Osteoarthritis (OA) is a severe and often crippling condition that typically affects older people. Researchers previously attributed OA to wear and tear in the joints as an inevitable part of aging, especially if the individual had a history of excessive joint strain due to trauma, obesity, or overuse. However, we now understand that it is more of a lifestyle disorder and is intimately related to food habits.
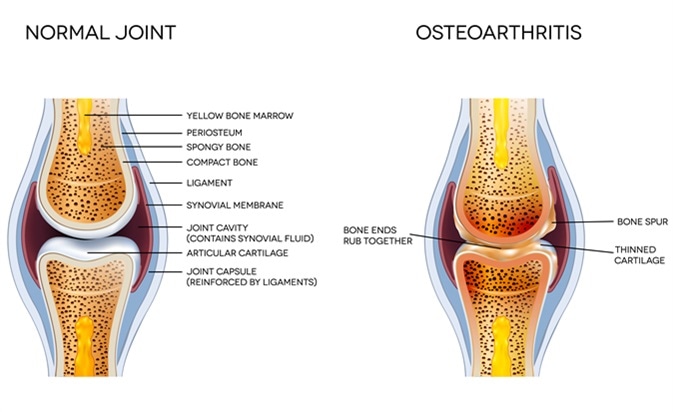
Osteoarthritis and normal joint anatomy. Image Credit: Tefi / Shutterstock
What Foods Worsen Osteoarthritis?
Highly processed and fried foods: Reducing the intake of fried foods and highly processed food can be an effective way to bring down inflammation of the joints and relieve the symptoms of OA. This is because fried foods contain high amounts of saturated fats which promote inflammation. Substituting these with olive oil and other unsaturated fats may cause significant alleviation of pain.
Food made out of processed white flour, white rice, as well as from potatoes, spells bad news for OA patients because of the highly refined carbohydrate content and increased AGE levels resulting in inflammation.
Although whole milk is a good source of protein, cheese could aggravate OA.
Processed sugars as in snacks and sweets often boost the levels of inflammatory cytokines in response to hyperglycemia, and worsen arthritis symptoms.
Red meat: Animal meat contains more fat and a higher calorie count that can result in an upsurge of inflammatory chemicals. High-temperature cooking such as frying, searing, or grilling meat increases the concentration of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) which could stimulate pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Alcoholic beverages: Too much alcohol is also known to promote inflammation.
Other foods: salty foods, caffeine, and vegetables from the nightshade family such as tomatoes and eggplant may also contribute to worsening of OA symptoms.
Nutrition and Osteoarthritis
Foods that Protect Against Osteoarthritis
The question lurks as to what kind of diet an OA patient should be looking at. A good start is to switch to whole grain or multi-grain foods as far as possible.
Protein: Soybean protein is beneficial for people with osteoarthritis, and research suggests that it works remarkably better in men. Adding soy protein isolate in milkshakes or smoothies, or having a serving of tofu or soybeans at least once a day, boosts the daily anti-oxidant intake.
Vegetables, fruits, and greens: Green leafy vegetables are rich in carotenoids and reduce inflammation. Glutathione is another essential antioxidant molecule found in large amounts in broccoli, cabbage, and cauliflower, as well as in grapefruit, avocados, watermelons, and oranges. Bulb vegetables also have sulfur-containing compounds which boost the effectiveness of the immune system. Fresh fruits and vegetables also add fiber to the diet, fiber lowering the risk of symptomatic OA. Bright-colored fruits such as cherries, berries, and oranges or apricots should be consumed as they are rich in anthocyanins and carotenoids. These have potent anti-inflammatory effects on the body. Grapes and mulberries contain resveratrol, while apples are rich in quercetin. Both phytochemicals have excellent antioxidant actions. Bromelain from pineapple has powerful proteolytic activity and is effective in swelling and inflammation of knee caused by OA.
Fish: Fish, especially oily fishes such as sardines, trout, and anchovies, or cold-water fish like tuna or salmon, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Consumption of fish at least two times a week is helpful in maintaining healthy omega-3 levels. . Other good sources of these anti-inflammatory fatty acids include walnuts, flaxseed, pumpkin seeds, and olive oil. Extra-virgin olive oil contains oleocanthal that is a prostaglandin inhibitor and has the effect of a painkiller. In addition to dietary intake of omega-3 fatty acids, daily intake of an omega-3 supplement is also recommended.
Nuts and chocolates: Tryptophan is an amino acid that fights pain sensitivity within an hour of consumption, and is abundant in sesame seeds, hazelnuts, sunflower seeds, soybeans, whole grains, milk products, beans, and lentils. Consumption of dark chocolate in moderation could not only satisfy that chocolate craving but also reduce inflammatory markers in OA.
Non-alcoholic beverages: Green tea is a good substitute for caffeine and alcohol, containing plenty of flavonoids to prevent oxidative cell damage that could worsen OA. It is better to avoid more than a glass of alcohol a day. This warning holds well despite the positive effects of resveratrol in red wine.
Conclusion
With limited treatment options for OA, OA patients can benefit by making certain lifestyle modifications especially with respect to diet. Maintaining ideal weight, incorporation of a daily exercise regimen, increased intake of omega-3 fatty acids and dietary fiber along with vitamin D supplementation can help alleviate many of the symptoms of OA and slow down progression of the disease.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Feb 27, 2019