Mar 7 2016
Aching knees and stiff fingers: osteoarthritis is a widespread joint disease with few treatment options. However, there may finally be some hope: American scientists are hoping to mechanically reinforce worn-out cartilage by incorporating a biomimetic gel. As they report in the journal Angewandte Chemie, their technique results in extensive interpenetration of the cartilage’s natural biopolymer network with the synthetic polymer network.
Osteoarthritis does not only occur in older individuals. Young people are also affected, often as a result of a misalignment; an accident; or stress from competitive sport, excessive weight, or asymmetrical physical labor. Healthy cartilage acts as cushioning in the joint. If it wears out, the bones begin to rub against each other, causing pain and deformation of the joint.
The cause of this wear is a depletion of glycosaminoglycans in the cartilage tissue. These polysaccharides carry a negative charge that allows them to bind to water molecules, which maintains the hydration of the tissue. In the early stages of osteoarthritis, the cartilage dries out and the “cushion“ becomes thinner and less able to withstand load bearing. No treatments to regenerate cartilage are currently available.
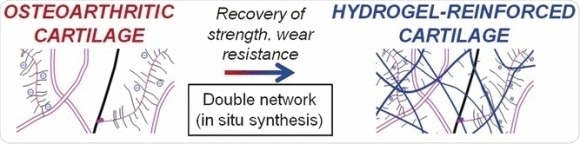
Researchers from Boston University, the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, and Boston Children’s Hospital (Boston, USA) aim to change this. By incorporating a second polymer network that contains the necessary charged groups, they propose to re-establish the cartilage cushion and restore its mechanical stability. This should not just patch up individual damaged areas, but is designed to strengthen the entire tissue network. In this method, the tissue is infiltrated with monomers, which are polymerized in place by exposure to light.
The team, led by Mark. W. Grinstaff, chose to use zwitterions (ions with both positively and negatively charged groups) based on phosphorylcholine as their monomers. Phosphorylcholine is known for its biocompatibility. These monomers are able to penetrate into the biopolymer tissue of the cartilage. Further reagents are used to crosslink the synthetic polymer and to start the polymerization as soon as the area is irradiated with green laser light. This results in a gel in which the synthetic polymer chains are extensively entangled with the polymer chains of the cartilage. The gel binds water well, allowing the hydration of treated cartilage to be maintained longer under strain.
Compression tests with enzymatically degraded bovine cartilage showed that the gel can restore the original mechanical stability of the cartilage. The gel preferentially aggregates in areas that are particularly affected. A simulation of accelerated wear showed that healthy cartilage can also be effectively protected against degeneration by using this method. This new process thus seems to be highly promising for the treatment of osteoarthritis in its early stages.