Elimination of ammonia
Ammonia can be produced by the break-down of amino acids, or by the gut bacteria in humans. If the level of ammonia in the blood becomes too high, then it becomes toxic to the brain.
The urea cycle removes ammonia from the blood and makes urea, which is eventually excreted as urine. This cycle is carried out by the cells of the liver, and, as the name suggests, the last step of the process feeds into an earlier step of the cycle.
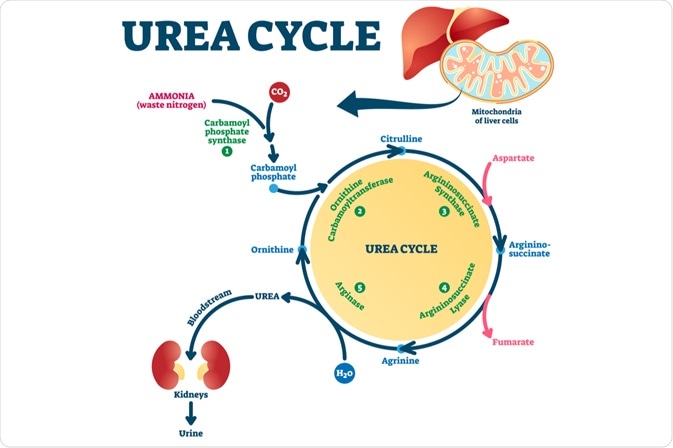
Image Credit: VectorMine / Shutterstock.com
Summary of the urea cycle
Ammonia is formed by the breakdown of amino acids/gut bacteria.
The mitochondrial stage:
- Carbamoyl phosphate is formed from ammonia and bicarbonate, by carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (CPS).
- Ornithine transcarbamoylase (OTC) condenses carbamoyl phosphate and ornithine to form citrulline.
- Citrulline is then transported to the cytosol by SLC25A15.
The cytosolic stage:
- Argininosuccinate synthetase (AS) condenses citrulline and aspartate to form argininosuccinate.
- Argininosuccinate is broken down into arginine and fumarate by argininosuccinate lyase (AL).
- Arginine is broken down into urea and ornithine by arginase.
- Ornithine translocase transports ornithine into the mitochondria.
The mitochondrial stage
The first two steps of the urea cycle occur in the mitochondria of the cell. First, the enzyme CPS takes ammonia and bicarbonate and forms carbamoyl phosphate with the use of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This is the step in the cycle that determines how fast the cycle progresses. N-acetylglucosamine is also required for CPS to function, and functions as a regulator for the formation of urea.
OTC then condenses carbamoyl phosphate and ornithine, which forms citrulline. This citrulline is then moved out of the mitochondria into the cytosol of the cell by the transporter SLC25A15.
The cytosolic stage
AS takes the citrulline formed in the mitochondrial stage and condenses it with aspartate to form argininosuccinate. This occurs by the formation of an intermediate, citrulline-AMP.
Argininosuccinate is then broken into arginine and fumarate by AL. Fumarate is then incorporated into another metabolic cycle, the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. The TCA cycle, which is also known as the citric acid cycle or the Krebs cycle, can then reform aspartate, which is used by AS.
Arginine is then further broken down into urea and ornithine by arginase. Arginine can also be acquired from the diet, and this can also be taken in by the liver cells and broken down into urea and ornithine by arginase.
The ornithine is then transported into the mitochondria by ornithine translocase. There, it is used by OTC again to form citrulline. The citrulline is then processed to form urea and ornithine again, and the cycle continues. During the cycle, urea is the only new product which is formed, while all other molecules used in the cycle are recycled.
What happens when the urea cycle goes wrong?
If there is a problem with the urea cycle, then the level of ammonia in the blood will rise, causing hyperammonemia. Ammonia is able to cross the barrier between the bloodstream and the brain. Once it enters the brain, it can stop the TCA cycle by depleting one of the metabolites, α-ketoglutarate. This means that these brain cells cannot make energy, ultimately leading to their death. This eventually will lead to neurological problems, which can be as severe as irreversible brain damage.
Problems can arise as a redsult of damage to the liver (cirrhosis) or by an inherited defect in one of the above enzymes. In both cases, the level of ammonia rises with the potential consequences previously detailed.
Inherited urea cycle defects are part of “inborn errors in metabolism”, and are known as “urea cycle disorders.” Symptoms usually present in newborns around 24-48 hours after birth. The most severe symptoms are seen in newborns with a defect in CPS.
Treatment for hyperammonemia consists of removing protein from the diet, removing the excess ammonia and supplementing with molecules of the urea cycle which are missing. Also, sodium benzoate and sodium acetate can be used to form ammonia-containing compounds that can be excreted through feces.
The sugar lactulose has been shown to reduce the production of ammonia by the gut bacteria, as well as promote the excretion of ammonia through the feces. Alternatively, antibiotics can be used to eliminate the ammonia-forming gut bacteria.
Urea Cycle Disorders
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Apr 25, 2021