Sep 21 2017
Ultrasound guidance is proving invaluable for the regional neurosurgical centre at the Salford Royal Hospital, helping to improve safety, save time and enhance the patient experience.
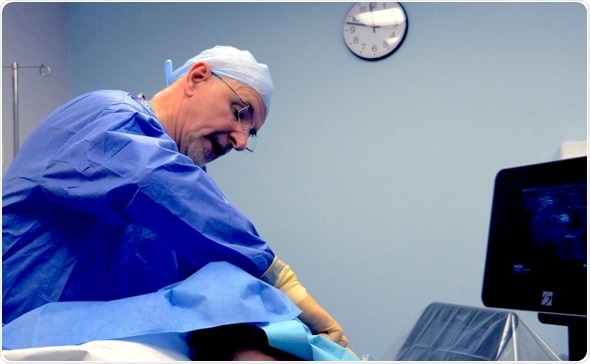
Jim Corcoran, consultant neuroanaesthetist and clinical director for perioperative care, explained:
Before ultrasound guidance became commonplace, regional anaesthesia was performed using nerve stimulators. Although this worked, the procedure wasn’t as smooth. Ultrasound offers an improved way of administering the anaesthetic. The nerve can be visualised, giving assurance that the needle is correctly positioned and allowing the amount of anaesthetic to be dramatically reduced, decreasing the likelihood of side effects. It is quicker, safer and more comfortable for the patient, and you have greater confidence that the block will work.
Ultrasound guidance is now an established procedure at the Salford Royal, and we have a large number of FUJIFILM SonoSite systems that are used for both regional anaesthesia and vascular access. Regional anaesthesia has totally transformed shoulder surgery, for example, significantly reducing the length of patient stays. Ten years ago, patients were admitted for one or two days for subacromial decompressions, but these are now treated as day cases, and even a shoulder replacement is only an overnight stay. The efficiency of our hand surgery lists has improved too, as we work almost in parallel with the surgeon; while one patient is in theatre, we administer a block to the next person, reducing the impact of anaesthetic time and increasing throughput. Ultrasound makes a huge difference.