Novel technologies were added when developing an innovative vivarium for a prominent Boston cancer research organization to enhance the facility’s overall effectiveness, value, and design program.
One technology utilized was a tested and applied substitution to the organization’s more conventional decontamination technique, the ionized Hydrogen Peroxide (iHP) decontamination system.
Rationale for change
Designers constantly seek new proficiencies in the systems that support sensitive, controlled research areas. This client wished to push the boundaries and explore the advantages of adopting innovative equipment where suitable for a new facility.
A new iHP system was employed to enhance throughput and reliability following research. Alongside other upgrades, the iHP technology can decontaminate vast materials arriving in the facility on pallets.
Benefits of iHP technology
The iHP system can process many supplies in a substantially shorter time, adding more efficacy to vivarium processes. Advantages include:
- Supply throughput can be achieved on a wider scale by using fogging pods

The pre-decontamination room is where the iHP process occurs. Image Credit: SteraMist Disinfection and Decontamination Technology
- Aerated disinfection technology offers a broader range, decontaminating all surfaces.
- Combining a dry process and lower concentrations of hydrogen peroxide is safer for staff than traditional misting. Rooms in this facility have interlocking and automated sliding doors to safeguard employees from the iHP process and to help transfer many supplies through the space.
The innovative iHP system increases operation efficiencies when integrated into various other support systems throughout the facility. It combines seamlessly with a large dry heat sterilizer dedicated to decontaminating the ABSL-2 space.
This unit can decontaminate ABSL waste and sizable equipment entering the facility, such as animal transfer stations and biosafety cabinets.
The iHP decontamination was incorporated beyond the barrier to offer optimal flexibility and bring disinfection to required spaces where a contamination risk existed from within.
The scale is defined by sizing the subject area in three ways:
- Large-scale application: Utilized as a “first line of defense” for decontamination in a sizeable space such as a single room.
- Medium-scale: A dry heat sterilizer decontaminates using iHP and a side-mounted pod. It is used for ABL2 items and larger equipment entering the facility.
- Small-scale: Smaller concentrations can be disinfected using a stand-alone mobile unit to sanitize fixed apparatus in the facility.
Design and layout considerations
Designing the whole facility when an iHP system is employed necessitates numerous actions and considerations to support the success, proficiency, and practical incorporation.
It must be accessible past the barrier and contained within it once products are processed. Providing sufficient set-up and lay-down space is also vital.
It is essential to provide enough space on the back end of the decontamination process to collect and store the products. This facility required sufficient space to fit multiple supplies in the area and a place to store them once the items were processed.
High-density stainless-steel storage and shelving units were incorporated throughout the facility to hold post-decontamination supplies before distribution. The doors needed to be integrated with the system controls to ensure safety.
This is pivotal to restrict access once the decontamination cycle is on and to ensure decontaminated items are not contaminated again. The suite’s doors, many of which are automated interlocking doors, are designed to accommodate large items and streamline the transfer process.
Autoclave equipment must be located inside the facility. The autoclave must be accessible from beyond the barrier and contained within it once products are processed.
A standard operation practice must be determined to inhibit back travel of supplies once decontaminated and the opening of any doors to the outside barrier. Placing doors on a timer or interlock can be part of these standard operating procedures.
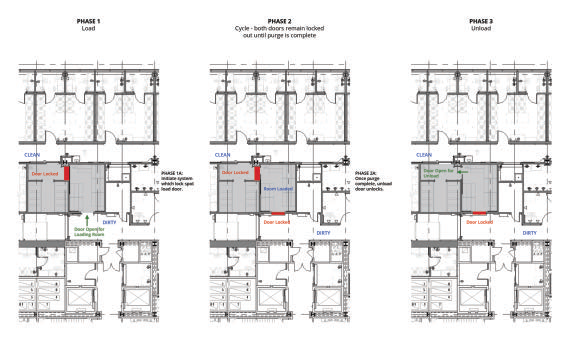
Figure 1. The sequencing of the decontamination process through each of the three phases. Image Credit: SteraMist Disinfection and Decontamination Technology
Sequence of operations for iHP process
The choice of a decontamination system informs the sequencing of the decontamination process. With an iHP system, the sequence involves a step-by-step method based on achieving operations efficiency and maintaining safety. Figure 1 highlights the sequencing:
- Phase 1 (Loading): The doors from the service corridor (non-barrier) open while doors between pre-decontamination and post-decontamination (barrier) stay shut using an interlock
- Phase 2 (Cycle): Doors from the service corridor close and lock. Doors from pre-decontamination to post-decontamination stay shut and secured until the purge is finished. The cycle dwells and purges. Once the purge is over, doors from pre- and post-decontamination open while doors to the service corridor stay shut.
- Phase 3 (Unload): Equipment is unloaded to post-decontamination and the doors between pre-and-post shut when unloading begins. The doors to the service corridor open and a new load process can start.
Lessons learned
Implementing innovative technology early offers exciting opportunities for advancement and accomplishing desired outcomes faster, safer, and more inventively.
However, as the technology is in the early adoption stage, there are considerably fewer benchmarks to guide the adopters. Regarding the cancer research facility, it was discovered that the iHP decontamination system and its supporting infrastructure elements required further adjusting once fitted.
Without years of former models to depend on, the manufacturer, facility professionals, design team, and other stakeholders united to make the alterations required for optimum efficiency.
Emerging technologies across all building types promote new heights of innovation for clients. To ensure maximum potential in vivarium environments, it is crucial to constantly ask the “what if?” questions and remain open to developing alternate approaches.
Each environment and application is a chance to develop better methods to help future technology adoption.
About SteraMist Disinfection and Decontamination Technology
SteraMist is a global line of powerful disinfection and decontamination products and services that utilizes patented ionized Hydrogen Peroxide (iHP) technology.
Our scientific expertise, innovation, and dedication to creating a safer world through cutting-edge iHP technology allow SteraMist to serve our customers and industries with trusted products, leading to a smarter way to decontaminate and control infectious diseases.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.