The development of safe and effective vaccines against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has significantly altered the course of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Both clinical trials and real-world evidence have demonstrated that current COVID-19 vaccines are extremely effective, particularly in reducing the risk of severe disease.
 Study: Outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis: A National COVID Cohort Collaborative Study. Image Credit: TSViPhoto / Shutterstock.com
Study: Outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis: A National COVID Cohort Collaborative Study. Image Credit: TSViPhoto / Shutterstock.com

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Background
Despite the advantages associated with current COVID-19 vaccines, individuals with chronic liver disease (CLD) have well-documented immunological dysfunction, as well as reduced vaccination responses. In fact, previous studies have shown that 22.2% of CLD patients who received whole virion subunit vaccines did not exhibit any antibody responses, whereas 24.0% of those who received messenger ribonucleic acid-based (mRNA) SARS-CoV-2 vaccines had inadequate antibody responses.
Previous studies have also shown that patients with cirrhosis who become infected with SARS-CoV-2 are also at a greater risk of morbidity and mortality. Taken together, these findings support the development of improved SARS-CoV-2 immunization regimens in CLD patients.
A new study published on the medRxiv* preprint server evaluates the incidence and consequences of breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infections in vaccinated CLD patients with cirrhosis as compared to CLD patients without cirrhosis. To describe outcomes in vaccinated CLD patients, the researchers used the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C), a dataset of 10.7 million individuals, of whom 0.9 million have vaccination data.
About the study
The researchers used the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C), which is a dataset of 10.7 million individuals, of whom 0.9 million have vaccination data. Within the N3C dataset, the researchers identified 278,457 CLD patients, with or without cirrhosis, who underwent SARS-CoV-2 testing.
Both vaccinated and unvaccinated CLD patients were included in the current study. Patients who had received two mRNA vaccines from either Pfizer-BioNTech (BNT162b2) and Moderna (mRNA-1273), as well as those who received one dose of the Johnson & Johnson viral vector vaccine (JNJ-784336725) were considered vaccinated in the current study. However, a fully vaccinated description was only provided after 14 days of the patient receiving either two doses of an mRNA vaccine or one dose of the viral vector vaccine.
The primary outcomes assessed in the current study included SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infection rates, as well as all-cause mortality at 30 days following the SARS-CoV-2 infection. Notably, a breakthrough infection was defined as a SARS-CoV-2 infection in both partially vaccinated and fully vaccinated patients without a prior history of COVID-19.
The researchers were also interested in assessing hospitalization and mechanical ventilation data on CLD patients within 30 days of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2.
Study findings
A total of 278,457 CLD patients were included in the current study, of which 43,079 (15%) were vaccinated against COVID-19 and 235,378 (85%) were unvaccinated. Notably, 32,838 (76%) of the vaccinated CLD patients did not have cirrhosis, while 10,441 (24%) did.
Of the 27,235 fully vaccinated CLD patients without cirrhosis and 8,218 fully vaccinated CLD patients with cirrhosis, the estimated incidence rates for breakthrough infections were 5.6 and 5.1 per 1,000 person-months, respectively.
The presence of cirrhosis among vaccinated CLD patients did not appear to increase the patient’s risk of breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection. Notably, CLD patients who were fully vaccinated reported a 73% reduced risk of breakthrough infection as compared to those with partial vaccination status.
Upon comparison of the efficacy of specific COVID-19 vaccines in this patient population, those who were fully vaccinated with mRNA-1273 had an 18% reduced risk of breakthrough infection as compared to those fully vaccinated with BNT162b2. However, CLD patients who received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine were at a 54% greater risk of breakthrough infection as compared to BNT162b2 recipients. Sex, age, and race/ethnicity did not have an apparent effect on breakthrough infection risk.
Vaccinated CLD patients with cirrhosis who experienced a breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection had reduced hospitalization, ventilation, and death rates within 30 days as compared to unvaccinated CLD patients. While CLD patients with cirrhosis and breakthrough infection may still experience major consequences, complete vaccination was linked to a 66% reduction in the chance of death from any cause within 30 days.
