Researchers found a small molecule that inhibits different virus proteins and significantly reduces infection in cells. Combined with the antiviral remdesivir, its potency increases significantly, suggesting it may be a potential antiviral candidate for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the cause of the COVID-19 pandemic, is a single-stranded RNA virus. The virus binds to the host angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and enters the host cell with the help of other mediating factors, where the virus spike protein is cleaved and the viral genome is released into the host cell.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
During viral replication in the host cell, different viral proteins suppress the interferon-mediated host response and activate the release of proinflammatory cytokines. In the initial phase of the infection, symptoms like fever, sore throat, and cough appear. In some patients, especially those with other diseases, the disease progresses to a severe phase with acute respiratory distress syndrome and multiple organ failure.
Although several vaccines have now been approved in different parts of the world, it will take several months to vaccinate a large majority of the population. In addition, the long-term safety and efficacy of the vaccine are not yet known, as is their use for children and pregnant women. Thus, other therapeutic treatments are also needed to combat the virus.
Currently, the only Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved antiviral for the treatment of COVID-19 in the US is remdesivir. A recent study showed that bromodomain and extra-terminal domain proteins (BET) BRD2/BRD4 interact with the SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein. BRD2 inhibition has also been shown to decrease ACE2 expression.
Small molecule inhibits SARS-CoV-2
Researchers report in a paper published on the bioRxiv* preprint server that the small molecule SF2523, which they previously developed and is known to inhibit BET proteins BRD2/BRD4 and mTOR, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. BRD2/BRD4 plays a role in cell cycle regulation and inflammation, and BRD4 helps the secretion of interleukins that lead to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thus, BET inhibitors may help in treating COVID-19 patients.
The researchers tested the antiviral effect of SF2523 and remdesivir against SARS-CoV-2 on Vero and human bronchial epithelial cell line UNCN1T cells. The Vero cells were modified to be highly susceptible to viral infection. The UNCN1T cells are a good in vitro model, which can represent what happens in the body.
Both SF2523 and remdesivir showed a significant decrease in viral loads in the cells 24 hours after SARS-CoV-2 infection. The amount of SF2523 needed to inhibit 50% infection was 1.5 mm, comparable to that of remdesivir (1.1 mm).
