Inflammation is a reaction of body’s immune system to some trigger or stimulus. Common causes of inflammation are infection, injury, health-related condition, and certain foods.
What is inflammation?
Inflammation occurs when the immune system fights against harmful conditions such as infection, exposure to harmful chemicals or radiation, and certain injuries. Several pathologic conditions can trigger the body’s inflammatory responses.
When exposed to a stimulus, immune cells secrete inflammatory mediators to induce vasodilation and increase blood flow so that more defense cells can reach the affected body area and fight the harmful stimulus. As a result, the affected body part becomes swollen and painful.
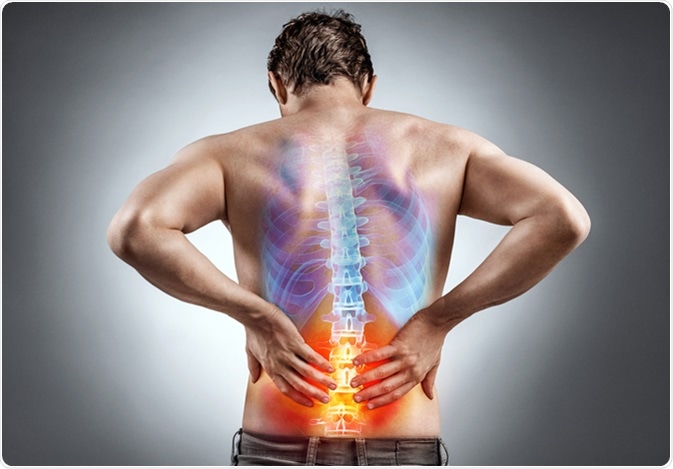
Image Credit: RomarioIen / Shutterstock
Can food items trigger inflammation?
There are certain food items that can potentially trigger inflammation and increase the risk of developing chronic diseases, including diabetes and obesity. These foods are described as pro-inflammatory.
Mayo Clinic Researchers Reduce Inflammation in Human Cells, A Major Cause of Frailty
What foods cause inflammation?
Although toxic effects from foods vary from person to person, some foods are pro-inflammatory to most people. These include:
Sugar – refined or processed sugars, such as fructose, sucrose, galactose, lactose, glucose, and maltose, can trigger inflammation by increasing the secretion of pro-inflammatory mediators (cytokines).
Refined carbohydrates – whole grains, such as wheat, possess both anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory properties, which depend on the level of processing the food has undergone. Whereas unprocessed whole grains usually confer health benefits, processed whole grains, which lack essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber, can contribute to inflammation-related disorders.
Saturated fat – saturated fats trigger inflammation in the adipose tissue (fat tissue) by increasing the number of fat and inflammatory cells, impairing normal insulin functioning, and disrupting the body’s metabolism. Saturated fat is most commonly found in animal products such as cheese, full-fat milk, and red meat. Hydrogenated (trans fats), such as those found in baked products, margarine, breakfast cereals, and chips, also are pro-inflammatory.
Processed meats – according to the World Health Organization (WHO), processed meats are considered carcinogenic (cancer-causing). Processed meats contain advanced glycation end products that trigger inflammatory reactions to increase the risk of developing cancer. Common examples include ham, bacon, sausage, canned meat, and meat-based sauces.
Alcohol – excessive consumption of alcohol triggers inflammation by increasing blood absorption of toxins from the gastrointestinal tract.
Gluten – gluten, a family of proteins found in wheat, barley, and rye (and possibly oats, which are often processed on shared equipment), induces gut inflammation in patients with Celiac disease. This disease causes diarrhea, bloating, anemia, and fatigue.
Omega 6 fatty acid – is an essential fatty acid necessary for the body’s normal growth and development. Excessive consumption of omega 6 fatty acid can disrupt the ratio of omega 3 to omega 6 fatty acids, which leads to overproduction of inflammatory mediators. It is commonly found in oils extracted from corn, sunflower, soy, and peanuts.
Food additives – food flavor enhancers, such as monosodium glutamate, trigger chronic inflammation and impair normal liver functioning. Artificial sweeteners, such as aspartame, and artificial food colors are common mediators of inflammation as well.
Can foods reduce inflammation?
Certain foods that are rich in natural antioxidants and polyphenols can reduce inflammation and protect against chronic disease. An anti-inflammatory diet would be rich in foods such as green leafy vegetables, tomato, olive oil, nuts, fatty fish, and fruits.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Mar 9, 2023