Infections are a dreaded threat that can have fatal consequences after an operation, in the treatment of wounds, and during tissue engineering. Biomimetic hydrogels with "built-in" antimicrobial properties can significantly decrease this danger. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, scientists have now introduced a gel that is activated by red light to produce reactive oxygen compounds that effectively kill bacteria and fungi.
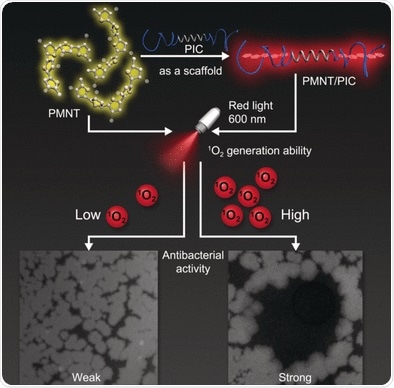
Hydrogels are molecule networks that hold water within their grid. Antimicrobial hydrogels can be produced by mixing with or attaching antimicrobial components to a polymer gel. Researchers at the Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin (China), Radboud University, Nijmegen (the Netherlands), and the University of Queensland, Brisbane (Australia) chose an alternative route and used photodynamic antimicrobial chemotherapy as their model. In this technique, photosensitizers enter an excited state when irradiated with light. Through a non-radiative transition, the photosensitizer enters a different, long-lived excited state. The transition can transfer energy to oxygen molecules, forming highly reactive oxygen species that kill microbes.
To date, synthetic gels with photodynamic antimicrobial activity have been neither biocompatible nor biodegradable. Products from biological sources, in contrast, harbor the risk of contamination or immune reactions and deliver results that are difficult to reproduce. The team led by Chengfen Xing overcame this challenge by using fully synthetic hydrogels with biomimetic properties, which are properties that mimic biological systems. They selected a polymer with a helical backbone (polyisocyanide with grafted ethylene glycol chains) that forms porous, highly biocompatible hydrogels with a thread-like architecture that resembles the structures and mechanical properties of biogels based on collagen and fibrin.
The researchers combined this type of hydrogel with a photosensitizer based on a polythiophene. In solution it forms disordered clumps and absorbs violet light. Incorporation into the spiral-shaped regions of the hydrogel forces the polythiophenes into a straight, linear configuration. In this form, the absorption is significantly stronger and shifted into the red region of the spectrum. This is preferable because red light can penetrate deeper and causes less bleaching of the pigment.
The researchers thus obtained a gel with outstanding antimicrobial power against bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis, as well as fungi like Candida albicans. This could be a starting point for making wound dressings with "built-in infection stoppers". The advantages of this method of fighting pathogens: it is non-invasive and its effect is controllable both in location and duration. Even antibiotic-resistant bacteria can be killed and the risk of causing new resistances is much lower.
Source:
Journal reference:
Yuan, H., et al. (2020) Biomimetic Networks with Enhanced Photodynamic Antimicrobial Activity from Conjugated Polythiophene/Polyisocyanide Hybrid Hydrogels. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. doi.org/10.1002/anie.201910979.