
 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
As of December 2021, the GISAID database consisted of more than six million genome sequences of SARS-CoV-2. These include genomic sequences of the recently discovered Omicron variant, as well as previous strains that have been collected from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients around the world since the beginning of the pandemic in 2020. Several previous studies have performed a genome-wide analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genomes using model-based approaches that assume an underlying phylogenetic tree structure.
About the study
In the current study, the researchers utilized an unsupervised genome-wide cluster analysis based on the Jaccard similarity matrix. Herein, a given set of nucleotide sequences were assigned to a reference sequence, which was followed by a principal component analysis (PCA).
Subsequently, all sequences were translated into a Hamming matrix, which indicated all the mismatch mutations as compared to the reference sequence. The Hamming matrix serves as an input to the Jaccard similarity matrix, which results in a similarity index between zero and one for all pairwise comparisons of sequences. PCA is then applied to the Jaccard similarity matrix to identify clusters of SARS-CoV-2 genomes.
The study results were displayed as the first two principal components of the Jaccard matrix, which show a progression of all nucleotide sequences in time. These components are color-coded by the World Health Organization (WHO) region, the location where each sequence was submitted from, submission date, and clade, respectively. Note that there are a total of 11 clades of the SARS-CoV-2 genome available on GISAID, which include G, GH, GK, GR, GRA, GRY, GV, L, O, S, and V.
Study findings
The researchers initially identified 132,065 genomic sequences, which satisfied all five data quality attributes offered by GISAID. This included complete (sequences with a minimum length of 29,000 base pairs), low coverage excluded (sequences with more than 5% N-bases), collection data complete (submissions with a complete year-month-day collection date), high coverage (sequences with less than 1% N-bases), and with patient status (sequences with meta information in the form of age, sex, and patient status).
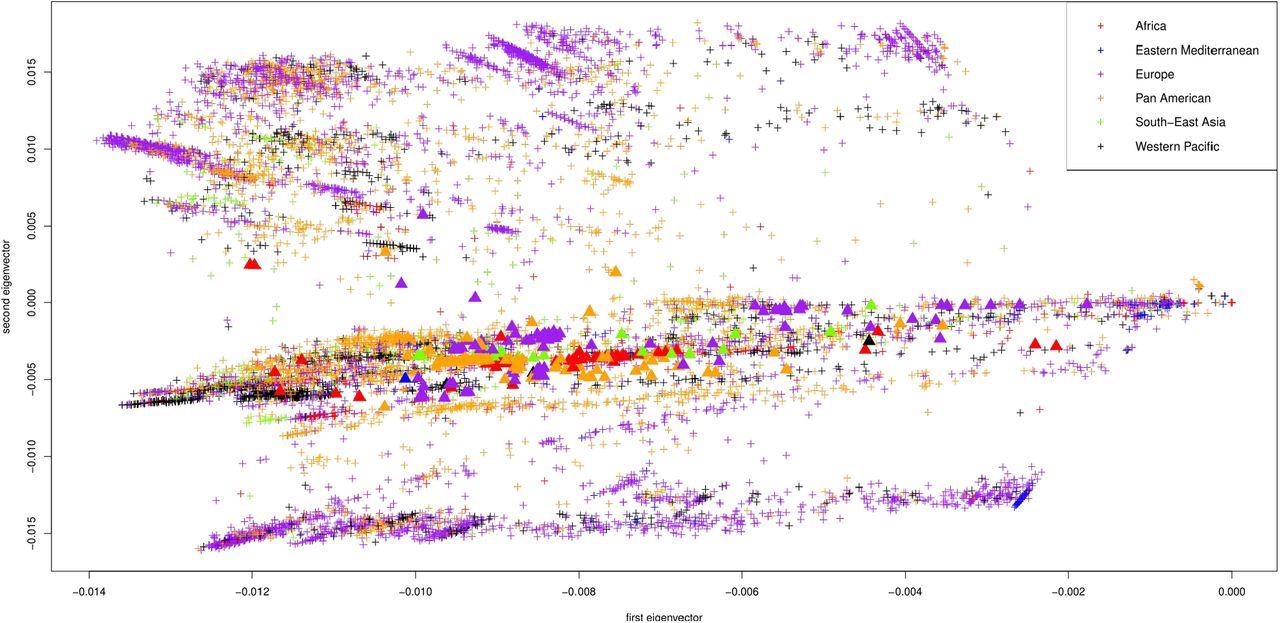
First two principal components of the Jaccard matrix, color coded by WHO region (AFRO in red, EMRO in blue, EURO in purple, PAHO in orange, SEARO in green, WPRO in black). Displayed are the 10013 sequences from GISAID, one point per sequence. The omicron samples are depicted as triangles.
Later, the dataset was down-sampled to 10,000 sequences due to the limit imposed on computing by the Jaccard similarity matrix and PCA. Finally, the researchers added all 287 sequences of the Omicron variants available on GISAID as of December 26, 2021, leading to a total of 10,287 genomic sequences for this study's analysis. The metadata information used for the study was the geographic location where sequences were collected.
