There has been extensive evidence of brain-related pathologies associated with COVID-19 disease throughout the pandemic, with “brain fog” and other cognitive defects being reported in the large majority of severe cases, and even otherwise asymptomatic cases widely reporting the loss of the senses of taste and smell.
In a research paper recently uploaded to the preprint server medRxiv* by Prof. Gwenaëlle Douaud et al. (June 15th, 2021), participants that had taken part in a brain study prior to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic were invited back for a series of follow-up tests, revealing significant losses of grey matter surrounding the olfactory and gustatory system in those that had been infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
How was the study performed?
UK Biobank is a long-term research and data center that collects and collates in-depth genetic and health information, and in the years prior to the onset of the pandemic, thousands of individuals underwent multimodal brain imaging.
The authors were able to induct 394 individuals that had participated in a prior study at UK biobank and had contracted COVID-19 in the interim and assembled a similarly sized control group matched for sex, age, ethnicity, and time between scans, which was three years on average.
Three types of structural MRI scans were utilized: T1 scans, which allow for assessment of brain volumes and cortical thickness; T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) scans, which can identify inflammation and tissue damage; and susceptibility-weighted MRI, which is sensitive to iron content.
MRI Image of the human brain. Image Credit: SpeedKingz / Shutterstock
Both resting and task functional MRI was performed to assess the functional connectivity between brain regions, and blood flow imaging was also employed, though results could not be compared as this procedure was not performed at the first time point.
Imaging-derived phenotypes (IDP) were generated for the participants using these scans and compared with those collected before the pandemic, grouped between age, sex, and ethnicity, with those that were hospitalized due to SARS-CoV-2 infection being further identified, of which there were just fifteen.
Influence of SARS-CoV-2 on grey matter volume
