Modern formulations contain recombinant antibodies. Asymmetrical Flow FFF (AF4) is the preferred method for the characterization of such antibodies owing to its ability to characterize both antibody species and their aggregates and fragments. Also, the method can detect even slight variations in the general heterogeneity and conformation of samples.
Experimental Results
Figure 1 shows the separation and characterization of antibodies as well as their two fragments and higher aggregates using the Postnova AF2000 system.
Further, the AF4 system also reveals the heterogeneity of the fractions of the antibody, as the peak shape is asymmetrical and highlights a broadening with higher retention times. This is indicative of the presence of the antibodies with a different conformation in this area.
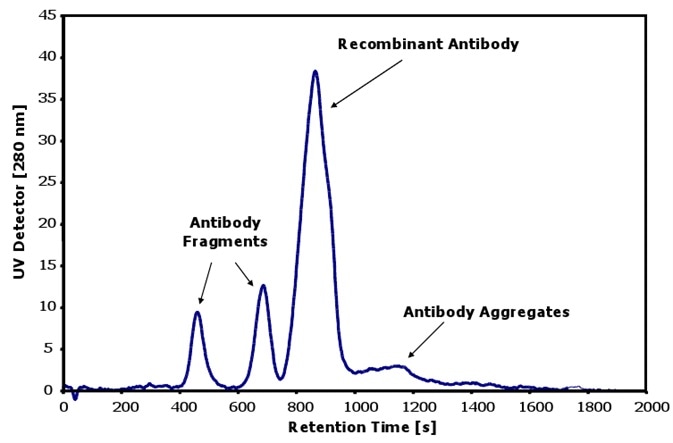
Figure 1. Characterization of antibodies with aggregates and fragments.
Processing Temperature 30°C
The dependence of antibodies at various processing temperatures is shown in Figure 2. It is clear from the results that the aggregates and fragments cannot be detected in the antibody at the processing temperature of 30°C.
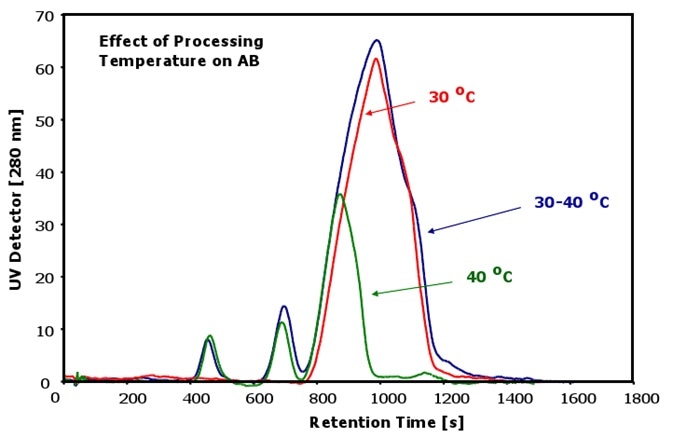
Figure 2. Antibodies at different temperatures
Processing Temperature 30 - 40°C
However, significant changes can be observed in the constitution of antibody fraction at a slightly higher processing temperature of 30 - 40°C. Two fragment peaks can be seen in the sample as a result of the increased temperature.
The main antibody peak does not show any obvious changes, but a slightly increased peak broadening can be observed with higher elution times. This indicates that there is an increase in the antibody species with a different conformation when the processing temperature is between 30 to 40°C.
In addition to that, there is a noticeable amount of aggregates generated as a result of the higher temperature. This is indicated by the tiny peak eluting immediately after the main antibody peak.
Processing Temperature 40°C
More pronounced changes are observed in the constitution of the antibody sample at the processing temperature of 40°C. It is to be noted that the injection volume was lower than in the previous measurements.
The main antibody peak shows dramatic changes as its size is considerably decreased. Furthermore, the antibody fraction with the different conformation is almost fully decomposed.
The corresponding antibody peak in the fractogram is more symmetric than the earlier peaks. In addition, the peak has moved toward earlier elution times, which indicates a smaller size with a higher diffusion coefficient than before.
The aggregates of the main antibody peak can also be determined in the sample. However, the pristine antibody appears to be significantly degraded, resulting in the formation of a higher amount of fragments that can now be observed in this sample.
Therefore, a higher amount of fragments are formed rather than a higher amount of aggregates when the processing temperature is increased.
Conclusion
This study explored the effects of temperature on the fragmentation, aggregation and stability of recombinant antibodies.
It shows that the combination of AF4 and UV serves as an effective monitoring tool for studying temperature-induced antibody decomposition, demonstrating how the antibody is decomposed into fragments instead of aggregates.
Acknowledgements
Produced from materials originally authored by Dr. Soheyl Tadjiki, Evelin Moldenhauer, Dr. Thorsten Klein from PostNova.
About Postnova Analytics
 Postnova Analytics' mission is to solve analytical problems in biotechnology, polymer and particle science.
Postnova Analytics' mission is to solve analytical problems in biotechnology, polymer and particle science.
Advanced Analytical Products
- Postnova always and only offers high quality products
- Postnova offers the newest and most innovative technologies available
- Postnova only chooses leading manufacturers as supply partner
Powerful Product Portfolio
- Postnova has formed a complete product portfolio (systems, supplies, services)
- Postnova has focused only Field-Flow Fractionation and Light Scattering
- Postnova offers complete solutions from one source with high expertise
Strong Customer Support
- Postnova has a highly qualified customer support team
- Postnova is always looking for long term partnerships with our customers
- Postnova provides the ultimate solution to make customers successful: Quality & Support
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.