At the 67th American Society for Mass Spectrometry Conference (ASMS) being held June 2-6 in Atlanta, Bruker is announcing highly innovative new mass spectrometry products and workflows:
A. SpatialOMx™ Life Sciences and Translational Mass Spectrometry Imaging

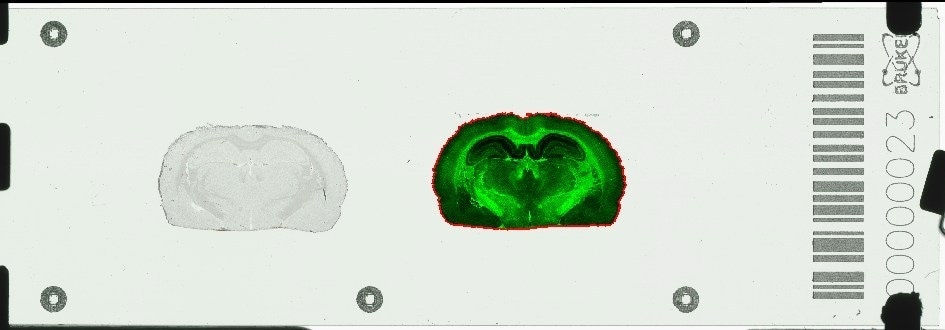
Bruker introduces the novel timsTOF fleX™ mass spectrometer, which includes a software-switchable MALDI source adapted to the ESI timsTOF Pro™ platform. This new, combined ESI/MALDI capability enables spatially-resolved omics, SpatialOMx™, on a single instrument.
The timsTOF fleX comes with Bruker's proprietary 10kHz SmartBeam™ 3D laser with true pixel fidelity for rapid, label-free MALDI imaging at high-spatial resolution, while fully preserving the unparalleled 4D proteomics and phenomics sensitivity of the timsTOF Pro in ESI mode.
With this unique SpatialOMx approach, researchers gain insights into spatial molecular distributions in tissues from MALDI imaging, to guide 4D omics molecular expression studies, e.g. on proteins, low-level cancer antigen peptides, lipids, glycans, metabolites, or xenobiotics, which cannot be observed by traditional staining or labeling techniques.
MALDI-guided SpatialOMx allows for specific targeting of cell sub-populations for subsequent ESI-TIMS/PASEF-based dda or dia 4D proteomics or 4D lipidomics/metabolomics. Both can now be performed on a single robust instrument, the timsTOF fleX, with the ultra-high sensitivity needed to advance single-cell biology research, as a perfect complement to single-cell transcriptomics by RNA-seq.
Professor Richard Drake, Director of the Proteomics Center at the Medical University of South Carolina, stated: "The data from our samples using the new timsTOF fleX system was unprecedented in terms of spatial resolution and depth of glycan coverage. As glycans are emerging as potential clinical markers in tissue and serum to monitor overall immune status, and healthy or unhealthy aging, the unique capabilities of the timsTOF flex will greatly accelerate these efforts. The timsTOF flex allows our cumulative approaches that we have developed for tissue and biofluid analysis of cancers and immunotherapies to converge on one platform. I can see unlimited applications of such an instrument in many research areas for rapid glycan tissue imaging and biofluid 4D omics analysis."
Dr. Rohan Thakur, Executive Vice President at Bruker Daltonics, added: "Most tissue proteomics studies blend cells from diverse subpopulations, with an undesirable averaging effect that obscures a lot of important biology and pathobiology. MALDI-guided spatialOMx on the timsTOF fleX enables the profiling of spatially-defined tissue regions, thereby allowing subsequent 4D proteomics to selectively target cell-type sub-populations.
The robust, ultra-high sensitivity timsTOF fleX bridges the divide between molecular tissue imaging and body fluids analysis by offering nanoLC-TIMS-MS/MS on the same instrument. This unique combination will make the timsTOF fleX an invaluable research tool for spatially-resolved 4D proteomics and phenomics, as well as for advancing single-cell biology, pharmaco-proteomics, and translational 4D cross-omics workflows on large cell numbers or patient cohorts."
Bruker is also launching IntelliSlides™ specifically designed to automate timsTOF fleX workflows. The IntelliSlidescome pre-inscribed with software-readable 'teach marks' on the conductive surface to indicate where to place the tissue sample, a bar code, and tracking number.
