Sponsored Content by BGI GenomicsReviewed by Olivia FrostDec 6 2023
Approximately 5.2% of the global population possesses abnormalities in hemoglobin, leading to the annual birth of 300,000 to 400,000 children with severe hemoglobinopathies.
Image Credit: cones/Shutterstock.com
Thalassemia, an inherited hemoglobinopathy, occurs in 4.4 out of every 10,000 live births and is notably prevalent in Mediterranean coastal areas, Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and southern China.
Thalassemia is often classified as α-thalassemia or β-thalassemia depending on whether the anomaly results from the synthesis of alpha (α) chains or beta (β) chains making up the protein.
Treatments for moderate to severe thalassemia include frequent blood transfusions, chelation therapy to remove excess iron from the blood, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), which can be quite expensive and can have a major impact on patients, their families, and the healthcare system.
The implementation of screening and antenatal diagnosis has effectively lowered the incidence of β-thalassemia in various Mediterranean countries.
Turning attention to regions with high thalassemia prevalence, BGI Genomics initiated a global survey to raise awareness about thalassemia. The aim of the survey was to evaluate the knowledge and attitudes regarding associated health risks, thalassemia carrier screening, and genetic counseling for carriers.
By examining these critical areas, the survey sought to underscore existing obstacles and potential avenues for improvement.
Covering 1,847 women across Azerbaijan, China, Indonesia, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Thailand, the survey’s findings highlight the pressing need to enhance awareness, address barriers, and improve access to screening.
- Most people do not know much about thalassemia: 70.5% of women lacked substantial knowledge about the symptoms and health risks linked to thalassemia, and an additional 14.4% mentioned they had never heard of thalassemia. The percentage of women with limited awareness regarding thalassemia remained relatively consistent across different age groups and marital statuses.
- Greater willingness to undergo thalassemia screening with more information: Upon understanding the health risks and substantial lifetime treatment expenses linked to thalassemia, a notable 84.5% of women express increased willingness to undergo various forms of thalassemia screening, including premarital, pre-pregnancy, and prenatal tests. Improved awareness about thalassemia is likely to foster more positive shifts in attitudes toward screening tests, ultimately contributing to improved health outcomes.
- Accessibility matters: The primary factors influencing the inclination to undergo thalassemia screening include the availability of screening services in nearby hospitals or agencies (43.1%), the cost associated with screening services (38.1%), and the consideration of screening before marriage or starting a family (35.3%).
- Thalassemia carriers are more open to genetic counseling: If both partners are thalassemia carriers, a significant 50.8% of women can successfully encourage their partners to pursue genetic counseling and contemplate preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD), thereby increasing the chances of having a thalassemia-free child. In instances where women have acquired information about thalassemia through health awareness programs, this percentage increased to 59.5%. Consequently, health awareness programs emerge as pivotal influencers in promoting genetic counseling and PGD.
Dr. Zhiyu Peng, BGI Genomics Deputy GM, notes: “This survey shows that enhancing awareness and accessibility is an important first step in thalassemia control programs. Region‐specific screening and treatment programs, customized to align with local healthcare resources and cultural values, are also vital to identify thalassemia patients and carriers. Such customization will facilitate the provision of information and care to obtain better health outcomes while reducing costs for their families and the healthcare system.”
Dr. Androulla Eleftheriou, Thalassemia International Federation Executive Director, comments: “Enhancing awareness is a crucial first step in promoting individual behavior changes and policy reforms, ultimately leading to improved prevention, control, and management of thalassemia. Screening services – a key component of any effective national control program – need to consider cultural and socio-economic backgrounds. We welcome BGI Genomics efforts and reaffirm our commitment to further expanding thalassemia awareness on a global scale.”
Thalassemia awareness
Around 80% of thalassemia cases are observed in low- or middle-income countries, where an uneven distribution of medical resources increases the potential threat to patients’ quality of life. Thalassemia control programs necessitate a focus on public awareness, screening, genetic counseling, and prenatal diagnosis.
This survey aims to gauge women’s awareness regarding thalassemia symptoms, associated health risks, and screening tests.
What is the level of thalassemia awareness worldwide?
Even though this survey was conducted in regions with high thalassemia prevalence, a substantial 70.5% of individuals worldwide lack significant knowledge about thalassemia symptoms and the associated health risks. Additionally, 14.4% indicate they have never come across information about thalassemia.