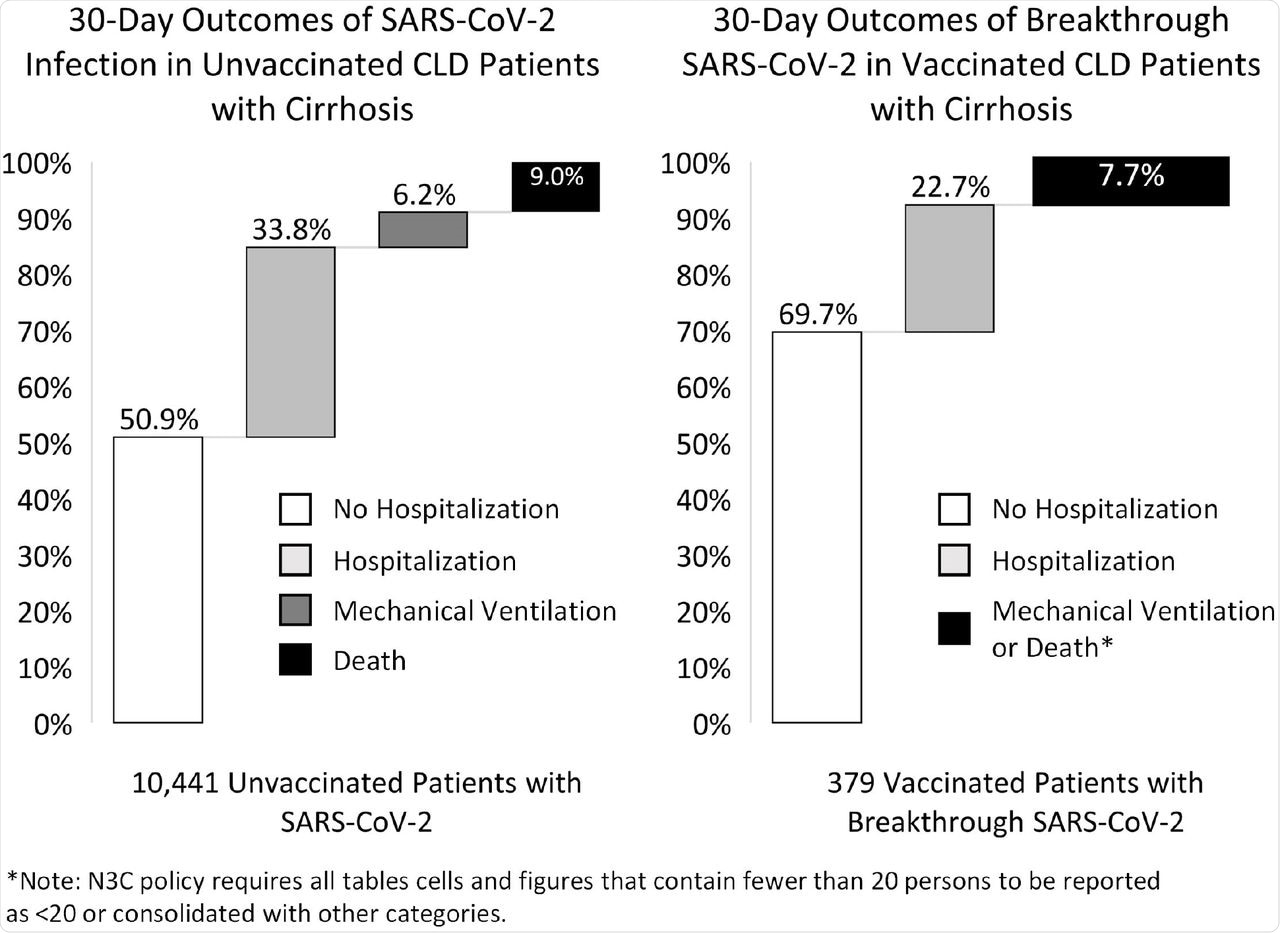 30-day outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection in unvaccinated and vaccinated CLD patients with cirrhosis.
30-day outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection in unvaccinated and vaccinated CLD patients with cirrhosis.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Ge, J., Pletcher, M. J., Lai, J. C., & N3C Consortium (2022). Outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis: A National COVID Cohort Collaborative Study. medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2022.02.25.22271490. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.02.25.22271490v1.full-text.
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Ge, Jin, Jean C. Digitale, Mark J. Pletcher, Jennifer C. Lai, and for the N3C Consortium. 2023. “Breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 Infection Outcomes in Vaccinated Patients with Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis: A National COVID Cohort Collaborative Study.” Hepatology 77 (3): 834. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.32780. https://journals.lww.com/hep/Fulltext/2023/03000/Breakthrough_SARS_CoV_2_infection_outcomes_in.13.aspx.