value if its origin cannot be traced and the environment in which it was collected is not understood.
While user groups of data often initially start small and specialized, the need to share even the most nuanced information outside of original communities can arise. The response to the COVID-19 pandemic, for example, saw public and private companies working together towards a vaccine.
To make data usable and preserve its lifespan, an element of traceability is required, something that lab automation can easily facilitate.
Removing manual interactions in the lab and controlling them digitally allows users to benefit from the dynamic information transfer capabilities of advanced software like LINQ Cloud.
LINQ Cloud is the software component of Automata’s LINQ end-to-end workflow automation platform. It enables users to dictate their needs, test their experiment’s parameters, and visualize the results.
Users can input parameters and run instructions, simulate and schedule experiments to ensure confidence in the results and analyze each action that has taken place during the run.
It can capture data from all events in the run, and users can easily export audit logs via permission-controlled access.
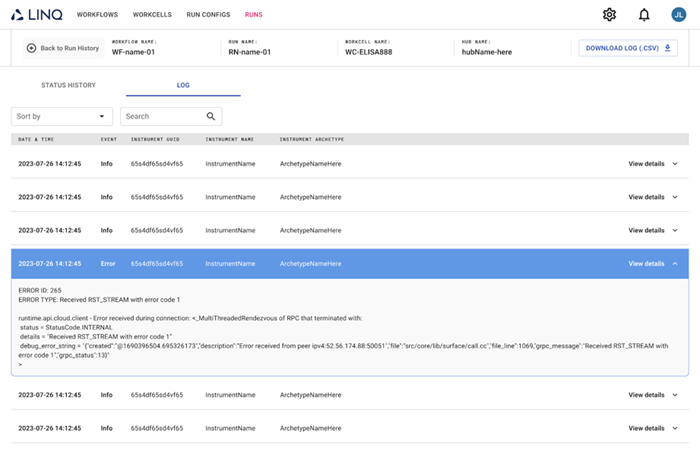
Image Credit: Automata
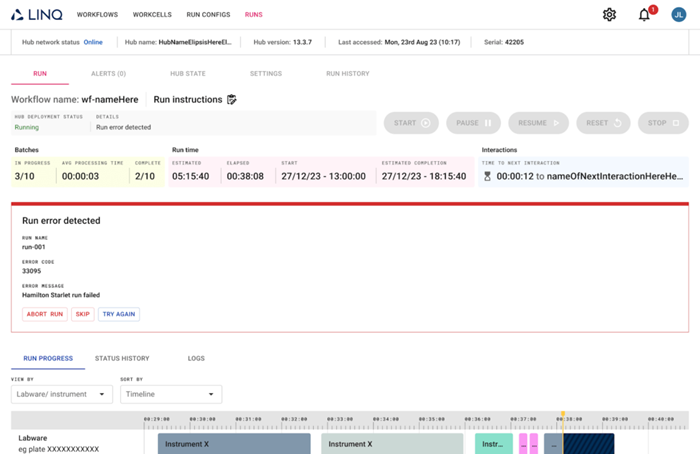
Image Credit: Automata
LINQ Cloud standardizes the information it receives from the workflow and its instruments and transfers it to any specified data lake, improving the traceability of the experimental data.
Connect automation for better collaboration
FAIR data is findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable, which means it also needs to be available digitally.
Cloud-based automation solutions like LINQ allow data to be sent to a centralized resource in real time for immediate use by whoever has access (across teams or entire organizations).
LINQ Cloud possesses 21 CFR-approved user management capabilities for internal collaboration, promoting confidence through secure access rules. Permissions can be set at operator, creator, and admin levels, meaning each user sees what they need to see. There will also be audit trails for transparency and traceability purposes.
Video Credit: Automata
LINQ Cloud aims to provide labs with the ability and confidence to work collaboratively, making that process more straightforward while safeguarding repeatability and reproducibility.
Infrastructure-wide collaboration and beyond
The advantages of centralizing design, execution, troubleshooting, and data collection increase exponentially when applied to infrastructure-level automation that connects all automation systems throughout a lab network to one highly capable software platform like LINQ Cloud.
Image Credit: Automata
Centralization produces a digitally shared bank of data and instruments that anyone can utilize to adapt, simulate, and analyze experiments without impacting the daily activities of systems.
Technology and life science can combine to generate the type of data required to revolutionize therapeutics and drug discovery. That data is now being generated at scale, so it is vital to utilize technology to ensure its interoperability and readiness for future connectivity advances.
Automata CEO Mosfata ElSayed summarized this in his most recent update:
“The rise of automation, high-throughput technologies, and sensor and data integration in wet labs represents a paradigm shift in scientific work. These technologies, coupled with the seamless integration of data production and analytics, are ushering in a new era of efficiency, precision, and scale.
“Automated labs can now perform repetitive tasks with unparalleled accuracy, liberating scientists to focus on more intricate aspects of their research; moreover, the data generated in these automated processes can be instantly captured, analyzed and visualized – at scale.”
“That not only accelerates the pace of scientific discovery but also opens the door to the machine learning and artificial intelligence applications that are just starting to transform the way diagnostics, drug discovery, and research is carried out.”
Acknowledgments
Produced from materials originally authored by Automata Technologies Ltd.
 About Automata
About Automata
Born from a world-leading research lab, Automata is making total workflow automation accessible to labs frustrated by the limitations of their own environment.
Accelerating the innovation evolution
When two architects from Zaha Hadid’s research lab first approached robotics, their idea was to explore applications specific to architectural engineering.
But they soon discovered that modern automation wasn’t just unnecessarily complex – it was actively restricting innovation. And not just within their industry – within many others too. It was clear that robotic automation was a field where their combined experience in computational research and design could make a real difference. Assembling a team of industry experts, Automata was founded, with a clear aim: to enable new opportunities for innovation with automation.
A clearer path to progress
Automata’s focus narrowed on an industry where they felt their expertise could have the most impact – life sciences, and particularly within biolab environments.
Since then, the team has been working closely with leading pathology labs to pioneer protocols that enable labs to scale with precision
Automata Labs is the product of that philosophy – simplifying lab environments and empowering the people working tirelessly in the pursuit of progress.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.