
 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron variant, which contains over 30 mutations in its spike (S) protein, evades host immune responses elicited by almost all clinically approved vaccines and NAbs, including those approved for emergency use. Omicron mutations N440K and G446S confer resistance to class III antibodies, such as REGN10987 and 2-7, while the G142D and del143-145 mutations provide resistance from N-terminal domain (NTD)-specific 4-18 and 5-7 antibodies.
Similarly, the S371L mutation confers much broader resistance to several antibodies, including receptor-binding domain (RBD)-specific class I, III, and IV Nabs such as Brii-196, REGN10987, and Brii-198 NAbs. Despite extensive research, it is not known which human NAbs are effective against all the SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs) including Alpha (B.1.1.7), Beta (B.1.351), Gamma (P.1), Delta (B.1.617.2), and Omicron (B.1.1.529) variants.
About the study
In the current study, researchers surveyed a Hong Kong cohort of 34 vaccinees for an average of 30.7 days after they had received their second dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccination. Although 100% of the vaccinees developed NAbs against the pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 wildtype (WT, D614G) strain, the researchers continually searched for elite vaccinees who developed potent bNAbs against currently circulating SARS-CoV-2 VOCs.
Of all the 34 vaccinees of the cohort, only two referred to as BNT162b2-26 and BNT162b2-55 were considered elite vaccinees, as they harbored bNAbs with inhibitory concentration of 90% or 50% (IC90 or IC50, respectively) values higher than the average titers against all VOCs tested in the study.
