The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic continues to challenge the public health response and epidemic management. Clinical experience and trial data obtained during the first wave of the pandemic in March and April 2020 led to improvements in the care of hospitalized patients.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Background
A thorough understanding of lockdown, mobility, and contact tracing policies improved in summer 2020 that allowed for the reopening of schools in autumn 2020. However, seroprevalence studies indicated that little was known about the total number of individuals who had been infected between March 2020 and November 2020 as well as how strongly the population susceptibility would affect the winter epidemic wave of 2020-2021.
The real-time estimation of seroprevalence or attack rate is challenging since it requires pre-planned periodic serum collections, a high-throughput validated assay, and the results are reported after a month lag. The estimation of attack rate requires the assumption of infection fatality rate (IFR), hospitalization incidence, or death incidence. These can then be used to infer the numbers of unreported or asymptomatic infections.
Since the onset of the pandemic, the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have collected cross-sectional serum samples from blood donors as well as residual samples from routine laboratory testing. Although these samples are considered to be a valuable epidemiological resource, they were not able to translate the seroprevalence estimates into attack rates effectively.
A new study published on the preprint server medRxiv* discusses a model-based reconstruction of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) attack rate and population-immunity curves for three New England states of Massachusetts (MA), Connecticut (CT), and Rhode Island (RI). The study took place during the first 15 months of the pandemic, from March 1, 2020, to May 31, 2021.
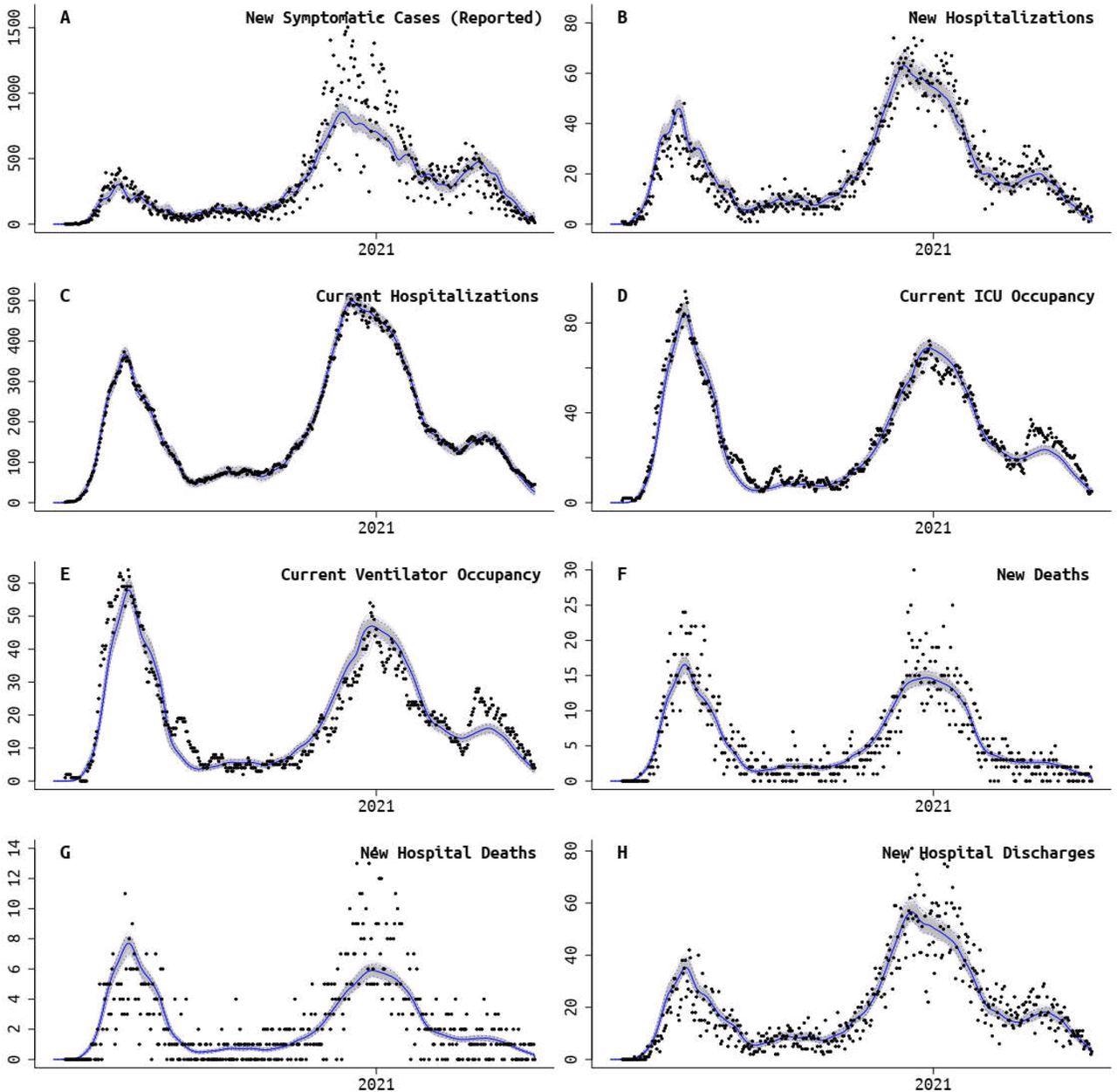 Rhode Island fit of model to data. Panels A, B, and F also have age-structured data streams, making a total of 11 data streams that were fit. Black dots are absolute daily counts. Blue line is model median from the posterior, and gray bands show 95% credible region.