Kuwait (77.4%) and Azerbaijan (75.2%) exhibit the highest levels of limited awareness regarding thalassemia. The proportion of women with limited knowledge about thalassemia remains relatively consistent across different age groups and marital statuses.
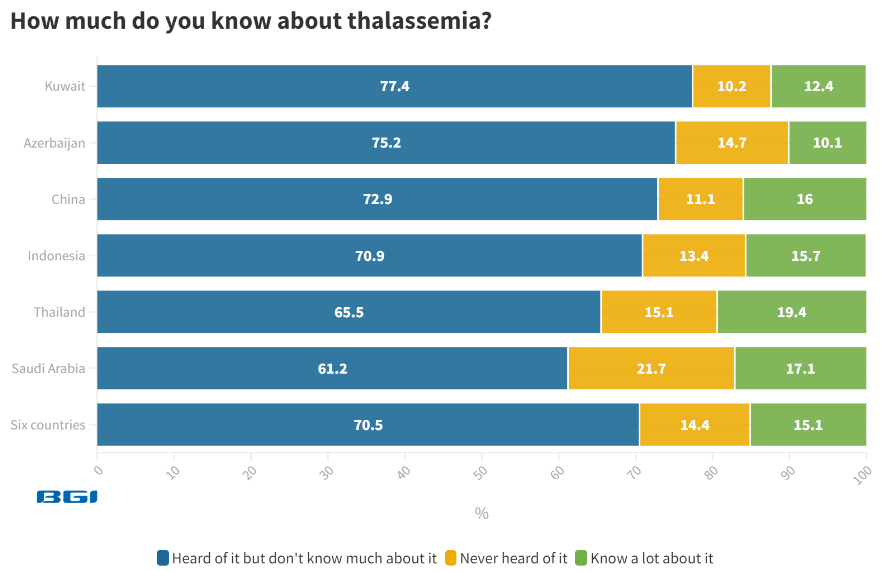
Image Credit: BGI Genomics
Globally, 51.7% are aware of blood transfusion treatment for thalassemia patients, and 36.5% are familiar with chelation therapy to remove excess iron from the blood. Kuwait (66.7%) and Indonesia (54.1%) lead in the percentage of individuals aware of blood transfusion treatment.
Among women who are thalassemia patients, carriers, or have a family history of thalassemia, 57.9% are informed about chelation therapy, surpassing the global average.
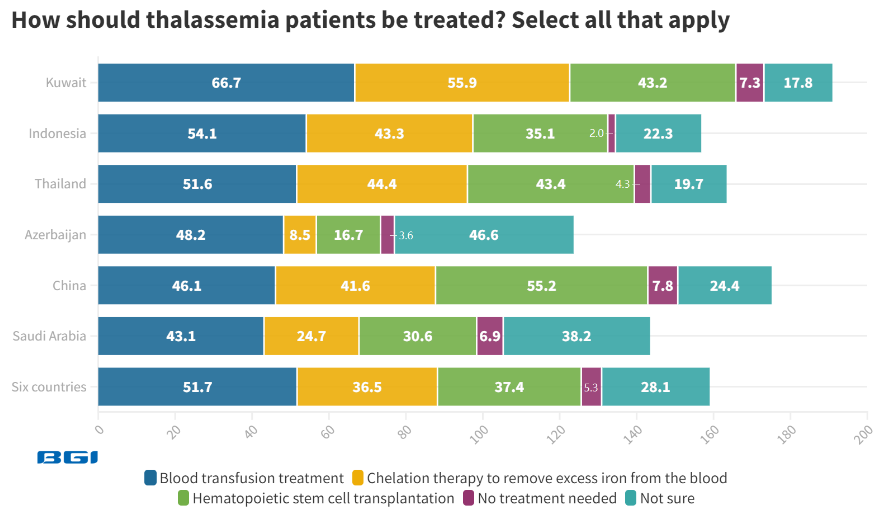
Image Credit: BGI Genomics
What do women know about thalassemia carrier screening?
38.0% of women express uncertainty or lack of awareness about thalassemia carrier screening globally. Azerbaijan (60.2%) and Saudi Arabia (53.5%) demonstrate the highest percentages in this category.
Kuwait stands out for having the highest awareness of thalassemia carrier screening, with only 17.2% stating they are uninformed or unsure while recognizing routine blood tests, hemoglobin electrophoresis, and genetic testing as available options.
