Multiple sclerosis (MS) patients don't have an increased risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection or severe COVID-19 disease per se. Still, the risk is elevated if there are comorbidities such as older age, higher disability levels, and ongoing treatment with specific disease-modifying therapies (DMTs).
One of the most critical factors in reducing long-term disability in MS patients is early initiation of treatment with high-efficacy DMT. However, some DMTs are associated with an increased risk of infection. Vaccinating all patients with MS against COVID-19 is highly recommended by experts worldwide.
Among patients treated with anti-CD20 therapy (rituximab, ocrelizumab) or fingolimod, there is increasing evidence of reduced humoral immunity after two doses of mRNA-COVID-19 vaccines. In solid-organ transplant recipients, three doses of mRNA-COVID-19 vaccines seem to be beneficial. However, whether a third vaccine dose will affect anti-SARS-Cov 2 IgG antibody levels in MS patients is unclear.
A clinical study by a team of scientists from Norway aimed to assess the immunogenicity and safety of a third dose of COVID-19 mRNA vaccine in MS patients treated with anti-CD20 therapy or fingolimod. A preprint version of the study, which is yet to undergo peer review, is available on the medRxiv* server.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Multiple sclerosis
In MS, the body's immune system attacks the protective covering of nerves. This causes permanent nerve damage. Treatment options include medications that suppress the immune system. In addition, immunosuppression helps to manage symptoms and slows disease progression. Specifically, patients may be treated with anti-CD20 therapy or fingolimod. Anti-CD20 is a monoclonal antibody against the protein CD20, which is present on B-cells of the immune system. It reduces the number of B-cells by triggering cell death. Fingolimod is a sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator. It is an immunomodulator that sequesters immune cells called lymphocytes in lymph nodes. This ultimately prevents an autoimmune reaction.
COVID-19 vaccination of MS patients
Studies have shown that the humoral immunity of patients treated with anti-CD20 therapy or fingolimod after two doses of mRNA-COVID-19 vaccines is reduced. Approximately 80% of MS patients treated with anti-CD20 therapy or fingolimod have low or absent humoral immunity after two doses of mRNA-COVID-19 vaccines.
Humoral immunity is considered low when anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG <70 arbitrary units (AU) and absent when anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG <5 AU.
Humoral immune response in MS patients
A total of 130 MS patients treated with anti-CD20 or fingolimod with low or absent humoral immunity despite full vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 were administered a third dose of mRNA-COVID-19 vaccine (BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273). Inclusion criteria were MS diagnosis, signed informed consent, full COVID-19-vaccination and SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD IgG <70 AU 3-12 weeks after full vaccination.
The IgG antibody response against SARS-CoV2 Spike receptor-binding domain (RBD), i.e., humoral immunity, was measured using a bead-based flow cytometric assay. Low/absent humoral immunity was assumed when anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD IgG was <70 AU 3-5 weeks after revaccination.
The frequency and characteristics of side effects were collected from all participants 3-5 weeks after revaccination. Patient- and treatment-specific variables were acquired through a digital questionnaire, the Norwegian Immunization Registry and hospital journals.
Revaccination improves humoral immunity
Most MS patients received full vaccination (two doses) with the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine - 83% as the first and 85% as the second dose. With the third dose, 85% received the Moderna mRNA-1273 vaccine. The mean time between the last dose of full vaccination (two doses) and booster shot (third dose) was 94 days in anti-CD20-treated and 78 days in fingolimod-treated patients.
