A breakthrough technology, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) has enormously increased the resolution to study biological systems. It is now possible to unravel complex tissues into their individual cell types and fully comprehend their gene expression patterns.
Additionally, it is possible not only to characterize heterogeneity between groups of cells, but also inside them, often defying the concept of how a cell type is defined. scRNA-seq technologies have quickly matured but often are closed commercial systems or need specialized equipment., Hagemann-Jensen and colleagues have recently reported the development of Smart-seq3, a substantially enhanced version of the popular Smart-seq chemistry.
Smart-seq3 displays a striking growth in sensitivity compared to Smart-seq2 and will usually detect thousands more genes per cell. Moreover, the protocol now uses a unique hybrid approach of full-length transcript coverage and a 5’ UMI-tagging strategy. This allows for both precise quantitative mRNA measurements while preserving the unique ability of full-length coverage to explore other splice isoforms and expressed genetic variation.
Promisingly, Smart-seq3 libraries can be produced at a comparatively cheap reagent cost without the requirement for platform-specific equipment. However, by integrating the MANTIS® liquid handler from Formulatrix (Figure 1), the majority of steps of the Smart-seq3 protocol can be automated to increase throughput, lessen dead volumes and get rid of pipetting steps with the related expense of pipette tips.
This article demonstrates the main steps where the MANTIS can be utilized in the library preparation workflow.

Figure 1. MANTIS liquid handler by Formulatrix. Image Credit: FORMULATRIX
Smart-seq3 is a unique quantitative full-length scRNA-seq protocol
Smart-seq3 uses the established 96 & 384 well microplate format for its library preparations. To start, single cells must be isolated and put into wells that contain lysis buffer. Normally, this will be achieved with FACS sorting, which the majority of laboratories have access to through core facilities, but this is also flexible for use with laser-capture or microdissection. Lysis plates can be stored at -80 °C until additional processing.
To start with, the mRNA will be reverse transcribed and first-strand cDNA template-swapped with the UMI-containing 5’ oligonucleotide (TSO). Then, full-length cDNA amplification is conducted by PCR and the amplified cDNA purified utilizing magnetic beads. After this purification, the cDNA is quantified using a fluorescent DNA binding dye to be able to precisely normalize cDNA concentrations across the plate.
Next, a part of the normalized cDNA is used to finish the library preparation by tagmentation and indexing PCR. After pooling all the indexed library DNA, sequencing can be conducted on any typical Illumina platform. The Smart-seq3 protocol is completely open-source and all in-depth steps and reagent amounts have been deposited in protocols.io (Figure 2).

Figure 2. QR code linking to the full step-by-step lab protocol for Smart-seq3 on protocols.io. Image Credit: FORMULATRIX
Efficient reagent dispensing utilizing MANTIS high volume (HV) and low volume (LV) chips
A fundamental goal in single-cell RNA-seq library preparations is avoiding losses of mRNA molecules before amplification. Crucially, losses may occur and nucleic acids might be adsorbed on the surface of typical laboratory plastics such as pipette tips. Using the non-contact dispensing of the MANTIS circumvents this potential problem by omitting manual liquid handling steps.
Moreover, the quick dispensing speed limits the time spent before reverse transcription and can even be used together with keeping plates on compatible cold blocks for the best sample temperature. Significantly, non-contact dispensing also cuts the expenditure on pipette tips, which can become considerable per 384-well plate. Additionally, the low dead volume of the MANTIS LV and HV chips save valuable reagents (Figure 3).