IntelliSlides automation removes sources of inefficiency from sample loading, as they are inherently correctly labelled, oriented properly, and MALDI image registration occurs at the touch of a button. With specialized software, IntelliSlides now make MALDI Imaging even easier for everyone.
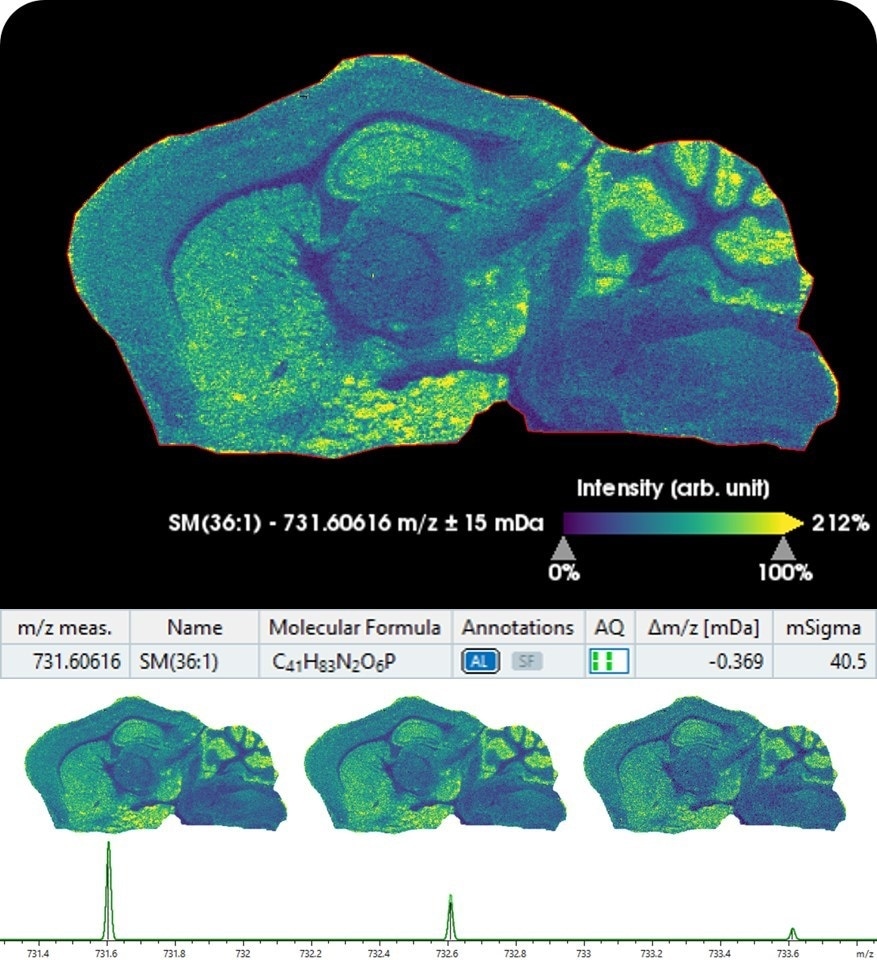
Moreover, Bruker introduces SCiLS Lab 2020 MALDI imaging software, now integrated with MetaboScape5.0 for providing automated annotations of lipids and metabolites in tissue molecular images in spatialOMx. This unique combination automatically matches ions measured on tissue to molecular information in metabolomics and lipidomics workflows, highlighting biologically relevant pathway information using MALDI imaging.
We use mass spectrometry in the fields of pharmaceutical research and spatial metabolomics. This includes, in particular, the analysis of myxobacterial secondary metabolomes for novel natural products. Our lab has been using Bruker's instrumentation and software for years, in particular, SCiLS Lab and MetaboScape.
The new molecular imaging workflow that integrates both of these software solutions greatly simplifies and speeds up the entire MALDI imaging pipeline. It translates ion images into molecular images with confidence in the annotated molecules."
Dr. Daniel Krug, Helmholtz Institute for Pharmaceutical Research Saarland (HIPS)
The new integrated imaging and metabolomics workflow also supports data from Bruker's scimaX™ MRMS platform, as well as from the new timsTOF fleX. MetaboScape's unique T-ReX 2D algorithm performs feature extraction, de-isotoping, and ion deconvolution on MALDI imaging datasets.
Within MetaboScape, molecular features are annotated based on accurate mass and isotopic fidelity using SmartFormula™ and molecular information, e.g. from public databases such as HMDB and LipidMaps. MetaboScape now also offers the unique ability to increase ID scoring confidence by integrating accurate TIMS collision cross-sections (CCS) from timsTOF analyses.
