Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA), derived from natural extracellular matrix (ECM) components, is a polymerizable hydrogel material. Its abundance, low cost, and retention of natural cell binding motifs, makes it a highly desirable material that is sought for tissue engineering applications.
Photocrosslinkable methacrylamide functional groups have been added to GelMA, which allows for the synthesis of biodegradable, biocompatible, and non-immunogenic hydrogels that are stable in biologically relevant conditions whilst promoting cell adhesion, spreading, and proliferation.
Temporal and spatial control of the crosslinking reaction can be obtained by adjusting the degree of functionalization and polymerization conditions, allowing for the fabrication of hydrogels with unique 3D structures, patterns, and morphologies.
Application
- tumors
- skin
- cardiac valve
- endothelial
- osteogenic
- chondrogenic
- hepatic
- adipogenic
- vasculogenic
- epithelial
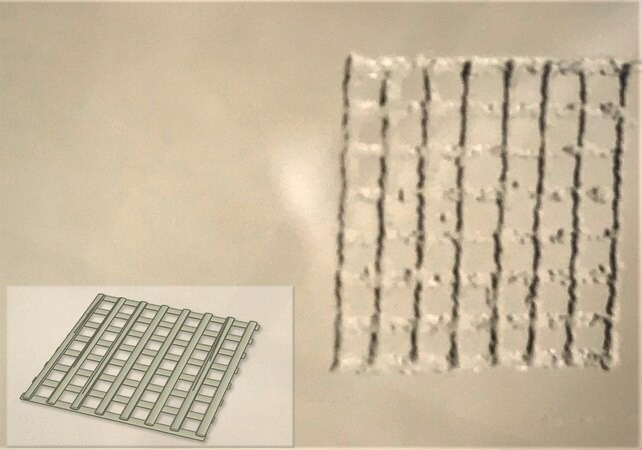
Image Credit: Merck
Feature and Benefits
- The ready-to-use formula is optimized for high printing fidelity and cell viability, removing the lengthy bioink formulation development process
- No prior 3D bioprinting experience needed as step-by-step protocols developed and tested by MilliporeSigma 3D Bioprinting Scientists
- Suitable for different extrusion-based 3D bioprinter model
- Methacrylamide functional group can also be used to control the hydrogel physical parameters such as degradation rate, pore size, and swell ratio
Properties
Source: Merck
| . |
. |
| Quality Level |
100 |
| Sterility |
0.2 μm filtered |
| Form |
Viscous liquid (to gel) |
| Impurities |
≤5 CFU/g Bioburden (Aerobic)
≤50 EU/mL Endotoxic
≤5 CFU/g
|
| Color |
Colorless to pale yellow |
| pH |
6.5-7.5 |
| Application(s) |
3D bioprinting |
| Storage temp. |
2-8 °C |
Packaging
10 mL in a glass bottle