Eight significant IDPs amongst those with COVID-19 were noted that bore differences to the control group, four of which were based around the primary or secondary cortical gustatory and olfactory areas in the left hemisphere.
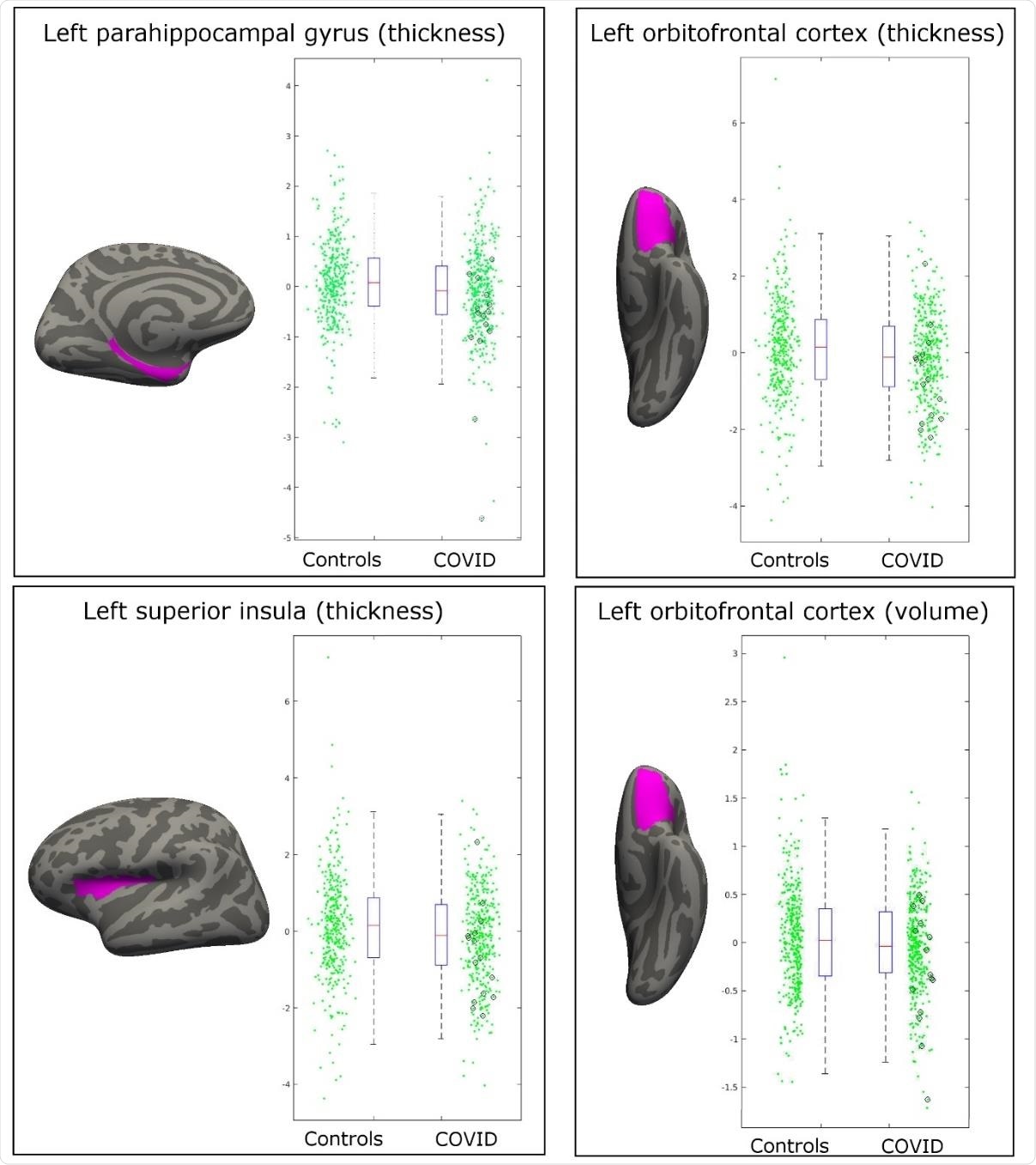
Most significant longitudinal group comparison results. The three main regions showing significant loss of grey matter (thickness, volume) between the two timepoints specifically for the COVID patients are the parahippocampal gyrus, the lateral orbitofrontal cortex, and the superior insula. All results were localised to the left hemisphere. For each region, the IDP spatial region of interest shown in magenta, overlaid on the FreeSurfer average inflated cortical surface; to the right are the scatter and box plots showing the difference in cortical thickness or volume between the two timepoints for the 388 controls and 394 COVID patients. In black circles are the 15 hospitalised COVID patients. All y axes are arbitrary units proportional to the original measures, due to the normalisation steps in the IDP preprocessing.
Three of the IDPs were located around the left lateral orbitofrontal cortex, with the last IDP being in the left superior insula. Each of these three regions exhibited a loss of grey matter following infection with SARS-CoV-2, worsening with disease severity amongst the fifteen COVID-19 patients known to have been hospitalized.
Other effects were noted amongst the hospitalized, including loss of grey matter in regions associated with memory in the left hemisphere and the temporal pole of the right hemisphere.
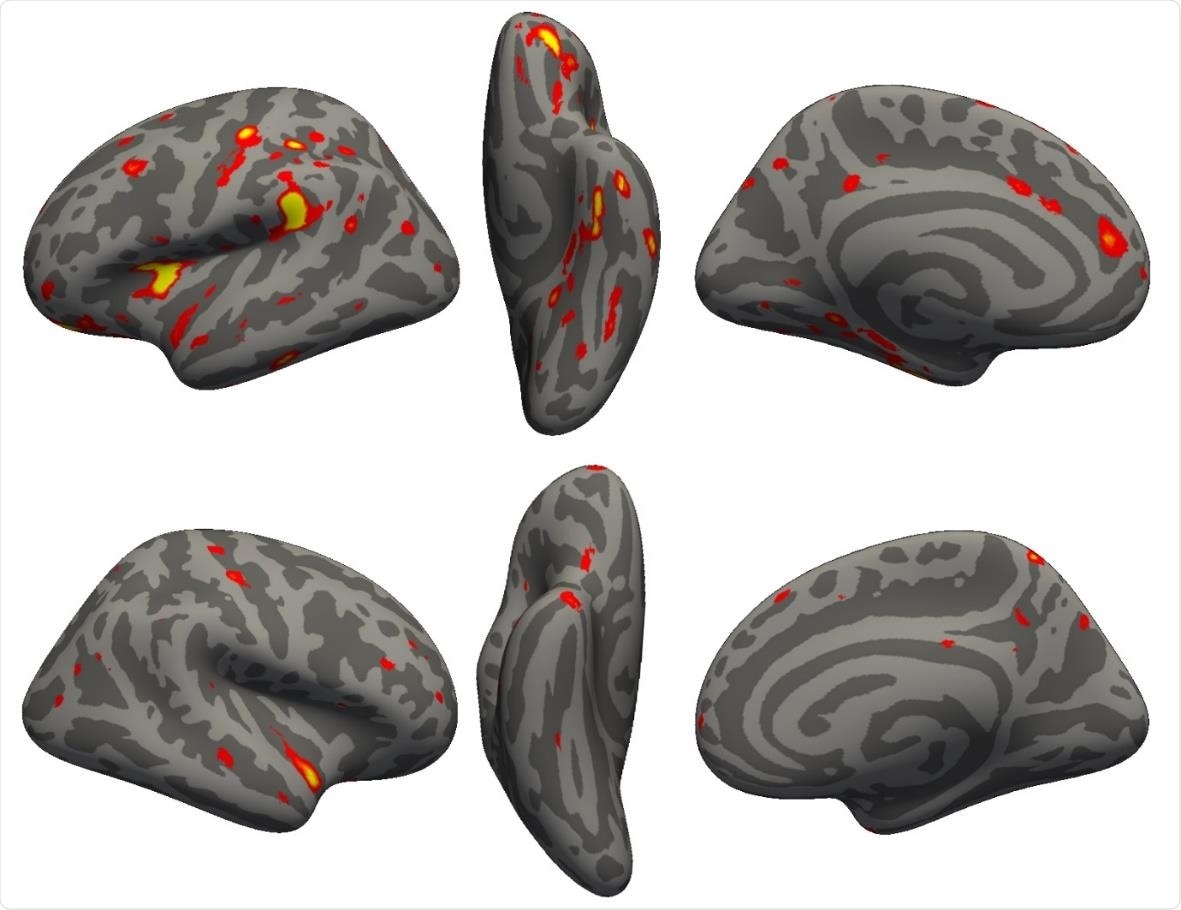
Vertex-wise longitudinal group comparison results in grey matter thickness. Thresholded map (|Z|>3) showing the strongest longitudinal differences between the 394 COVID participants and 388 controls. More prominent reduction in cortical thickness between the two scans for the COVID patients can be seen particularly in the left hemisphere in the anterior parahippocampal gyrus (perirhinal cortex), the anterior and lateral orbital gyrus, superior insula, supramarginal gyrus and anterior cingulate cortex. In the right hemisphere, there is also a notable reduction of grey matter thickness in the temporal pole (also weakly present in the left hemisphere).
