The magnetic bead separation block - an essential piece of equipment for every NGS laboratory - has been optimized for miniaturized SPRI bead clean-ups with mosquito® HV genomics.
The magnetic bead separation block and the corresponding mosquito protocol deliver a semi-automated process that provides substantial cost savings with high recovery rates.
This new bead clean-up process will be beneficial for both single-cell and bulk library preparation workflows, such as the most recent on-bead tagmentation methods.
This enhanced magnetic bead clean-up process may be employed with all mosquito genomics models, while the separation block also fits the non-contact low volume liquid dispenser, dragonfly® discovery.
It provides high DNA recovery rates and reliable clean-up or size selection in 384-well PCR plates (as shown in Table 2 and Figure 2). It also delivers optimized bead clean-ups to volumes as low as 5 μL.
Technical specification
The tested plates are:
- Bio-Rad Hard-Shell 384-well PCR plate
- Eppendorf twin.tec 384-well PCR plate
Table 1. Recommended volumes for miniaturized bead clean-up process performed with SPT Labtech magnetic bead separation block. Source: SPT Labtech
| Sample volume |
Bead volume |
EtOH volume |
Elution volume |
| 2-10 μL |
2-10 μL |
4.5-10 μL |
2-20 μL |
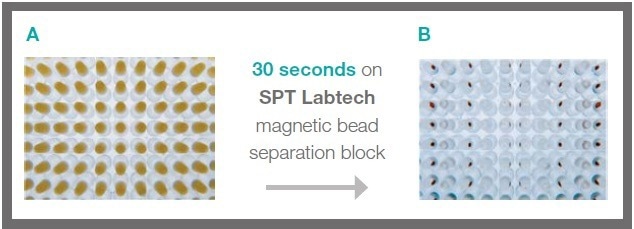
Figure 1. Separation of magnetic beads in a 384-well PCR plate. 5 μL of SPRIselect beads were added to 5 μL of sample and mixed thoroughly before placing on the magnetic bead separation block (SPT Labtech). A: Immediately after resuspension. B: 30 seconds after the separation process. Image Credit: SPT Labtech
Table 2. Control DNA (Mid Range DNA Ladder, Jena Bioscience # M-203, 2.6 ng/μl) was treated with SPRIselect beads according to the manufacturer's Purification or Size Selection protocols (Beckman Coulter). Bead ratios (-fold volume of bead suspension vs. initial sample volume) used: Purification 0.5x or 0.8x, respectively; Size Selection: first step 0.95x; second step 0.85x. Samples were analyzed on a Fragment Analyzer with HS NGS Fragment Kit (Advanced Analytical Technologies). Source: SPT Labtech
| Purification 0.5x |
Full volume manual |
Miniaturized manual |
Miniaturized mosquito HV |
| Recovery (%) |
67 +/- 1.0 |
62 +/- 0.7 |
69 +/- 0.8 |
| Clean-up rate (%) |
100 |
100 |
100 |
| Purification 0.8x |
Full volume manual |
Miniaturized manual |
Miniaturized mosquito HV |
| Recovery (%) |
72 +/- 0.3 |
70 +/- 0.8 |
76 +/- 0.3 |
| Clean-up rate (%) |
100 |
100 |
100 |
| Size selection |
Full volume manual |
Miniaturized manual |
Miniaturized mosquito HV |
| Recovery (%) |
50 +/- 0.3 |
45 +/- 0.5 |
61 +/- 0.9 |
| Clean-up rate (%) |
100 |
100 |
100 |
The full-volume manual comprised 50 μl of control DNA within 500 μl PCR-grade microtubes, while the miniaturized manual comprised 5 μl of control DNA in Eppendorf twin.tec 384-well PCR plate with the magnetic bead separation block manufactured by SPT Labtech.
The miniaturized and automated refers to the miniaturized manual process but with all pipetting steps conducted on mosquito HV genomics.