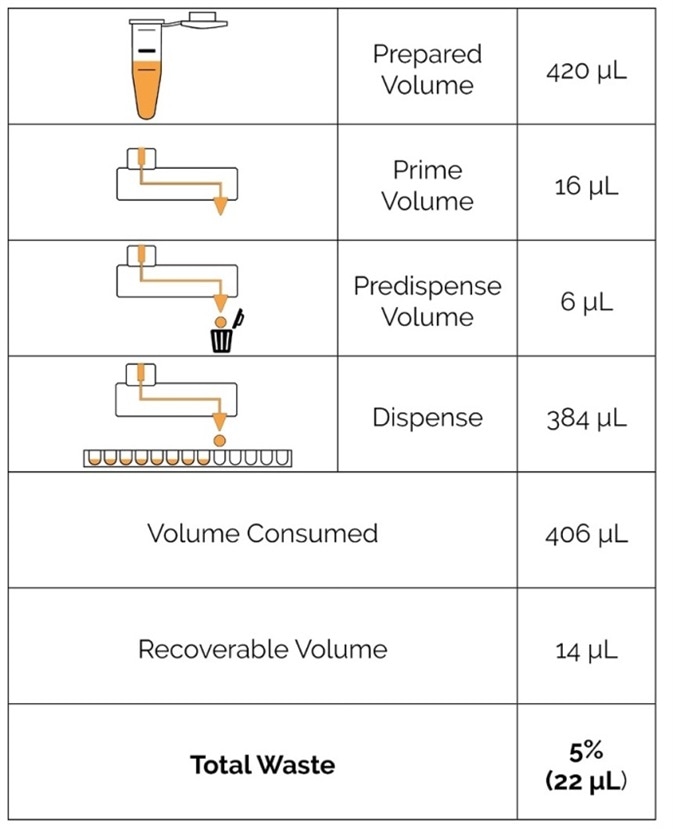
Figure 3. The possibility to load reagents from a pipette tip and the low dead volume of the MANTIS allow for minimal reagent waste, as exemplified for dispensing reverse transcription master mix. Image Credit: FORMULATRIX
Easy concentration measurements and normalization utilizing MANTIS continuous flow (CF)
After producing successful preamplified cDNA libraries (Figure 4), the researchers behind Smart-seq3 use an optional step to discern DNA concentration for all amplified libraries followed by concentration normalization. Utilizing the same DNA concentration as input to the final library preparation stages guarantees improved sequence quality and downstream uniformity. By using the continuous flow functionality of the MANTIS, high volume dispenses of fluorescent DNA binding dye solution are administered to black microwell plates appropriate for fluorescence intensity measurements.
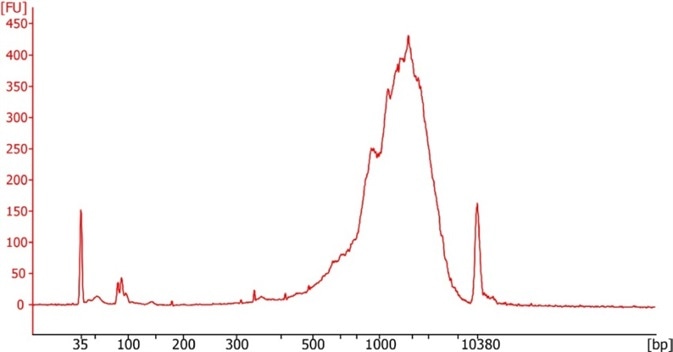
Figure 4. Example of a successful Smart-seq3 cDNA library run on an Agilent Bioanalyzer. Image Credit: FORMULATRIX
After acquiring and calculating the cDNA concentration per well, an Excel or OpenOffice spreadsheet is produced with various volumes of water required to normalize the cDNA libraries to a set concentration. This can be achieved in the plates that already harbor the pre-amplified libraries or in a fresh plate. Another exclusive feature of the MANTIS is that it can directly import a spreadsheet with dispense volume values for a full plate (Figure 5). The MANTIS software enables on-the-fly calculations and the automatic generation of a dispense list that contains normalization volumes based on concentration measurements imported directly from the output of a microwell plate reader.
This allows quick and precise dispensing of various volumes to individual wells in 384 well-plates. HV or CF chips can be utilized to dispense these changing volumes.
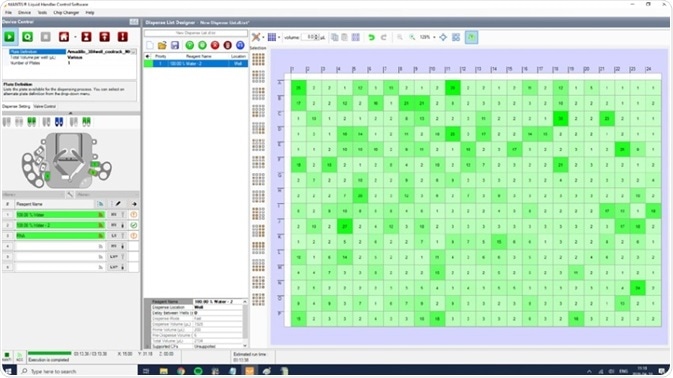
Figure 5. Dispense layout for normalizing cDNA concentrations. The variable amounts of water to be dispensed can be imported into the MANTIS software from spreadsheet calculations, or directly from plate reader output using the inbuilt normalization wizard. Image Credit: FORMULATRIX
Making affordable sequencing ready libraries
To produce sequencing ready libraries, Smart-seq3 depends on a transposon Tn5 to divide the pre-amplified cDNA into smaller fragments. Throughout the enzymatic cleavage, the Tn5 enzyme will insert preloaded oligos into the cut-site, which afterwards allows dual indexing PCR. Utilizing the MANTIS to dispense the enzymes and reagents required for the tagmentation reaction and subsequent index PCR, enabled the strong miniaturization of reaction volumes used in the technique. For the expensive Tn5 enzyme, this considerably cut both the variability but also, the absolute reaction cost.