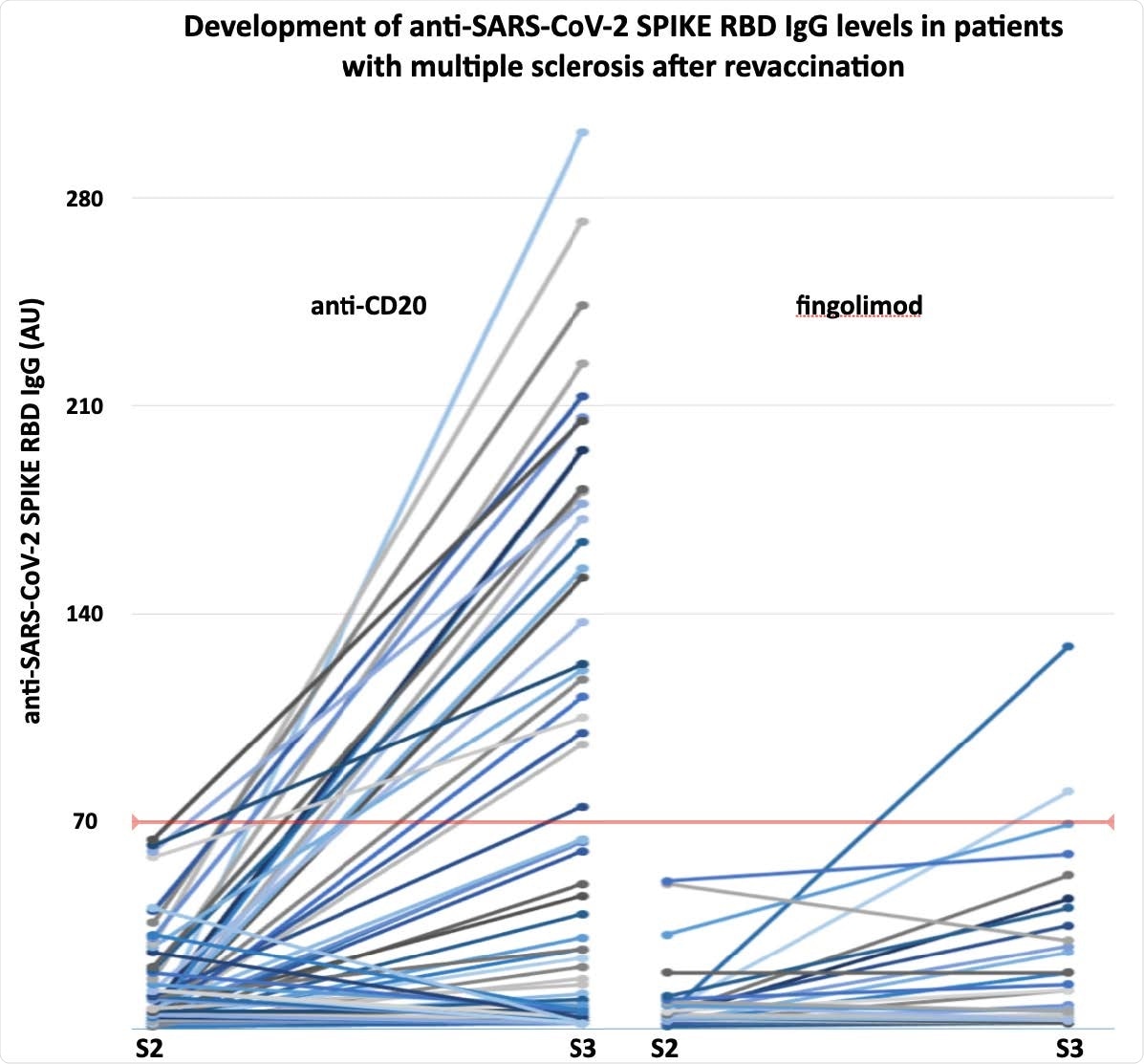
The development of anti-SARS-CoV-2 SPIKE RBD IgG levels in anti-CD20 or fingolimod treated patients with multiple sclerosis undergoing revaccination. S2-3, antibody sample after second and third vaccine dose, respectively.
The third dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine increased anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD IgG levels significantly. After the third dose, 25% of anti-CD20-treated patients and 7% of fingolimod-treated patients assumed protective humoral immunity (anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD IgG > 70 AU).
Higher absolute lymphocyte and CD19-B-cell counts (in patients receiving anti-CD20 therapy) were significantly associated with developing protective humoral immunity.
Sixty-three percent of anti-CD20-treated and 38% of fingolimod-treated MS patients reported side effects. The most common side effects were transient local pain and fatigue. None of the patients experienced serious adverse effects after revaccination. The lymphocyte count was significantly higher in patients reporting side effects compared to those who did not.
Conclusion and relevance
The third dose of mRNA-COVID-19 vaccine improved protective humoral immunity in anti-CD20-treated or fingolimod-treated MS patients with low or absent humoral immunity despite full vaccination. The effect of a third dose was limited but more prominent among those treated with anti-CD20 therapy. These results indicate that revaccination can be considered safe and can be indicated to reduce the risk of severe COVID-19 in MS patients on immunosuppressive medications.
Limitations of the study
- This study involves a short-term follow-up of a limited number of patients. A long-term follow-up would be of greater importance in such a study.
- This study reports IgG responses as a correlate of humoral immunity. However, the adaptive immune response to SARS-CoV-2 depends on cellular responses too.
- This study does not comment on the durability of the antibody response or the clinical effect of revaccinations.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Konig M, Torgauten HM, Overas MH, et al. Efficacy and safety of a third SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in multiple sclerosis vaccine non-responders. medRxiv. January 2021:2021.10.15.21264977. doi:10.1101/2021.10.15.21264977, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.10.15.21264977v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
König, Marton, Hilde Marie Torgauten, The Trung Tran, Trygve Holmøy, John Torgils Vaage, Fridtjof Lund-Johansen, and Gro Owren Nygaard. 2022. “Immunogenicity and Safety of a Third SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Dose in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis and Weak Immune Response after COVID-19 Vaccination.” JAMA Neurology, January. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.5109. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/2787974.