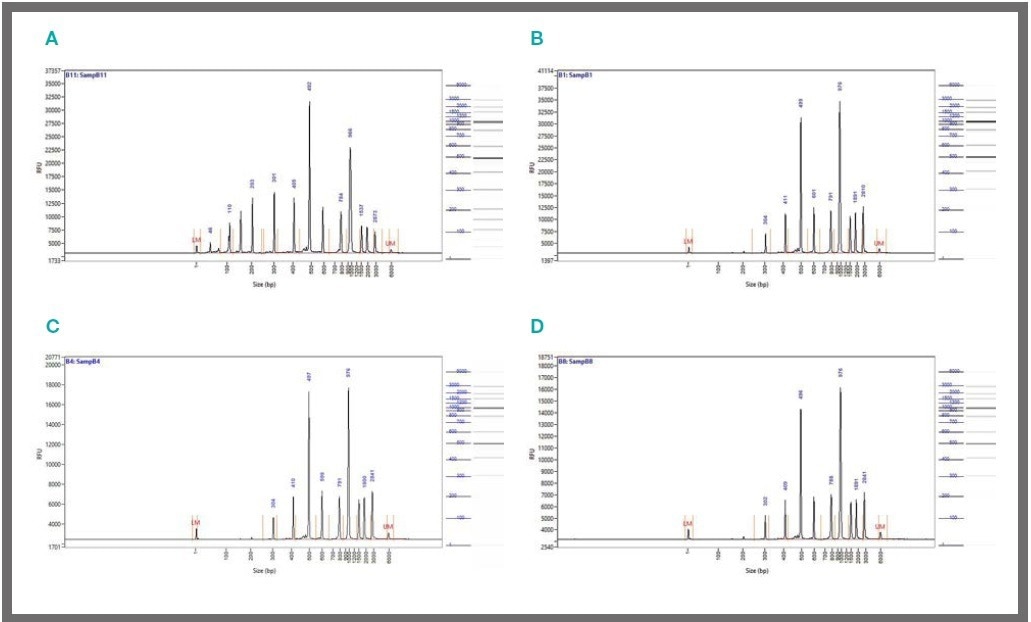
Figure 2. Control DNA (Mid Range DNA Ladder, Jena Bioscience # M-203, 2.6 ng/μl) was treated according to the SPRIselect purification protocol with a 0.8x volume of bead suspension. Samples were analyzed on a Fragment Analyzer using the HS NGS Fragment Kit. Representative results are shown. A: Input control (before clean-up). B: Full-volume manual purification with 50 μl of control DNA in 500 μl PCR-grade microtubes. C: Miniaturized manual purification with 5 μl of control DNA in Eppendorf twin.tec 384-well plate with magnetic bead separation block. D: Miniaturized, automated purification: as in C but all pipetting steps carried out on mosquito HV genomics. Image Credit: SPT Labtech
The results were validated with the following:
- SPRIselect beads (Beckman Coulter)
- AMPure XP beads (Beckman Coulter)
- Illumina DNA Prep (previously known as Nextera DNA Flex)
Conclusion
The new magnetic bead separation block manufactured by SPT Labtech was used in combination with a protocol optimized for bead clean-ups with mosquito HV genomics. This enabled significant cost savings to be made regarding miniaturized NGS library preparation workflows.
About SPT Labtech
We Design and Manufacture Robust, Reliable and Easy-to-Use Solutions for Life Science
We enable life scientists through collaboration, deep application knowledge, and leading engineering to accelerate research and make a difference together. We offer a portfolio of products within sample management, liquid handling, and multiplexed detection that minimize assay volumes, reduce material handling costs and put the discovery tools back in the hands of the scientist.
At the Heart of What We Do
Many of our innovations have been born out of the desire to create solutions to existing customer problems; and it’s this ethos that drives SPT Labtech’s R&D efforts. Our strengths come from the trust our customers have with us to develop truly unique, automated technologies to meet their needs. We combine cutting edge science with first-rate engineering to put customers at the heart of everything we do.
A Problem-Solving State of Mind
The substantial breadth of expertise within our company enables us to be involved in the full life cycle of our products from the initial design concept, mechanical and software engineering and prototyping, to final manufacture and sale. These qualities allow us to offer the best possible technical and mechanical support to all the equipment that we supply, hence maintaining excellent client relationships.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.