Rhode Island fit of model to data. Panels A, B, and F also have age-structured data streams, making a total of 11 data streams that were fit. Black dots are absolute daily counts. Blue line is model median from the posterior, and gray bands show 95% credible region.
About the study
The current study used a Bayesian inferential framework based on a dynamical epidemic model to fit hospitalization, death, and case data from the three states. The study involved eleven daily data streams from each state that included cumulative confirmed cases, cumulative confirmed cases by age, cumulative hospitalized cases by age, cumulative hospitalized cases, number of patients currently in the intensive care unit (ICU), number of patients currently hospitalized, cumulative deaths, cumulative hospital deaths, cumulative deaths by age, number of patients currently on mechanical ventilation, and cumulative hospital discharges.
Vaccination campaigns, as well as temporally varying patterns of clinical care and changing age-contact rates, were also included in the model. The attack rate was estimated by obtaining a sum of unreported symptomatic cases, reported symptomatic cases, and asymptomatic infections. Additionally, two types of IFRs, population-weighted infection fatality rate (pIFR), and epidemic infection fatality rate (eIFR) were also reported in the study.
Study findings
The results indicated that the population-level attack rates as of May 31, 2021, were 41.5% in RI, 28% in MA, and 25.8% in CT.
COVID-19 vaccination began in all three states in December 2020, although the initial rollout was slower than expected. However, by January 2021, 2.1 to 2.3% of each state’s population was vaccinated, which increased to 8 to 9.6% in February 2021.
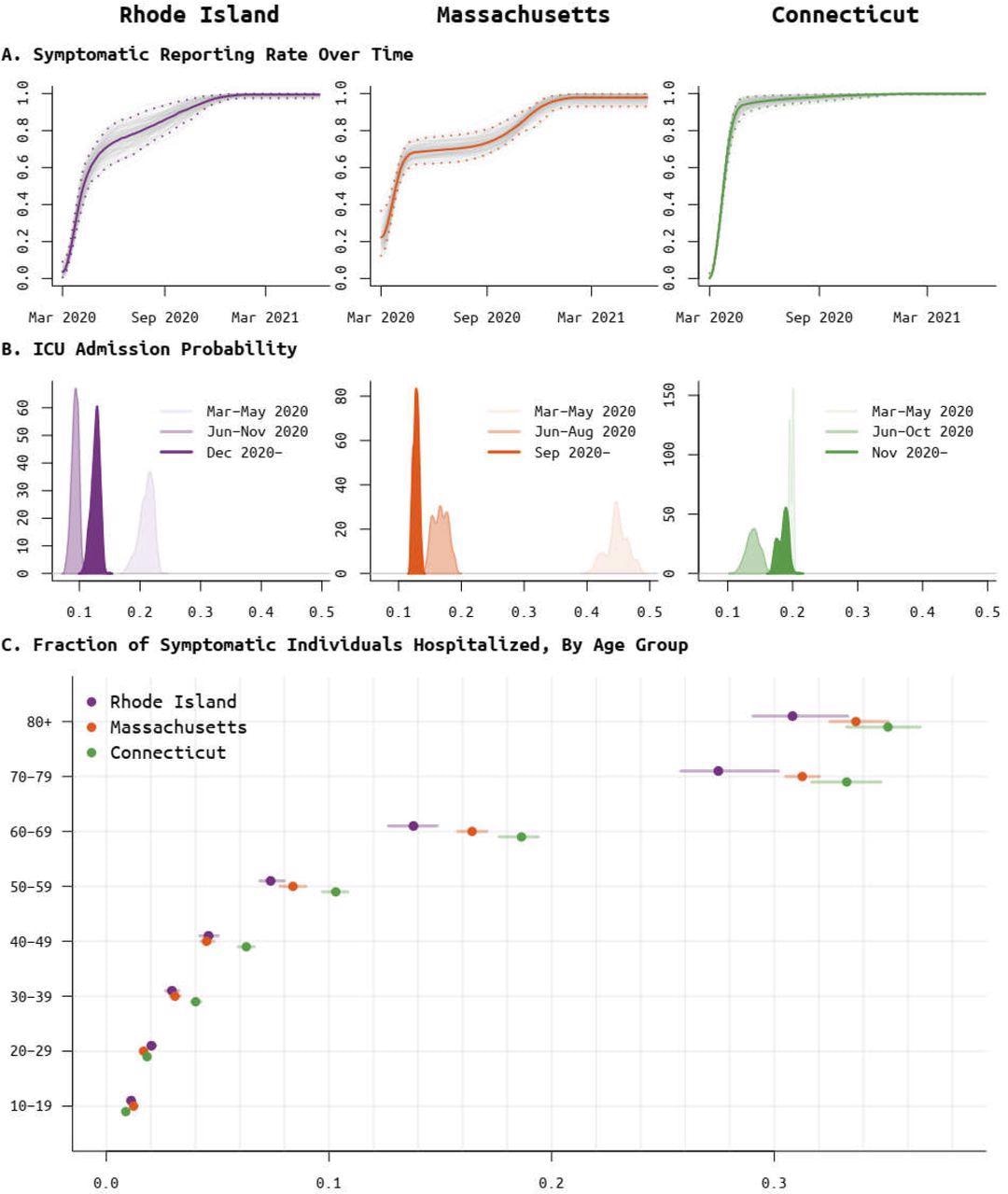 Posterior distributions for the (A) per-symptomatic-case reporting rate, (B) ICU admission probability, per hospitalized case, for different phases of the epidemic, and (C) the age-specific probability of hospitalization for symptomatic cases.
Posterior distributions for the (A) per-symptomatic-case reporting rate, (B) ICU admission probability, per hospitalized case, for different phases of the epidemic, and (C) the age-specific probability of hospitalization for symptomatic cases.
The population immunity was estimated to be 64.1% in CT, 73.4% in RI, and 66.3% in MA. This suggested that more than 33% of southern New England was immunologically naive during the next wave brought about by the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant in July 2021.