Further analysis revealed that a combination of the two produced a more potent viral inhibition. The required dose to reduce viral infection in the human bronchial epithelial cell line by the same amount as when used individually decreased 25-fold for SF2523 and 4-fold for remdesivir when the two were combined. The dose reduction for remdesivir can also reduce adverse side effects that have been seen before.
Using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), they found that remdesivir did not change the potency of SF2523, and it did not interfere with its binding to BRD4. Remdesivir did not bind to BRD4, but SF2523 binds to the bromodomain 1 (BD2) and BD2 and not to the extra-terminal (ET) domain of BRD4. This suggests they target distinct molecular pathways.
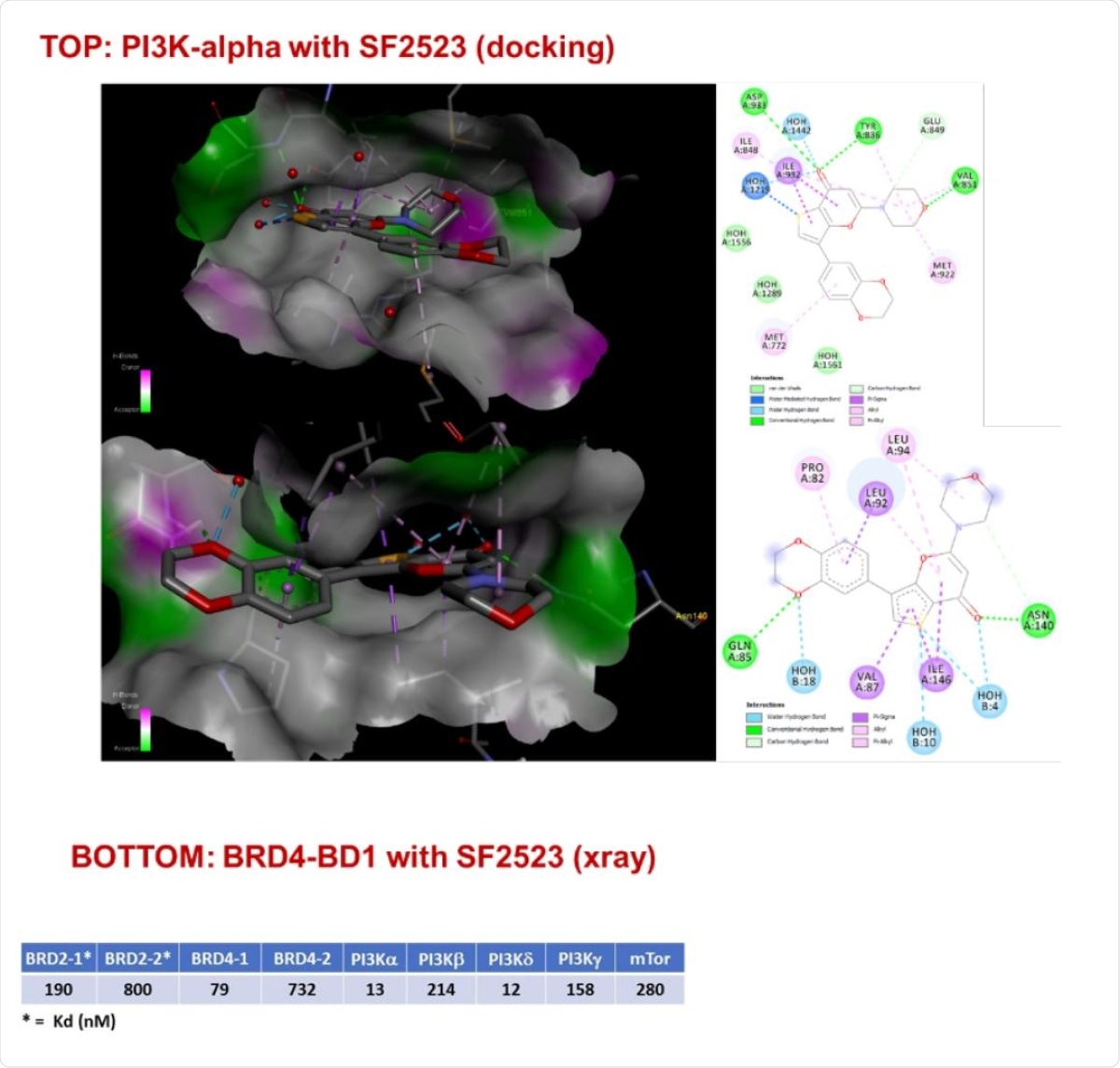
Predicted binding (docking) of SF2523 in PI3K-a catalytic domain (upper panel) and observed binding in crystal structure of SF2523 bound to BRD4-BD1 acetyl lysine binding site (1.8 Angstroms resolution) (bottom panel). In vitro (enzymatic) potency of SF2523 against targets.
A potential antiviral candidate
SF2523 is the only known inhibitor of both PI3K-α/mTOR and BRD4 and is in line for clinical development, making it a good candidate for developing a treatment for COVID-19. Furthermore, the molecule results from extensive computer-based molecular design engineered to inhibit two or three targets, such as BRD4, PI3K, and mTOR, together.
The molecule was designed to take advantage of the hydrogen bond interaction of PI3K-α with the NH group of Val851. For BRD4, the molecule used amino acids, the sequence obtained from a small-molecule BRD4 inhibitor JQ1.
Previous studies on influenza have shown that a combination of drugs is more effective than a single drug. In COVID-19, like influenza, viral loads peak with the onset of symptoms, thus a combination of these therapies may work better.
Based on these promising findings, the authors plan to study the efficacy of the drug combination in animal models of COVID-19.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Acharya, A. et al. (2021) Blockage of SARS-CoV-2 infection in-vitro by highly potent PI3K-α/mTOR/BRD4 inhibitor. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.02.433604, https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.03.02.433604v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Acharya, Arpan, Kabita Pandey, Michellie Thurman, Elizabeth Klug, Jay Trivedi, Kalicharan Sharma, Christian L. Lorson, Kamal Singh, and Siddappa N. Byrareddy. 2021. “Discovery and Evaluation of Entry Inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 and Its Emerging Variants.” Journal of Virology, September. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.01437-21. https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/JVI.01437-21.