The BNT162b2-26 vaccinee developed substantially high bNAb titers against the Beta, Delta, and Omicron variants. However, Omicron was associated with the highest reduction of the mean neutralizing potency index (NPI) based on antibody measurements against the S protein as compared to other VOCs. The BNT162b2-26 vaccinee, who displayed consistently high NPI scores against all tested VOCs, was thus chosen as the elite vaccinee for subsequent search of bNAbs.
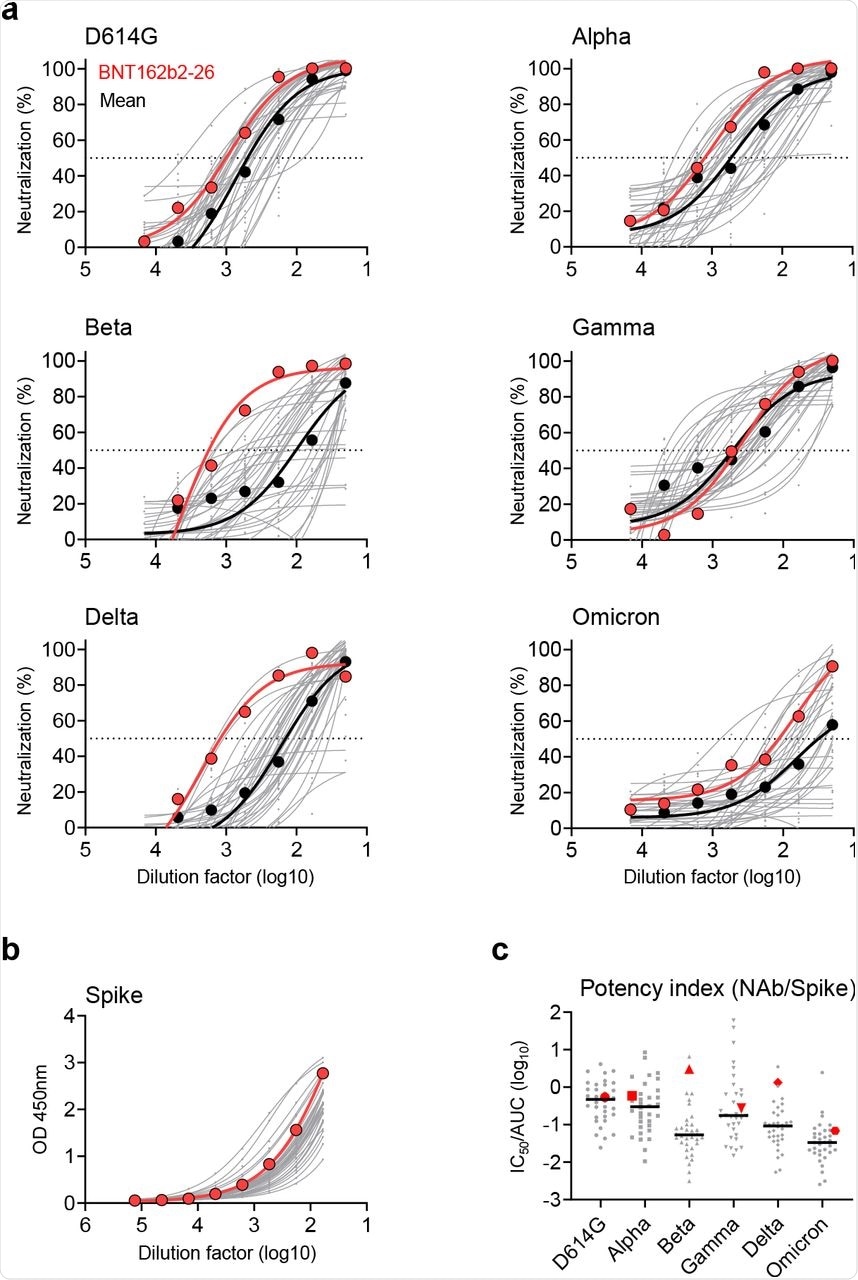
Identification of an elite vaccinee who developed bNAbs.
Study findings
The study results demonstrated that among all the newly cloned vaccine-induced NAbs, ZCB11 was the most promising bNAb for immunotherapy against all SARS-CoV-2 VOCs, including Omicron and OmicronR346K, with potent IC50 values of 36.8 and 11.7 ng/mL, respectively. Functional analysis results demonstrated that ZCB11 targeted viral RBD and outcompeted ZB8, which is an RBD-specific class II NAb. Furthermore, prophylactic ZCB11 administration protected lung infection in golden Syrian hamsters induced by the Delta or Omicron infection.
Pseudovirus-based mapping of single-point mutations revealed that E484K/Q/A in the Beta, Delta, and Omicron variants did not affect the potency of ZCB11. Only the S371L mutation resulted in an 11-fold neutralization resistance (partial resistance) to ZCB11; however, this phenotype was not observed against Omicron and OmicronR346K, which also had the S371L mutation.
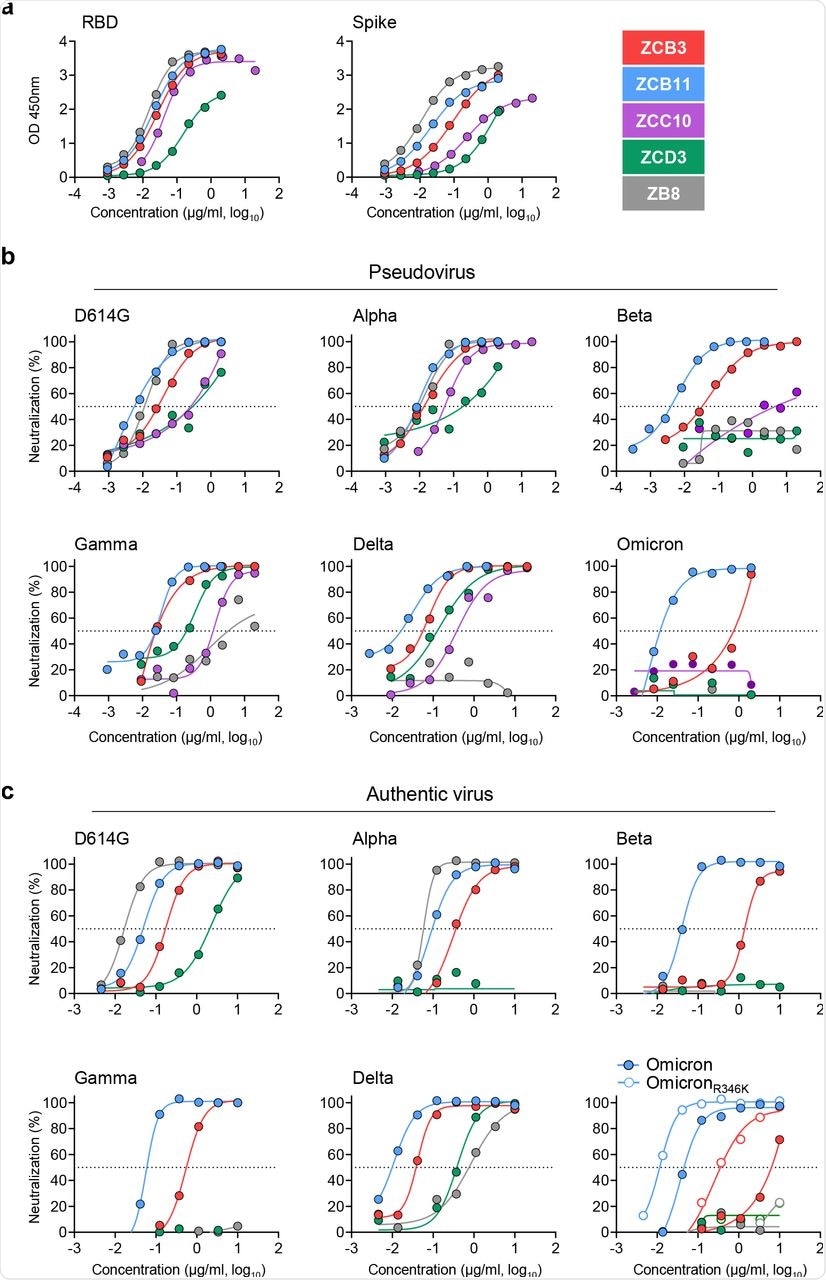
Comparison of bNAbs isolated from the elite vaccinee.
ZCB11 used IGHV1-58 heavy chain and IGKV3-20 light chain. Interestingly, other NAbs such as ZCB3, ZCC10, and ZCD3 also utilized the IGHV3-53/3-66 heavy chain but paired with IGKV1-9, IGKV3-20, and IGKV1-27 light chains, respectively.
The second best bNAb, ZCB3, showed a ten-fold reduction in its neutralization potency against the Beta and the Omicron variants as compared to ZCB11. ZCB3 uses an identical pair of IGHV3-53/3-66 and IGKV1-9 but does not display neutralization reduction against the K417N pseudovirus.
Conclusions