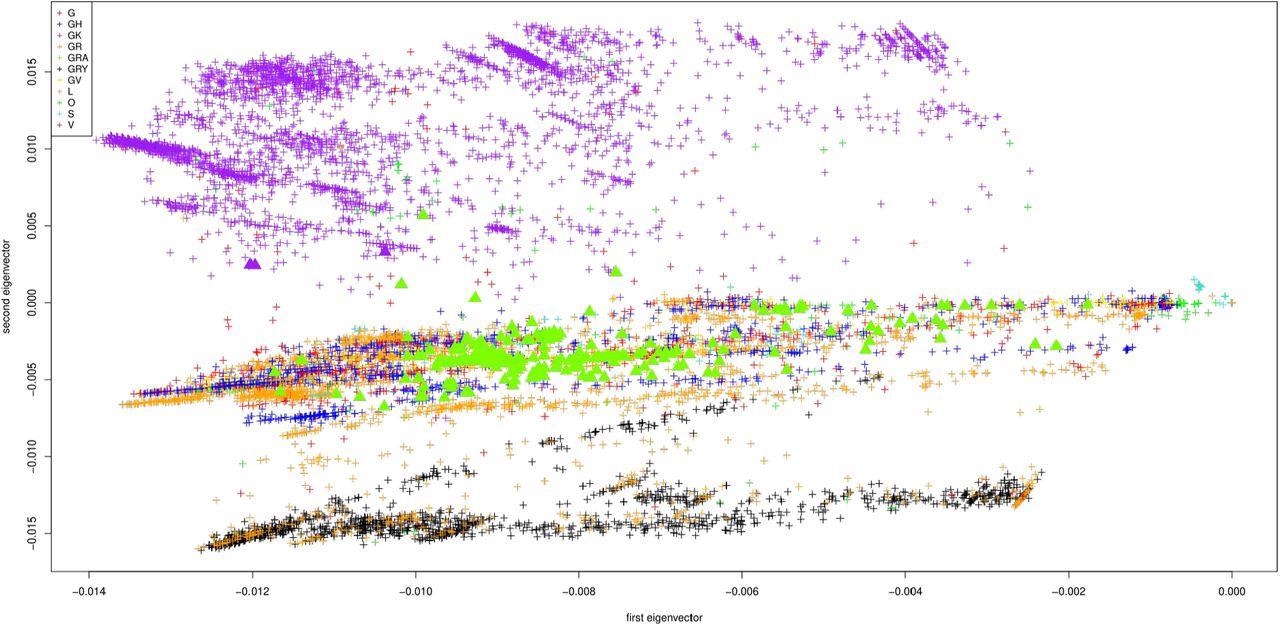
First two principal components of the Jaccard matrix, color coded by the clade of each sequence (clade G in red, GH in blue, GK in purple, GR in orange, GRA in green, GRY in black, GV in yellow, L in maroon, O in light green, S in turquoise, V in brown). Displayed are the 10013 sequences from GISAID, one point per sequence. The omicron samples are depicted as triangles.
Using the multiple sequence alignment program MAFFT, all sequences were aligned to the official SARS-CoV-2 reference published on GISAID. All other parameters were set to the default values for establishing a well-defined window for comparison of 29,891 base pairs.
The study analysis showed that the SARS-CoV-2 nucleotide sequences extended from the origin (0,0) on the Jaccard matrix in a distinctive way and formed numerous distinct clusters according to their geographical origin. Genomic clusters from Africa were identified in the upper left quadrant of the plot, whereas those from Europe were found in the lower left quadrant. Notably, Omicron genomic sequences were somewhat far off the European cluster and closer to the origin.
Conclusions
The study relates the emergence of new COVID-19 cases due to the Omicron variant using a non-parametric PCA on single-stranded nucleotide sequences of the SARS-CoV-2 genomic sequences collected from the publicly available GISAID database during the past two years of the pandemic. The study demonstrated that the new Omicron genomic sequences were closely related to sequences submitted to GISAID in the early months of the pandemic, around January 2020.
Further, these Omicron sequences in GISAID are spread across the entire range of the first principal component and did not cluster. This supports the hypothesis that the Omicron variant has been in circulation for some time and is responsible for long-term SARS-CoV-2 infections.
The study findings also established that unsupervised cluster analysis is a great tool for continuous data monitoring from public databases such as GISAID due to its simplicity and computational speed. This tool has also proven essential in classifying all SARS-CoV-2 emerging variants of interest for further follow-up analyses.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Hahn, G., Lee, S., Prokopenko, D., et al. (2021). Unsupervised genome-wide cluster analysis: nucleotide sequences of the omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 are similar to sequences from early 2020. bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/2021.12.29.474469. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.29.474469v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Hahn, Georg, Sanghun Lee, Dmitry Prokopenko, Jonathan Abraham, Tanya Novak, Julian Hecker, Michael Cho, et al. 2022. “Unsupervised Outlier Detection Applied to SARS-CoV-2 Nucleotide Sequences Can Identify Sequences of Common Variants and Other Variants of Interest.” BMC Bioinformatics 23 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-022-05105-y. https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12859-022-05105-y.