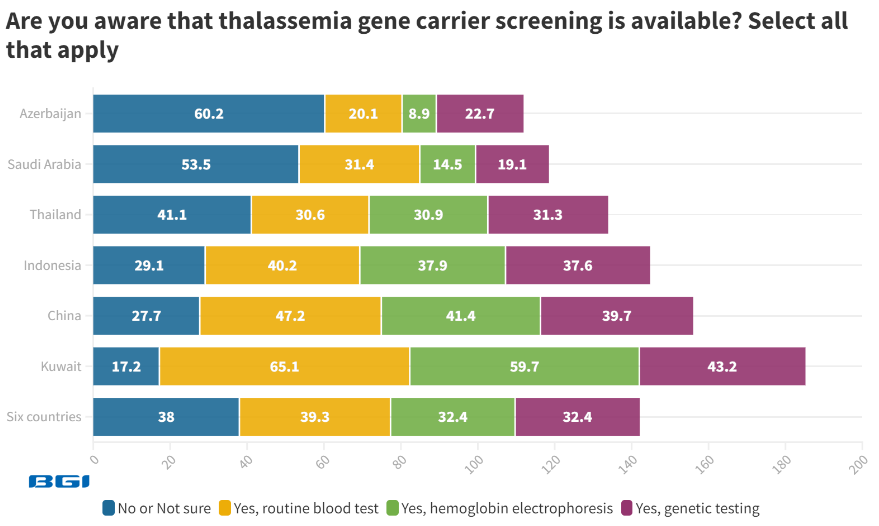
Image Credit: BGI Genomics
44.6% worldwide are aware that hereditary genetic mutations cause thalassemia. Thailand (67.8%) displays the highest level of awareness about hereditary genetic mutations, whereas Indonesia (21.2%) records the lowest level of comprehension.
When it comes to acquiring thalassemia-related information, women globally cite websites (45.1%) and health awareness programs (43.2%) as the top channels. China (58.3%) and Kuwait (56.4%) exhibit the highest percentages, with health awareness programs being a primary source of information.

Image Credit: BGI Genomics
What is holding women back from thalassemia carrier screening?
A significant 86.0% of the global population has not undergone a thalassemia screening test. Azerbaijan (96.4%) and Indonesia (95.4%) show the highest percentages of individuals who have not taken the test, while Kuwait (61.5%) exhibits the lowest rate.
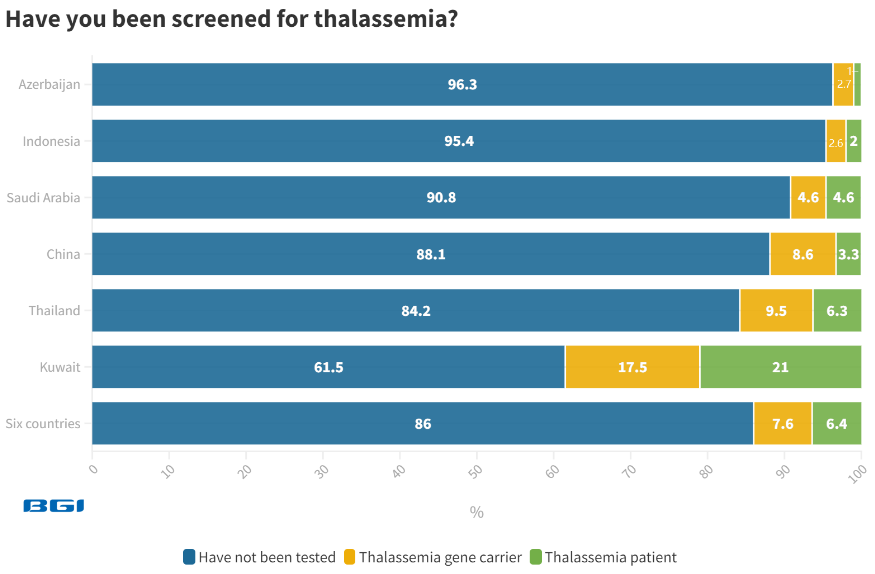
Image Credit: BGI Genomics
Accessibility to thalassemia tests is important. The primary factors influencing the willingness to undergo thalassemia screening include the availability of screening services in nearby hospitals or agencies (43.1%), the cost associated with screening services (38.1%), and the consideration of screening before marriage or starting a family (35.3%).
Nearby hospitals or agencies are most influential in China (60.7%) and Kuwait (54.2%), while the notion of screening before getting married or having children is highest in Azerbaijan (44.0%) and China (39.6%).