Identifications flow back to SCiLS Lab for fully annotated molecular images. SCiLS Lab is the market-leading software for MS imaging, while MetaboScape is the software solution of choice for identification of metabolite markers and pathway mapping.
B. 4D Proteomics and 4D Phenomics Innovations
DiaPASEF and MBR-ddaPASEF Advances in 4D Proteomics
Bruker's revolutionary timsTOF™ Pro for next-generation nLC-TIMS-MS/MS 4D proteomics has been further enhanced by combining PASEF with data-independent (DIA) acquisition, in diaPASEF for ultra-high sensitivity bottom-up proteomics.
While the unmatched duty-cycle of data-dependent acquisition (DDA) PASEF dramatically improved sensitivity and depth of coverage using short nanoLC runtimes, the stochastic nature of DDA results in missing values, an issue significantly improved by diaPASEF worflows, or by match-between-runs (MBR) for ddaPASEF.
The novel diaPASEF1 workflow, shown at ASMS 2019 as work-in-progress available to methods development customers, uses overlapping windows in the ion mobility domain to trigger MS/MS, efficiently using the quadrupole to transmit the precursor ions at high sensitivity.
By using the inherent duty-cycle advantage of PASEF, the new diaPASEF workflow typically results in a 30% improvement, now with over 7,000 proteins identified in a 120 minute single-shot experiments with 200 ng of HeLa digest injected. Data analysis, including 4D feature alignment in mass, retention time, ion mobility and intensity, is performed using the new Mobi-DIK software, which is based on the OpenMS software developed in the group of Professor Hannes Roest at the University of Toronto.
Dr. Gary Kruppa, Bruker's Vice President of Proteomics, explained: "Adding the diaPASEF workflow is a major step forward in addressing the missing values problem in bottom-up proteomics, and in improving label free quantification (LFQ). The timsTOF Pro is fast gaining a reputation of delivering increased depth of coverage using short gradients, and for providing industry-leading robustness due to its orthogonal source and dual-TIMS funnel design."
"Furthermore, peptide CCS values obtained on the timsTOF Pro are proving fundamental to increasing protein ID numbers in diaPASEF workflows, and also in using CCS for match-between-runs (MBR) in ddaPASEF, in order to further improve data completeness and LFQ performance at low protein abundance. We would like to thank our scientific partners Drs. Matthias Mann, Ruedi Aebersold, Ben Collins and Hannes Roest for the most fruitful diaPASEF collaboration, and Dr. Juergen Cox for the excellent further progress with MBR-ddaPASEF."
Dr. Juergen Cox, Group Leader of Computational Systems Biochemistry at the Max-Planck Institute of Biochemistry in Martinsried, stated:
We have developed a highly parallelizable 4D feature detection algorithm for timsTOF Pro datasets that extracts peaks which are assembled to isotope patterns, followed by mass re-calibration using non-linear fitting of m/z, and also alignment in retention time, ion mobility and signal intensity.
The missing value problem in label-free protein quantification over many samples can now be greatly reduced by MS1-level CCS-aware match-between-runs (MBR)2, resulting in significantly improved assay precision and accuracy using a benchmark."
New Consumables and Software for 4D Proteomics
Bruker and PreOmics GmbH announced a co-development and co-marketing agreement, which will focus on PreOmics iST sample preparation technology on the timsTOF Pro.
The inStageTip (iST) technology removes detergents, polymers, salts, lipids and other contaminants, and has exceptional peptide recovery. New iST protocols enable robust and reproducible sample preparation with a significant time advantage (over 40 hrs saved) compared to common protocols, and iST is suitable for integration in semi-automated, high-throughput sample prep.
We are very excited to work with Bruker on end-to-end workflows that make protein analysis simply better, and to share these improvements with our highly valued academic and biopharma customers around the world. We are convinced that the power of the timsTOF Pro for 4D proteomics is a perfect match for our iST sample processing technology."
Drs. Nils Kulak and Garwin Pichler, Managing Directors at PreOmics
For proteomics software, Bruker and Genedata announced a partnership for the Genedata Expressionist software platform, which now supports the timsTOF Pro 4D omics format. Native support of the latest timsTOF Pro data file format opens new opportunities for streamlining and automating the most complex proteomics, metabolomics and biotherapeutics characterization studies.
