Isotonic beverages have become increasingly popular in the last few years, with almost every drink being available in an isotonic version. This article explains the term “isotonic” and describes its various benefits, and demonstrates whether beverages are actually isotonic. It also talks about osmolality.
Every liquid containing substances such as minerals, carbohydrates, or proteins has an osmotic pressure. The term iso-osmotic or isotonic refers to liquids having the same osmotic pressure as that of human blood. This characteristic enables rapid ingestion of salt and sugars present in the drink, resulting in a faster recovery following sporting activity.
Determining the number of osmotically active molecules solved in a liquid can be easily and quickly checked by determining its osmolality. Being a general measure for the number of molecules, the osmolality is typically given in mOsmol/kg solvent.
Shown in Figure 1 are isotonic drinks, which are defined to have a 300±10% mOsmol/kg osmolality. These limit values are specified by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) [1], for instance.

Figure 1. Isotonic beverages
Materials and method
The KNAUER K-7400S Semi-Micro Osmometer was used to make all measurements. Osmolality values of 2000, 850 and 300 mOsmol/kg were present in the used calibration standards. The system parameters were set to -8 °C for freeze and -16 °C for cooling limit.
With the help of an ultrasonic bath, the beer and soft drink samples were degassed to remove the carbon dioxide and later 150 μL of these samples were filled in a plastic sample tube.

Results
Six different samples of isotonic and non-isotonic drinks were determined and the osmolality was established using the KNAUER K-7400S osmometer which associates freezing point depression with osmolality.
For isotonic samples, the K-7400S osmometer was calibrated in a range from 0 to 850 mOsmol/kg, and for non-isotonic drinks in a range from 0 to 2000 mOsmol/kg. Using a sample volume of 150 μL, 10 replicates were measured for each sample.
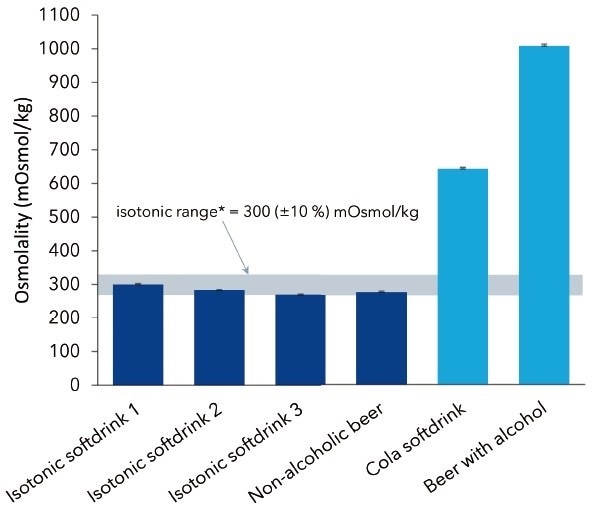
Figure 2. Measured osmolalities of four different as isotonic declared as well as two non-isotonic beverages. Graph shows average values and standard deviations of 10 replicates
Figure 2 illustrates the average osmolality values for the isotonic samples along with the EFSA-defined limits, but shows a much higher osmolality value for the non-isotonic beverages. For caffeine samples containing beer and soft drink, osmolalities of 1008 mOsmol/kg and 644 mOsmol/kg, respectively, were established. The osmolality of alcoholic beer is relatively higher than its non-alcoholic isotonic substitute because alcohol also depresses the freezing point.
Additional results
Figure 3. Temperature-time-curve
Conclusion
It was observed that the osmolalities of all isotonic samples analyzed were within the EFSA-defined range. The values were generally below 300 mOsmol/kg, which could be attributed to sample preparation (degassing) and the ensuing reduction of carbon dioxide. Non-isotonic beverages had considerably higher osmolalities because of a higher content of solved compounds like alcohol or sugars present in, for example, beer.
Additional materials and methods
Table A1. Average osmolalities of isotonic and non-isotonic beverages
|
Beverage
|
Isotonic softdrink 1
|
Isotonic
softdrink 2
|
Isotonic
softdrink 3
|
Non-alcoholic beer
|
Cola soft drink
|
Beer with alcohol
|
|
Average Osmolality (n=10)
|
300
|
284
|
270
|
278
|
644
|
1009
|
|
σ
|
2.7
|
0.7
|
1.6
|
3.2
|
3.8
|
5.7
|
Table A2. Method parameters
|
Calibration 1
|
0 mOsmol/kg
|
300 mOsmol/kg
|
850 mOsmol/kg
|
|
Calibration 2
|
0 mOsmol/kg
|
850 mOsmol/kg
|
2000 mOsmol/kg
|
|
Sample volume
|
150 μL
|
|
|
|
Freeze
|
-8 °C
|
|
|
|
Cooling limit
|
-16 °C
|
|
|
Table A3. System configuration & data
|
Instrument
|
Description
|
Article No.
|
|
Osmometer
|
KNAUER K-7400S Semi-Micro Osmometer
|
A0006AC
|
|
Sample tubes
|
Approved plastic sample tubes, 500 pcs.
|
A0272
|
|
Software
|
EuroOsmo 7400
|
A3705
|
References
- Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to carbohydrate-electrolyte solutions and reduction in rated perceived exertion/eff ort during exercise (ID 460, 466, 467, 468), enhancement of water absorption during exercise (ID 314, 315, 316, 317, 319, 322, 325, 332, 408, 465, 473, 1168, 1574, 1593, 1618, 4302, 4309), and maintenance of endurance performance (ID 466, 469) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/20061 EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2211/pdf.
About KNAUER
 KNAUER is an owner-managed middle-sized company with more than 120 employees situated in Berlin, Germany. Since 1962, KNAUER has been producing and developing high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) systems.
KNAUER is an owner-managed middle-sized company with more than 120 employees situated in Berlin, Germany. Since 1962, KNAUER has been producing and developing high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) systems.
The HPLC technique is used to separate, identify and quantify substances in a mixture. It can be used for many applications, including the analysis of toxics in drinking water, the detection of drugs in blood as well as for the purification or quality inspection of pharmaceutical and chemical products.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.