A team of researchers from the United States and China recently discuss the effects of the new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron variant, its likely impact on current convalescent therapies, and the immunity of vaccinated individuals against this variant in a new study published on the bioRxiv* preprint server.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Background
The emergence of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) was originally identified in November 2021 and has since been detected in more than 60 countries. The Omicron variant could become dominant in the next few weeks across the globe due to its increased transmissibility, similar to what was observed during the Delta variant outbreak.
About 37 mutations of the spike protein have been reported in the Omicron variant, which raises concerns about the efficacy of the current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines and the use of therapeutic antibodies for convalescent therapy.
About the study
In the present study, the team collected sera from individuals who were infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the spring of 2020, as well as from vaccinated individuals who received any of the BNT162b2, mRNA-1273, Ad26.COV2.S, or ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccines to test the neutralization activity of these samples against both wild-type and the B.1.1.529 pseudoviruses. The researchers analyzed the activity of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against all known epitopes of the spike protein.
Besides the 37 reported mutations in the spike protein of the B.1.1.529 variant, about 10% of Omicron sequences in the GISAID database contain an additional R346K mutation, which was also found in the Mu variant (B.1.621). This finding prompted the researchers to work on an additional pseudovirus with this mutation.
About 19 mAbs approved for COVID-19 treatment were tested for their neutralization activity, either individually or in combination, 17 of which target the receptor-binding domain (RBD) and two of which are directed at the N-terminal domain (NTD) of the spike protein. They further investigated the amino acid substitutions that confer antibody resistance to the Omicron variant.
Study findings
The study found that the neutralization activity of sera from infected and vaccinated individuals was significantly lower against the B.1.1.529 variant. A 32-fold reduction in infectious dose of 50% (ID50) titers was observed in samples of infected individuals against the Omicron variant. Individuals vaccinated with mRNA vaccines showed a 21-fold (BNT162b2) and 8.6-fold (mRNA-1273) reduction in ID50 titers. The sera of individuals who received Ad26.COV2.S and ChAdOx1 nCOV-19 vaccines elicited lower titer values below the limit of detection (LOD) against the Omicron variant.