The percentage of vaccines administered to seropositive individuals was 34.1% in RI, 24.6% in CT, and 27.6% in MA. These results also suggest that the pandemic was more deadly in RI and MA as compared to CT. However, 55 to 60% more infections per population were reported in RI as compared to CT and MA.
The lower eIFR in Rhode Island suggests that the larger epidemic extended to less vulnerable groups, which lowered the average fatality rate for the epidemic as a whole. Comparatively, the pIFR was found to be two to three times higher during the earlier period of the pandemic as compared to the later phases.
The current study also included change points in the ICU admission fraction that help to monitor changes in clinical management for hospitalized patients. The first change point was reported on June 2, 2021, for RI, May 26, 2021, for MA, and June 5, 2021, for CT, while the second change point was reported on December 10, 2021, for RI, September 12, 2021, for MA, and November 6, 2021, for CT.
Conclusions
The current study was quite effective in determining the attack rates and susceptibility estimation. However, during the next phase of attack rate and population immunity estimation, the rate of antibody waning following SARS-CoV-2 infection and SARS-CoV-2 vaccination must be integrated.
This will not only help to evaluate the invasion ability of new highly transmissible variants like the Delta or Alpha variants but also the immune escape variants such as Omicron lineage. Understanding the susceptibility of the epidemic curve while it is changing and the importance of IFR estimation as the epidemic passes through different vulnerability strata during different periods will help to reduce the risk that may be posed by any new variant.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Tran, T. N. A., Wikle, N. B., Yang, F., et al. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 attack rate and population immunity in southern New England, March 2020 - May 2021. medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2021.12.06.21267375. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.06.21267375v1.
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Tran, Thu Nguyen-Anh, Nathan B. Wikle, Fuhan Yang, Haider Inam, Scott Leighow, Bethany Gentilesco, Philip Chan, et al. 2022. “SARS-CoV-2 Attack Rate and Population Immunity in Southern New England, March 2020 to May 2021.” JAMA Network Open 5 (5): e2214171. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.14171. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2792721.