Hearing loss, impairment or deafness may be of two major types:
- one that develops some time in life
- one that a baby is born with – or congenital deafness
Most commonly, hearing loss is seen with age or is caused by exposure to loud noises.
How many people does hearing loss affect?
More than 10 million people in the United Kingdom have some form of hearing loss. Of these about 688,000 are severely or profoundly deaf.
Each year nearly 840 babies are born with significant deafness in the UK. Around 1 in a 1000 is deaf at the age of three and nearly 20,000 children aged up to 15 are moderately to profoundly deaf. 1-6
Normal hearing mechanism
The ear consists of a narrow canal or tube that lets in the sound waves. These waves enter the ear canal and strike the ear drum.
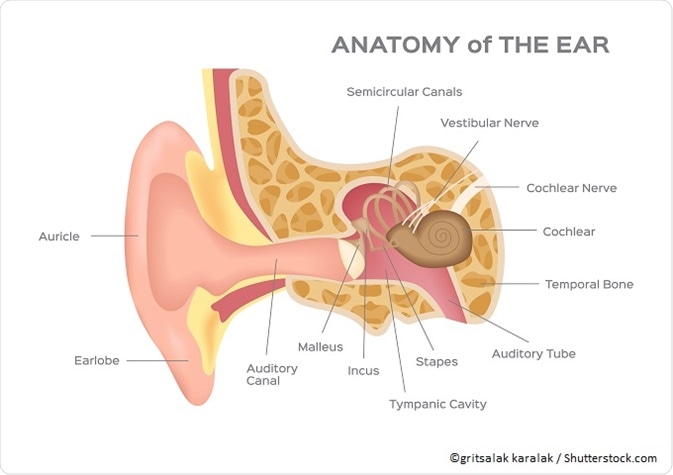
The ear drum or the tympanic membrane is a membrane that vibrates as the sound waves hit it. These vibrations are passed to the three small bones (ossicles) inside the middle ear. These are shaped like a tiny hammer, anvil and a stirrup and are called malleus, incus and stapes bones respectively.
The ossicles amplify the vibrations and pass them on to the inner ear. The inner ear contains a shell shaped organ called the cochlea. Within the cochlea are tiny hair cells all along the inner walls. These move in response to the vibrations and send a signal through the auditory nerve to the brain.
Types of hearing loss
Hearing loss is of two major types. Some people may get conductive hearing loss. This occurs when any of the passages of the sound waves is blocked and the sound waves cannot be transmitted to the ear. The most common causes are:
- blockage of the ear canal by ear wax
- perforation of the ear drum
- build-up of fluid due to an ear infection called glue ear
Another type of hearing loss is sensorineural hearing loss where the auditory nerve and other nerves that carry the information from the sounds heard to the brain are damaged due to age or injury. When people get both types together, the condition is termed mixed type of hearing loss.
Who is affected by hearing loss?
The most common cause of hearing loss is ageing, and three-quarters of people who are deaf are aged over 60. Above the age of 40 more men than women become hard of hearing.
Among those over 80 more women than men are deaf or hard of hearing. This could be because women tend to live longer and there are more of them.
Symptoms and diagnosis of hearing loss
Hearing loss may be mild, moderate, severe or profound. The degree of hearing loss is detected by hearing test called the whisper test. It detects the quietest sound which that person can hear.
The normal hearing range is 0-20 decibels (dB). Around 30 dB are for whispers, 50 dB for average home noises and 60 dB for conversational speech. Sounds like jet engine noises are over 140 dB and are painful.
Hearing loss is measured in decibels hearing loss (dB HL).
- 25-39 dB HL means mild hearing loss (cannot hear whispers)
- 40-69 dB HL means moderate (cannot hear conversational speech)
- 70-94 dB HL is severe (cannot hear shouting)
- more than 95 dB HL is profound (cannot hear sounds that would be painful for a hearing person)
Some patients have additional symptoms along with hearing loss like tinnitus (buzzing or ringing of the ears), dizziness and fullness of one or both ears.
Diagnosis involves examination of the ear canal for wax, ear drug for perforations etc. An Audiometry is recommended to determine the extent of hearing loss.
Treatment of hearing loss
Type of hearing loss is determinant of the method of therapy. In cases where there is sensorineural damage the patient is recommended:
- digital hearing aids
- surgically implanted hearing aids within the middle ear
- cochlear implants
- learning a sign language for communication
For those with conductive hearing loss a Bone Anchored Hearing Aid (BAHA) is often suggested. Causes like ear wax can be corrected easily by removal. A perforated ear drum may also be repaired.
Hearing loss due to diseases and age cannot be prevented but reduction of exposure to repeated loud noises can reduce the risk of hearing loss from loud, consistent noise.
Not having music or the television on at a very loud volume and wearing ear protective gear when exposed to noise work environment helps prevents hearing loss.
Further Reading