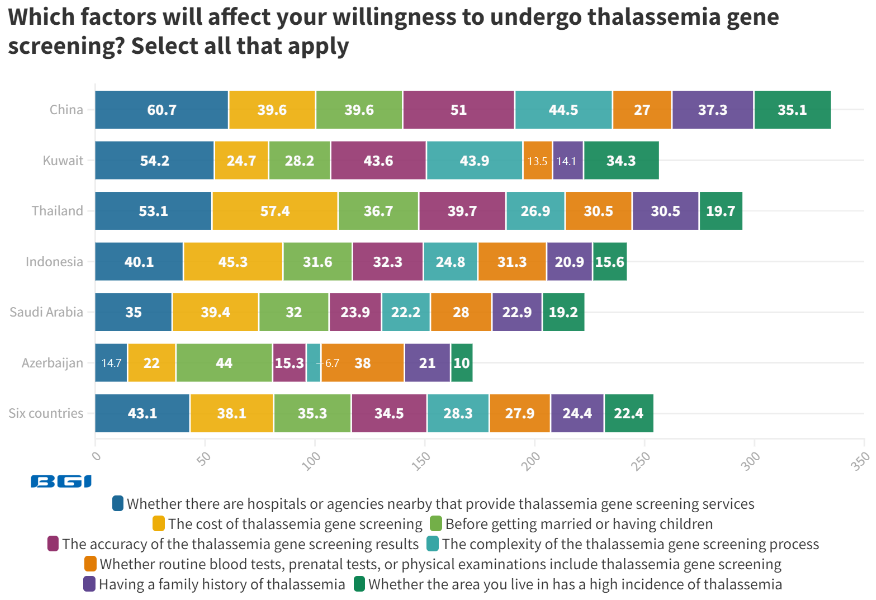
Image Credit: BGI Genomics
Changing attitudes with awareness
Over the past two decades, the experience and knowledge, notably in Southern Mediterranean countries, have resulted in the development of guidelines for the management and control of thalassemia. These guidelines were initially published by the WHO and subsequently by the Thalassemia International Federation (TIF).
Increased awareness empowers individuals to make more informed decisions regarding thalassemia screening, including premarital, pre-pregnancy, and prenatal tests, as well as making choices related to genetic counseling and preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD).
How does awareness shape attitudes towards screening?
Upon understanding the health risks and the considerable lifetime treatment costs linked to thalassemia, 84.5% of women express increased willingness to undergo various forms of thalassemia screening, encompassing premarital, pre-pregnancy, and prenatal tests.
Kuwait (94.1%) and Thailand (91.2%) have the highest percentages of individuals expressing increased willingness to undergo some form of thalassemia screening.
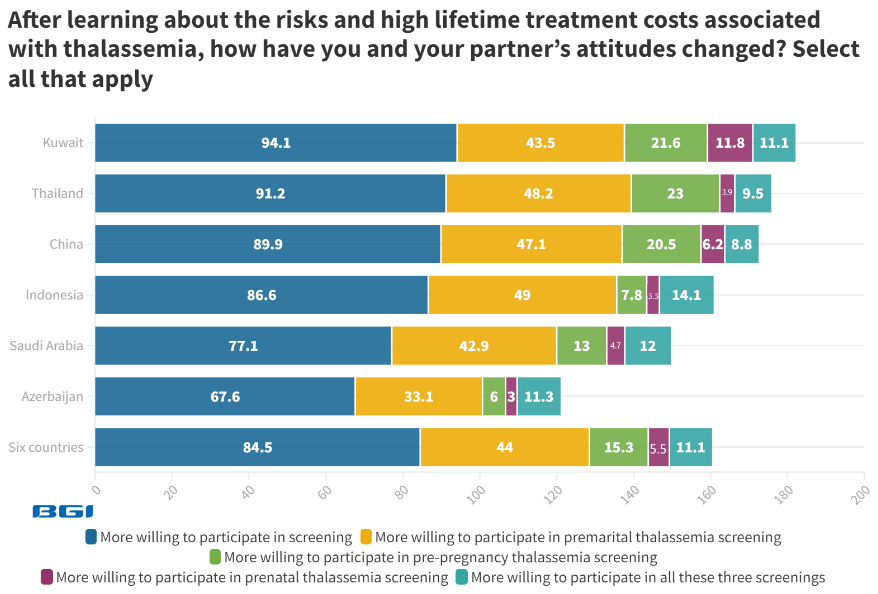
Image Credit: BGI Genomics
With heightened awareness, the premarital thalassemia screening test emerges as the most favored option, selected by 44.0% of individuals. Indonesia (49.0%) and Thailand (48.2%) lead in the preference for premarital screening tests.