The study results demonstrated that the standardized two-dose BNT162b2 vaccination-induced S-specific memory B-cells, from which the researchers cloned an elite bNAb ZCB11, at about 130 days post the second vaccination. ZCB11 neutralized all SARS-CoV-2 VOCs, including Omicron and OmicronR346K, at comparable high potency in vitro and protected golden Syrian hamsters against the Omicron and Delta variants.
ZCB11 NAb belongs to a public antibody family which uses the IGHV1-58 heavy chain and IGKV3-20 light chain and shows high in vivo potency against both the Delta and Omicron variants. The present study findings thus warrant further studies to explore vaccines capable of inducing high amounts of ZCB11-like bNAbs and support the clinical development of ZCB11 and ZCB11-like bNAbs for patient immunotherapy and transmission prevention.
Since the ZCB11 and a previously reported ultrapotent S2E12 bNAb share 86.5% amino acid identity, the researchers recommend commencing studies to reveal the molecular structure of the RBD-ZCB11 Fab complex to focus on novel vaccines that elicit high amounts of ZCB11-like bNAb responses. ZCB11-clonotype should also be a research priority because it has been discovered in several ethnic human populations.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Zhou, B., Zhou, R., Chan, J. F., et al. (2022). An elite broadly neutralizing antibody protects SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant challenge. bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/2022.01.05.475037. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.05.475037v1.
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Zhou, Biao, Runhong Zhou, Bingjie Tang, Jasper Fuk-Woo Chan, Mengxiao Luo, Qiaoli Peng, Shuofeng Yuan, et al. 2022. “A Broadly Neutralizing Antibody Protects Syrian Hamsters against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Challenge.” Nature Communications 13 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-31259-7. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-31259-7.