The team reported that 18 mAbs lost neutralization activity completely or partially against the B.1.1.529 variant. More than a 100-fold reduction was observed for mAbs of RBD classes 1, 2, and 3. A modest 10-fold decrease was reported for class 4 mAbs. The pseudoviral Omicron constructs with R346K substitution rendered all the mAbs inactive.
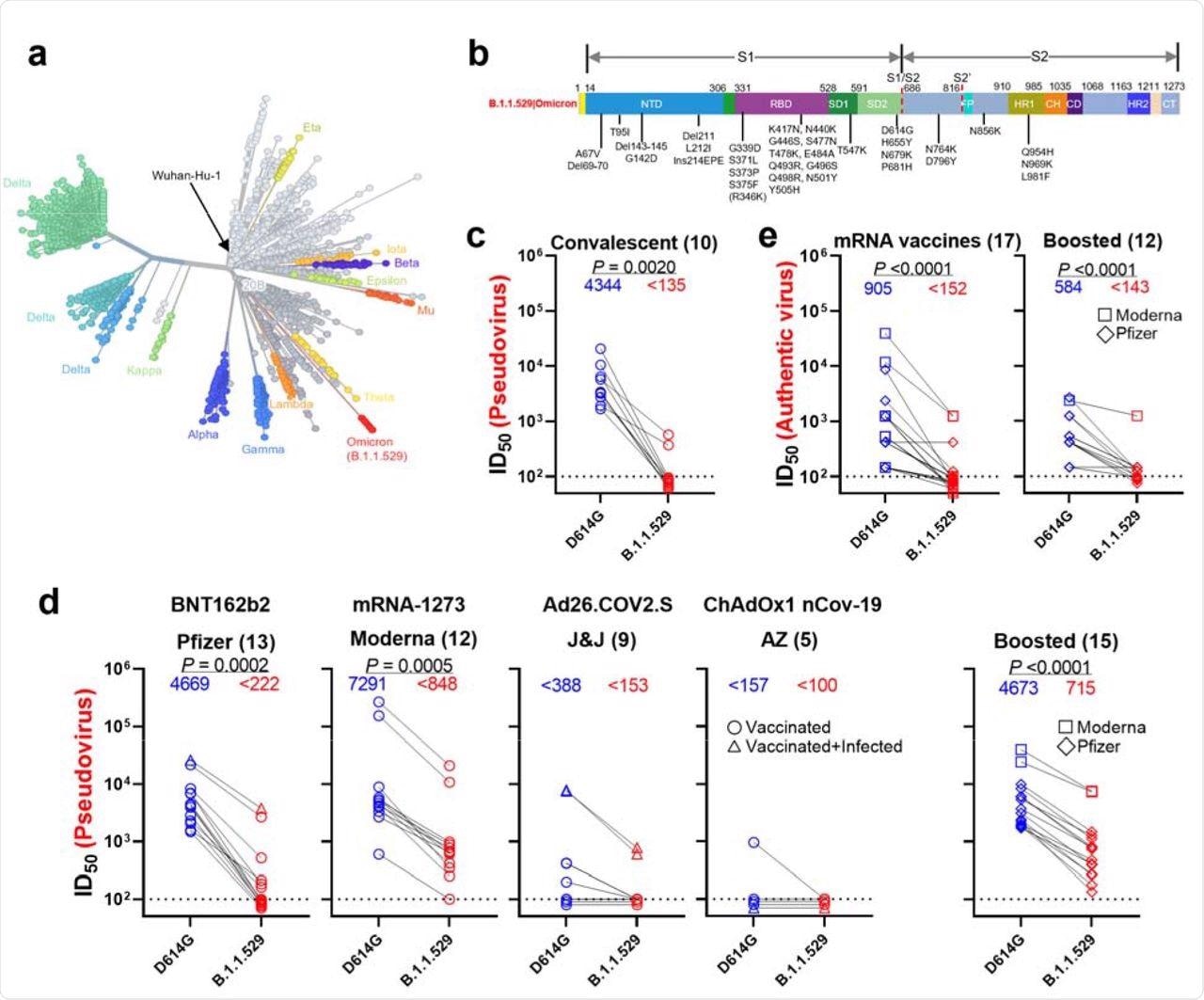 Resistance of B.1.1.529 to neutralization by sera. a, Unrooted phylogenetic tree of B.1.1.529 with other major SARS-CoV-2 variants. b, Key spike mutations found in the viruses isolated in the major lineage of B.1.1.529 are denoted. c, Neutralization of D614G and B.1.1.529 pseudoviruses by convalescent patient sera. d, Neutralization of D614G and B.1.1.529 pseudoviruses by vaccinee sera. Within the four standard vaccination groups, individuals that were vaccinated without documented infection are denoted as circles and individuals that were both vaccinated and infected are denoted as triangles. Within the boosted group, Moderna vaccinees are denoted as squares and Pfizer vaccinees are denoted as diamonds. e, Neutralization of authentic D614G and B.1.1.529 viruses by vaccinee sera. Moderna vaccinees are denoted as squares and Pfizer vaccinees are denoted as diamonds.
Resistance of B.1.1.529 to neutralization by sera. a, Unrooted phylogenetic tree of B.1.1.529 with other major SARS-CoV-2 variants. b, Key spike mutations found in the viruses isolated in the major lineage of B.1.1.529 are denoted. c, Neutralization of D614G and B.1.1.529 pseudoviruses by convalescent patient sera. d, Neutralization of D614G and B.1.1.529 pseudoviruses by vaccinee sera. Within the four standard vaccination groups, individuals that were vaccinated without documented infection are denoted as circles and individuals that were both vaccinated and infected are denoted as triangles. Within the boosted group, Moderna vaccinees are denoted as squares and Pfizer vaccinees are denoted as diamonds. e, Neutralization of authentic D614G and B.1.1.529 viruses by vaccinee sera. Moderna vaccinees are denoted as squares and Pfizer vaccinees are denoted as diamonds.
Further, the researchers discovered four new mutations of S371L, N440K, G446S, and Q493R in the Omicron spike protein, which confer enhanced antibody resistance to the variant. The Q493R substitution was shown to provide resistance to mAbs of RBD classes 1 and 2, whereas N440K and G446S mutations showed resistance to class 3 mAbs.
Remarkably, the S371L substitution conferred resistance to mAbs of all four classes. Steric hindrance was reported as the most likely reason for antibody resistance in the Omicron variant. Detailed analysis revealed that the B.1.1.529 variant evades all available mAbs that target either RBD or NTD.