Pre-pregnancy and prenatal thalassemia tests are chosen by 15.3% and 5.5%, respectively. Kuwait (11.8%) and China (6.2%) exhibit the highest percentages of individuals opting for prenatal thalassemia tests.
Are thalassemia carriers more willing to go for genetic counseling?
When two individuals carrying the same form of thalassemia trait have a child, there is a one in four (25%) chance that the child will be born with a severe form of thalassemia.
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) is an established procedure that enables couples to test for specific genetic conditions, such as thalassemia, in the early embryo. This occurs before the selection of embryos for transfer to the uterus to establish a pregnancy.
If both partners are thalassemia carriers, 50.9% of women can successfully encourage their partners to seek genetic counseling and contemplate PGD.
If women have acquired information about thalassemia through health awareness programs, this percentage increases to 59.5%. Consequently, health awareness programs emerge as pivotal influencers in promoting genetic counseling and PGD.
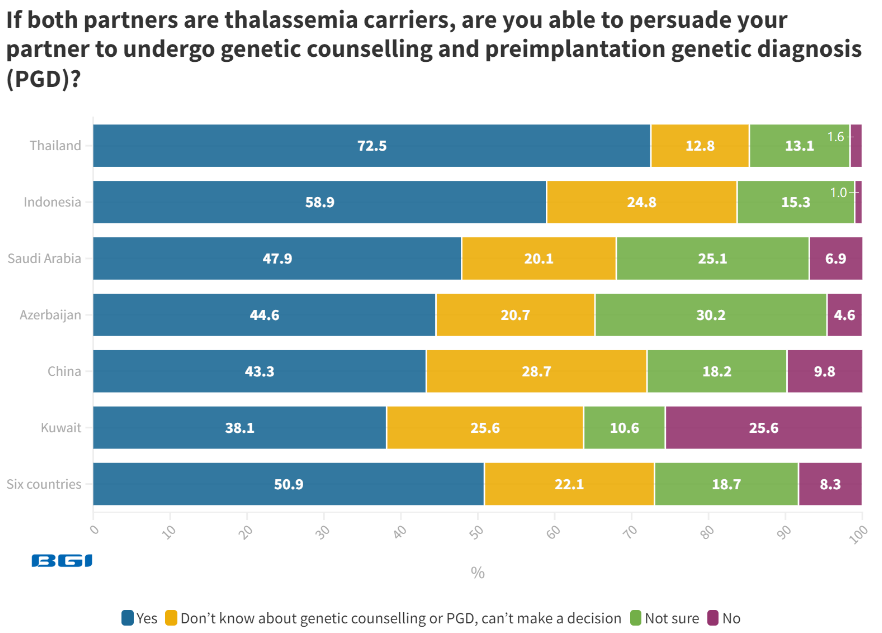
Image Credit: BGI Genomics
Thailand (72.5%) and Indonesia (58.9%) exhibit the highest percentages of women, indicating that genetic counseling and PGD are options they will consider. These options enhance the likelihood of giving birth to a child free from thalassemia.
22.1% of women, however, are unaware of genetic counseling or PGD and are unable to evaluate these options. China (28.7%) and Kuwait (25.6%) record the highest percentages of individuals unaware of these options.
Methodology
The survey conducted in October 2023 involved 1,847 female respondents from Azerbaijan (306), China (308), Indonesia (307), Kuwait (315), Saudi Arabia (306), and Thailand (305).
Respondents were located in their respective countries or regions during the survey period. Momentive Global conducted surveys in local languages. Respondents were aged between 21 to 49 years old.
About BGI Genomics
BGI Genomics is the world's leading integrated solutions provider of precision medicine, now serving customers in more than 100 countries.
They provide academic institutions, pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, and other organizations with integrated genomic sequencing, proteomic services, clinical testing, and solutions across a broad range of applications.
They have more than 20 years of genomics experience helping customers and partners achieve their goals by delivering rapid, high-quality results using a broad array of cost-effective, cutting-edge technologies, including their own innovative DNBSEQ™ sequencing technology.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.