The epigenetic modification, DNA methylation, is characterized by 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) and found in specific genomic locations, most notably regulatory regions such as promoters and enhancers. These regions’ methylation status impacts a range of biological processes, including aging, disease, and development.
Almost all current methods for examining DNA methylation use sodium bisulfite treatment to distinguish between methylated and unmethylated CpGs. A significant number of PCR systems, for example, dPCR systems, are incompatible with bisulfite treatment of DNA.
This incompatibility is due to the utilization of uracil DNA glycosylase (UNG) in reagents; UNG use can result in the degradation of bisulfite-converted DNA, often severely compromising test results.
Image Credit: Roche Diagnostics
The Digital LightCycler® dPCR System is a new dPCR-based method for DNA methylation analysis. This method does not rely on bisulfite treatment; rather, it leverages methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes (MSRE) to show the methylation status of specific regions of DNA. This method boasts a high degree of accuracy, even when working with CpG-rich regions.
This robust combination of dPCR and MSRE offers rapid, cost-effective, and accurate methylation analysis.
The example presented here highlights the use of a multiplex dPCR assay in examining the methylation status of an RASSF1A promoter—a tumor suppressor gene whose dysregulated expression has been linked to various cancers. It is also important to note that hypermethylation of the RASSF1A promoter is linked to decreased gene expression.
The two samples used in this example are:
- A human genomic DNA sample. The methylation status of this sample is typical of a healthy person.
- Another DNA sample that has been enzymatically treated to maximize CpG methylation (methylated DNA). This sample is completely resistant to digestion by the MSRE HhaI.
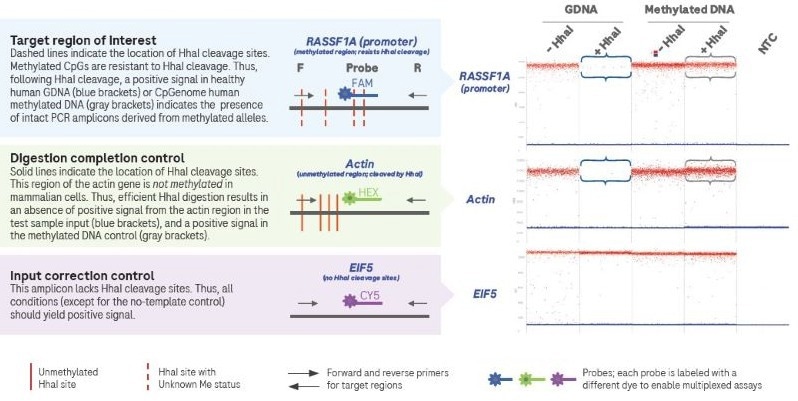
Image Credit: Roche Diagnostics
It is possible to use “high-GC enhancers” to overcome the challenge of amplifying methylated DNA. The amplification of RASSF1A promoters and other high-GC regions is typically inefficient, however, even in regions that are not methylated.
This is highlighted in the first set of data presented in the chart below. Here, the GC content of the amplicon tested was known to be 72% GC, making it a good choice for demonstrating the value of using "high-GC enhancers in methylation analysis studies.
This phenomenon can pose a particular challenge to the accurate quantification of template amounts, irrespective of methylation status. It is possible to significantly enhance amplification efficiency and quantitative accuracy by adding high-GC enhancers to the amplification reactions when using the Digital LightCycler® dPCR System.
This approach will notably improve the accuracy and sensitivity of dPCR-based DNA methylation analysis.
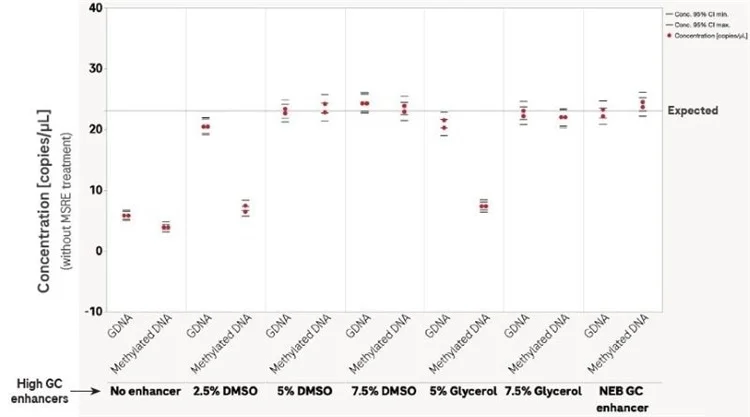
Image Credit: Roche Diagnostics
Source: Roche Diagnostics
| Overall benefits of dPCR |
Value of dPCR in DNA methylation analysis |
| Absolute quantification |
No need for standards |
| High precision |
Improved reproducibility and accuracy by detecting very small fold differences |
| Increased sensitivity |
Enhanced target concentration |
| Reduced competition |
| Inhibitor tolerance |
Greater tolerance to residual matrix inhibitors |
Source: Roche Diagnostics
| Digital LightCycler® Nanowell plates |
 |
HiSens
45 μL, ~20 k partitions
cf residual DNA testing | Microbial detection | Rare Mutation
|
 |
Uni
30 μL, ~28 k partitions
Gene expression
Absolute quantitation
|
 |
HIRes
15 μL, ~100 k partitions
Copy number variation
|
About Roche Sequencing and Life Science
 Roche Sequencing & Life Science is part of Roche Diagnostics, which, along with Roche Pharmaceuticals, plays an important role in modern healthcare. Roche Diagnostics’ broad range of innovative diagnostic tests and systems play a pivotal role in the groundbreaking area of integrated healthcare solutions and cover the early detection, targeted screening, evaluation and monitoring of disease. Roche Diagnostics is active in all market segments, from scientific research and clinical laboratory systems to patient self-monitoring.
Roche Sequencing & Life Science is part of Roche Diagnostics, which, along with Roche Pharmaceuticals, plays an important role in modern healthcare. Roche Diagnostics’ broad range of innovative diagnostic tests and systems play a pivotal role in the groundbreaking area of integrated healthcare solutions and cover the early detection, targeted screening, evaluation and monitoring of disease. Roche Diagnostics is active in all market segments, from scientific research and clinical laboratory systems to patient self-monitoring.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.