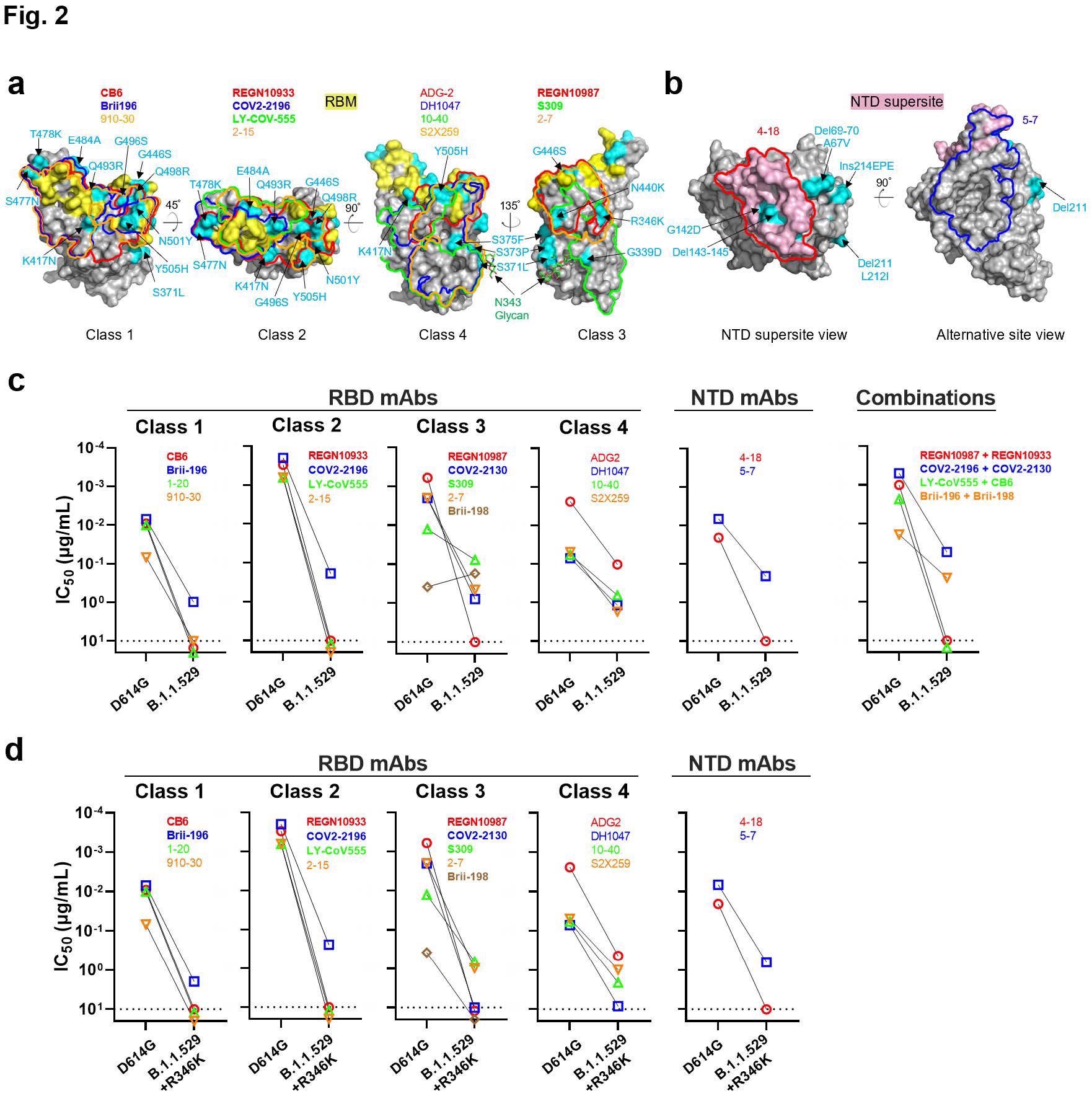 Resistance of B.1.1.529 to neutralization by monoclonal antibodies. a, Footprints of RBD-directed antibodies, with mutations within B.1.1.529 highlighted in cyan. Approved or authorized antibodies are bolded. The receptor-binding motif (RBM) residues are highlighted in yellow. b, Footprints of NTD-directed antibodies, with mutations within B.1.1.529 highlighted in cyan. The NTD supersite residues are highlighted in light pink. c, Neutralization of D614G and B.1.1.529 pseudoviruses by RBD-directed and NTD-directed mAbs. d, Neutralization D614G and B.1.1.529+R346K pseudoviruses by RBD-directed and NTD-directed mAbs.
Resistance of B.1.1.529 to neutralization by monoclonal antibodies. a, Footprints of RBD-directed antibodies, with mutations within B.1.1.529 highlighted in cyan. Approved or authorized antibodies are bolded. The receptor-binding motif (RBM) residues are highlighted in yellow. b, Footprints of NTD-directed antibodies, with mutations within B.1.1.529 highlighted in cyan. The NTD supersite residues are highlighted in light pink. c, Neutralization of D614G and B.1.1.529 pseudoviruses by RBD-directed and NTD-directed mAbs. d, Neutralization D614G and B.1.1.529+R346K pseudoviruses by RBD-directed and NTD-directed mAbs.
Conclusions
The findings of the current study demonstrate the diminished efficacy of the most widely used vaccines against the Omicron variant. Sera from convalescent patients presented similar results adding to the growing concerns of vaccine breakthroughs and the high rate of reinfections by the Omicron variant.
The current study also investigated serum samples from individuals who received mRNA vaccine boosters and found that even a third dose could not elicit adequate neutralization activity confirming the suspicions of their low efficacy against the Omicron variant. The B.1.1.529 variant, with the additional R346K substitution, decreases the scope of convalescent therapy, thus highlighting the pressing need to rethink existing therapies. At this rate, any newer mutations could render the virus pan-resistant to all current therapies.
The SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant presents new threats to global healthcare systems, thus compelling them to intervene with advanced strategies to tackle the ongoing crisis. The emergence of potentially dangerous new variants calls for more extensive research that could help detect new variants and also predict their evolution.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Liu, L., Iketani, S., Guo, Y., et al. (2021). Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.14.472719v1.
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Liu, Lihong, Sho Iketani, Yicheng Guo, Jasper F-W. Chan, Maple Wang, Liyuan Liu, Yang Luo, et al. 2021. “Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2.” Nature, December. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04388-0. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-04388-0.