The findings of COVIDENCE UK could complement research work identifying risk factors for developing predominantly mild and moderate COVID-19. Patients with mild or moderate COVID-19 can transmit severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) to high-risk individuals more rapidly. Moreover, understanding the susceptibility factors can provide insights into SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis.
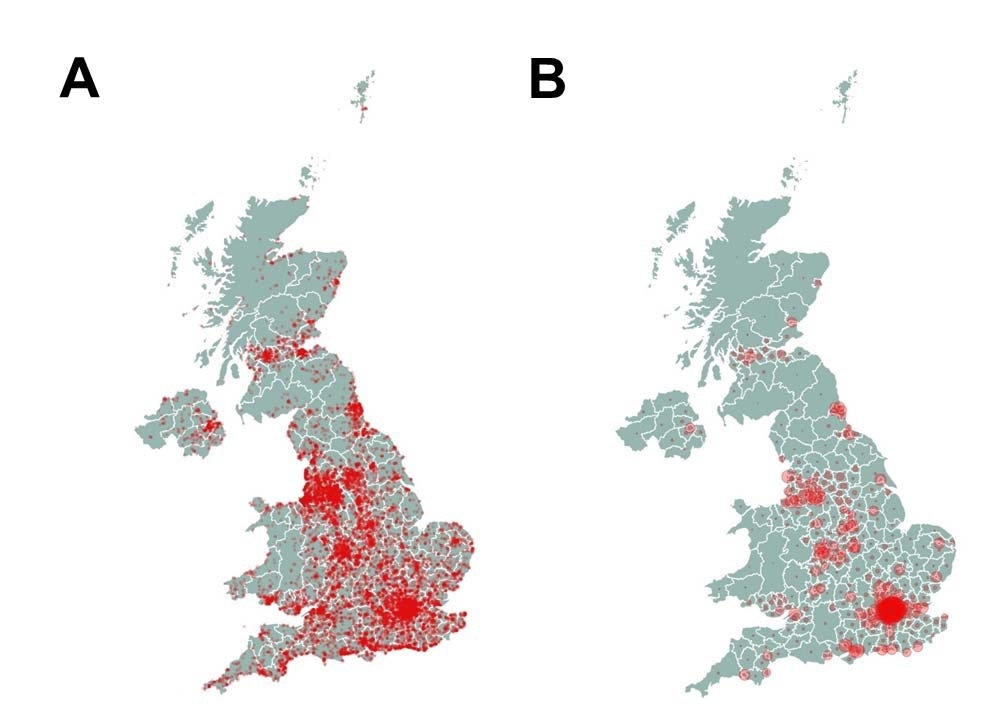
Geographical location of participants and COVID-19 cases. A, heatmap of COVIDENCE UK participants’ location of residence by postcode. B, heatmap of cumulative COVID-19 notifications in the UK, by postcode, from https://coronavirus.data.gov.uk/details/download (download dated June 10, 2022).
About the study
In the present study, researchers investigated the risk factors for COVID-19 and its impact on UK residents over 16 years. They recruited these participants via national-level campaigns on print and digital media, including newspapers, radio, television advertisements, social media, and online advertising. First, the team asked all the participants to provide consent for access to a five-year follow-up of their linked medical records. In case of the death of any participant or failure to complete questionnaires, the researchers could still capture their health data.
Next, the researchers asked each participant to fill out an online baseline questionnaire that captured information on socio-demographic characteristics, profession, weight, height, medical conditions, vaccination status, etc., of each study participant. Furthermore, the participants provided monthly information about their COVID-19 and other acute respiratory infection symptoms, quality of life, etc., via questionnaires.
Although the study population under-represented certain sections, including younger adults, men, and ethnic minorities; yet, it effectively addressed several aetiological questions. On the other hand, it over-represented older adults and people with comorbidities and studied them well. Overall, the study findings are not particularly generalizable.
Study findings
In total, 19,981 participants enrolled for the COVIDENCE UK study between May 1, 2020, and October 6, 2021, and consented to a five-year follow-up. The mean age of the study participants was 59.1 years; 87.7% resided in England, 70.2% were female, and 93.7% belonged to the White ethnicity. The authors observed increased odds of developing SARS-CoV-2 infection among the study participants of Asian/Asian British origin. After infection and vaccination, they also had higher titers of combined immunoglobulin G (IgG), IgA, and IgM antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein. Therefore, there is a need to investigate how biological determinants of ethnic diversity make one susceptible to COVID-19.
Further, the authors found that a higher body mass index increased susceptibility to COVID-19. These individuals had higher titers of anti-S antibodies following natural SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. Conversely, factors associated with COVID-19 severity, including ischemic heart disease, hypertension, and diabetes, did not increase susceptibility to COVID-19. The overlap between factors influencing susceptibility to COVID-19 and COVID-19 severity was clearly limited.
The post-vaccination study data showed that titers of anti-S antibodies were higher after vaccination. Conversely, a shorter interval between vaccine doses and suppressed immunity lowered anti-S antibody titers following vaccination. However, a booster dose of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA)-based COVID-19 vaccine effectively seroconverted immunosuppressed individuals. Furthermore, the risk of breakthrough infection was independently associated with younger age, administering the ChAdOx1 COVID-19 vaccine, and more frequent visits to indoor public places. In addition, health economic analyses revealed that COVID-19 resulted in a vicious cycle of impaired health and adverse economic outcomes.
Conclusions
Overall, the COVIDENCE UK dataset presented granular information on all factors influencing vulnerability to COVID-19 and its impact on UK adults. All the study participants consented to provide access to their medical records for up to five years. Additionally, the researchers followed up with the participants monthly to reduce issues associated with longer intervals between questionnaires, and poor recall of symptoms did not arise. Further, they engaged participants continuously via monthly webinars; hence the withdrawal rate was as low as 8%. More importantly, COVIDENCE UK reliably identified potential risk factors for developing mild and moderate COVID-19, which likely affected SARS-CoV-2 transmission.
One of the distinguishing features of COVIDENCE UK was that it flexibly used trials-within-cohort methodology and rapidly, efficiently, and successfully tested interventions to prevent COVID-19 and other respiratory illnesses. Accordingly, the phase III randomized trial-within-cohort study (CORONAVIT) evaluated the test-and-treat approach to correct sub-optimal vitamin D status on incidence and severity of COVID-19 and other acute respiratory infections. The treatment, however, did not reduce the incidence or severity of COVID-19.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Cohort Profile: Longitudinal population-based study of COVID-19 in UK adults (COVIDENCE UK), Hayley Holt, Clare Relton, Mohammad Talaei, Jane Symons, Molly R Davies, David A Jolliffe, Giulia Vivaldi, Florence Tydeman, Anne Williamson, Paul E Pfeffer, Christopher Orton, David Ford, Gwyneth A Davies, Ronan A Lyons, Chris J Griffiths, Frank Kee, Aziz Sheikh, Gerome Breen, Seif Shaheen, Adrian R Martineau, medRxiv pre-print 2022, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.20.22276205, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.06.20.22276205v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Holt, Hayley, Clare Relton, Mohammad Talaei, Jane Symons, Molly R Davies, David A Jolliffe, Giulia Vivaldi, et al. 2022. “Cohort Profile: Longitudinal Population-Based Study of COVID-19 in UK Adults (COVIDENCE UK).” International Journal of Epidemiology 52 (1): e46–56. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyac189. https://academic.oup.com/ije/article/52/1/e46/6731614.