The power of intelligent precursor selection for deep proteome coverage with fast gradients of the timsTOF Pro in combination with the scalability and speed of Genedata Expressionist enables the implementation of a next-generation host cell protein (HCP) analysis platform.
Dr. Peter Hufnagel, Life Sciences Software Manager at Bruker, expanded: "Our API-driven open data file format philosophy is helping to accelerate the adoption of timsTOF data into many important third party software solutions. Incorporation into Genedata Expressionist is an important further step requested by mutual biopharma customers for HCP analysis, and this was rapidly accomplished by Genedata due to our open file format architecture."
Dr. Markus Brosch, Business Unit Head for Genedata Expressionist, said: "Genedata Expressionist® builds on its proven proteomics capabilities to identify and quantify host cell proteins (HCPs) right down to the detection limit. It uniquely supports a wide range of HCP search and analysis strategies leveraging a high-performance enterprise architecture, offering unprecedented speed and scalability required to process large volumes of complex proteomics data. Our joint customers can now not only automate and accelerate HCP analysis, but utilize one software platform for all their needs across proteomics, metabolomics and biotherapeutics characterization."
Novel Ultra-high Sensitivity 4D Lipidomics Workflow
Building on the success of MetaboScape® and CCSPredict™, Bruker announces advances to ultra-high sensitivity 4D lipidomics workflows on the timsTOF Pro and timsTOF fleX platforms, demonstrating high-throughput and high-sensitivity measurements using LC-TIMS-MS/MS.
Optimization of novel PASEF 4D lipidomics methods now enables the number of identified lipids in single-shot analysis to be almost doubled, whilst obtaining attomole sensitivity. This innovative workflow uses nanoLC-TIMS-PASEF to quantify approximately 500 lipids with very high quantitative accuracy and reproducibility from just a few thousand cells, in addition to building a library of more than 1,000 accurate CCS values from human plasma, mouse liver and human cancer cells.
Dr. Florian Meier, postdoctoral fellow at Max-Planck Institute of Biochemistry and senior author of the study3, added: "Our study establishes 4D lipidomics and paves the way for more sensitive lipidomics using PASEF. The precision and accuracy obtained using TIMS can be leveraged to facilitate lipid assignment, in addition to the comprehensive MS/MS information generated by PASEF. Additionally, high-precision CCS values provide a basis for machine learning techniques to predict CCS values more accurately and for a broader range of lipid classes."
Please join us on Sunday, June 2nd, from 7:30 am to 12:30 pm for our eXceed Symposium at the Marriott Marquis Atlanta to listen to Prof. Vicki Wysocki speak about results obtained in her laboratory with the timsTOF Pro. Moreover, Prof. Jeff Spraggins and Prof. Nathalie Agar will share their experience and initial results on the new timsTOF fleX. Two parallel sessions follow on 4D Proteomics/Biopharma and MS Imaging/SpatialOMx.
Bruker will host a scientific press conference on Monday, June 3, 2019, at 9:30 am EDT at the Omni Hotel, Grand Ballroom D, North Tower M4, including Bruker management and guest speaker Prof. Vicki Wysocki .
Customers are invited to visit the Bruker's ASMS booth #515 throughout the conference.
References:
- Parallel accumulation serial fragmentation combined with data independent acquisition (diaPASEF): Bottom up proteomics with near optimal ion usage, by Florian Meier, Andreas-David Brunner, Max Frank, Annie Ha, Eugenia Voytik, Stephanie Kaspar-Schoenefeld, Markus Lubeck, Oliver Raether, Ruedi Aebersold, Ben C Collins, Hannes L Rost, and Matthias Mann. biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/656207v1
- MaxQuant software for ion mobility enhanced shotgun proteomics, by Nikita Prianichnikov, Heiner Koch, Scarlet Koch, Markus Lubeck, Raphael Heilig, Sven Brehmer, Roman Fischer, Jürgen Cox. biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/651760v1
- Trapped ion mobility spectrometry (TIMS) and parallel accumulation - serial fragmentation (PASEF) enable in-depth lipidomics from minimal sample amounts, by Catherine G Vasilopoulou, Karolina Sulek, Andreas-David Brunner, Ningombam Sanjib Meitei, Ulrike Schweiger-Hufnagel, Sven W. Meyer, Aiko Barsch, Matthias Mann, and Florian Meier. biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/654491v1