The 1960s saw the initial discovery of benzodiazepines, with these widely used drugs reaching their peak around 1970 with the development of diazepam (Valium).
Diazepam and its contemporaries were widely prescribed as analgesic, antihypertensive, or psychotropic medications, but the benefits of this class of drug led to a growing trend of addiction, which was difficult to effectively diagnose and treat.1
Benzodiazepines’ popularity was primarily due to their relative safety when used to treat insomnia and anxiety. This was especially the case when considering their use versus the previously used sedatives, barbiturates.2
Benzodiazepines are comprised of a benzene ring fused to a 7-member diazepine ring with variable side chains. The drug’s composition can impact its potency, duration of action, metabolite activity, and elimination rate.
This class of prescription drugs is generally well tolerated and widely considered to be socially acceptable, but its addictive effects can pose problems for its users, particularly when benzodiazepines are mixed with other drugs.
Over-the-counter cold and flu preparations or ethanol are commonly mixed with benzodiazepines, leading to exacerbated effects.3 Despite this common occurrence, the majority of benzodiazepine metabolite toxicology screens are only performed for oxazepam-glucuronide.
To detect and prevent abuse of these drugs, it is important to analyze a range of metabolites from benzodiazepines.
While most benzodiazepines metabolize to a single compound in the form of oxazolam, it is possible to detect other metabolites via liquid chromatography, such as temazepam, α-hydroxyalprazolam, 7-aminoclonazepam, α-hydroxy-midazolam, and the glucuronides of lorazepam, oxazepam, and temazepam (LOT).
The data presented below shows chromatography results for these metabolites from benzodiazepine use. This analysis used Hamilton’s PRP-1, 5 µm, 50 x 4.1 mm HPLC column with an ammonium acetate 20 mM buffer.
This setup achieved a run time of less than 10 minutes while still achieving good separation between components. Should a more sensitive detection limit be necessary, ammonium acetate instead of UV could facilitate mass spectrometry detection.
Chromatogram and compound results
Source: Hamilton Company
| Column Information |
| Packing Material |
PRP-1, 5 µm |
| Dimensions |
50 x 4.1 mm |
| P/N |
79443 |
| Chromatographic Conditions |
| Gradient |
0.00–2.00 min, 20 % B
2.01–10 min, 20–52 % B |
| Temperature |
35 °C |
| Injection Volume |
5 µL |
| Detection |
UV at 240 nm |
| Eluent A |
20 mM CH3COONH4 |
| Eluent B |
CH3CN:CH3COONH4 20:1 |
| Flow Rate |
3.0 mL/min |
Compounds:
- Oxazepam Glucuronide
- Lorazepam Glucuronide
- Temazepam Glucuronide
- 7-Aminoclonazepam
- Alpha-Hydroxyalprazolam
- Oxazepam
- Alpha Hydroxyalprazolam
- Temazepam
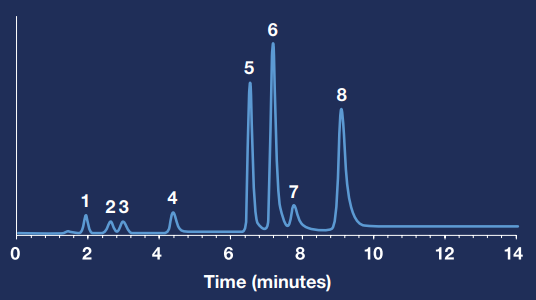
Image Credit: Hamilton Company
Acknowledgments
Produced from materials originally authored by Adam L. Moore PhD. from Hamilton Company.
References and further reading
- Dodds TJ. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2017. 02:19(2).
- Miller N.S., Gold M.S. Adv Alcohol Subst Abuse. 1990. 8(3–4):67–84.
- Araujo EJF, Rezende-Junior LM, Lima LKF, Silva-Junior MPD, Silva OA, Sousa Neto BP, Almeida AAC, Gutierrez SJC, Tome ADR, Lopes LDS, Ferriera PMP, Lima FDCA. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018. 103:973–981.
About Hamilton Company
Hamilton — The Measure of Excellence
Hamilton Company specializes in the development, manufacturing and customization of precision measurement devices, automated liquid handling workstations, and sample management systems. Hamilton's processes are optimized for quality and flexibility. Whether it's a custom needle with a quick delivery time frame, a special length pH sensor, or a comprehensive solution to fully automate your assay workflow, trust that Hamilton products will always meet your needs.
Hamilton Company has been a leading global manufacturer for more than 60 years, with headquarters in Reno, Nevada; Franklin, Massachusetts; Timișoara, Romania; Bonaduz, Switzerland; and subsidiary offices throughout the world.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.