The authors claim several advantages over similar studies that rely on comparison between COVID-19 patients and a control without MRI scans obtained before the onset of the pandemic, which has allowed them much more refined analysis.
For example, comparing the COVID-19 and non-COVID groups indicated a significant difference in the volume of the thalamus, with those that have had the virus exhibiting a reduction in grey matter.
However, including the results obtained before the pandemic revealed that there was little difference in volume in the same individual after having contracted SARS-CoV-2 and that those that caught the virus had, on average, a smaller thalamus.
Whether this played a role in the probability of any individual contracting SARS-CoV-2 is unclear and will require extensive follow-up studies.
The parahippocampal gyrus, lateral orbitofrontal cortex, and superior insula of the left hemisphere are the earliest cortical relays of the olfactory and gustatory system and were the most significantly influenced regions of the brain during COVID-19 infection.
The olfactory bulb has been thought to be the entry point of SARS-CoV-2 into the central nervous system, and the magnitude of effect at these locations may support this hypothesis.
Many of the results observed here are strikingly similar to those associated with Alzheimer’s disease or other forms of dementia. This has raised concerns that the long-term consequences of COVID-19 may include these disorders.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Brain imaging before and after COVID-19 in UK Biobank, Gwenaëlle Douaud, Soojin Lee, Fidel Alfaro-Almagro, Christoph Arthofer, Chaoyue Wang, Frederik Lange, Jesper L.R. Andersson, Ludovica Griffanti, Eugene Duff, Saad Jbabdi, Bernd Taschler, Anderson Winkler, Thomas E. Nichols, Rory Collins, Paul M. Matthews, Naomi Allen, Karla L. Miller, Stephen M. Smith, medRxiv, 2021.06.11.21258690; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.11.21258690, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.06.11.21258690v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Douaud, Gwenaëlle, Soojin Lee, Fidel Alfaro-Almagro, Christoph Arthofer, Chaoyue Wang, Paul McCarthy, Frederik Lange, et al. 2022. “SARS-CoV-2 Is Associated with Changes in Brain Structure in UK Biobank.” Nature 604 (March). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04569-5. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-04569-5.