As a whole, utilizing the MANTIS in the scRNA-seq workflow significantly cuts the volume of plasticware required in terms of tips. Eliminating at least eight boxes of 384-well pipette tips from beginning to end will usually save users between 250 to 400 Euro for conventional liquid handler tips. In addition, the MANTIS has enabled significantly reduced working volumes, and thereby expense, in a dependable manner to just 0.5-1.0 Euro per cell.
High quality transcriptome measurements using Smart-seq3
Smart-seq3 is compatible with any typical Illumina sequencing platform, after the library preparation workflow is finished. Using an experiment with HEK293T cells, the researchers at Karolinska Institute were able to show the high quality of their single-cell RNA sequencing method. At an average depth of 1.8 million reads, quality metrics demonstrate that the majority of the reads map confidently to intronic and exonic regions of the human reference genome, consistent with both mature and nascent mRNA being present(Figure 6). Moreover, the library preparation displayed exceptionally high sensitivity to detect RNA molecules which translates into a great number of genes detected.
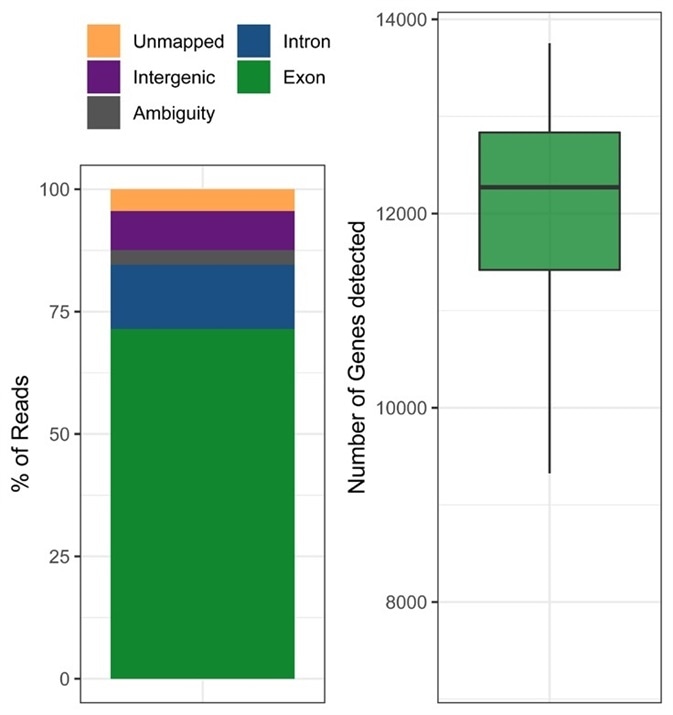
Figure 6. Quality statistics of an exemplary Smart-seq3 experiment. HEK293T cells were processed in a 384-well plate and sequenced to an average depth of 1.8 million reads per cell. Image Credit: FORMULATRIX
The researchers at Karolinska Institute demonstrate that utilizing the MANTIS technology in their workflow for producing sequencing ready libraries from single cells with Smart-seq3 is a brilliant way to produce high quality and repeatable results at a greater throughput, while cutting plastic consumption, manual labor, and overall costs.
Additionally, the MANTIS technology showcases both the versatility and potential to be implemented in other current plate based single-cell RNA sequencing techniques, as well as helping to lay the groundwork for novel methods.
Acknowledgments
FORMULATRIX thank Christoph Ziegenhein and Michael HagemannJensen and colleagues at Karolinska Institutet for their work in evaluating the MANTIS dispenser for their Smart-seq3 workflow and for providing the results in the article.
About FORMULATRIX
FORMULATRIX® was established in 2002 to provide protein crystallization automation solutions. Since then, we've started developing other laboratory automation solutions including the next generation of liquid handlers using microfluidic technology.
Headquartered in Bedford, Massachusetts, we supply software and robotic automation solutions to leading pharmaceutical companies and academic research institutions around the world. Our team works tirelessly to provide the best products in the industry with support that is second to none.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.