© Andrea Danti/shutterstock.com
Depression is the most commonly suffered neuropsychiatric disorder in the world, with one in five people experiencing it at some point in their lives.
According to the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), anxiety disorders that often occur along with other psychiatric illnesses such as depression, affect around 40 million American adults each year.
Cases of depression are increasing in all age groups, particularly among young people. It is estimated that if the increase continues at the current rate, then by 2020, depression will be the second most disabling condition in the world next to heart disease.
The increase in depression rate, as well as the rates of depression recurrence indicate that although clinically used antidepressants may enable a person to manage their symptoms, they do not generally result in people being depression-free for the rest of their lives.
There are also major drawbacks associated with use of the drugs, with adverse side effects ranging from increased appetite and weight gain to sexual dysfunction. Anxiety can also be treated with sedatives, but the drawbacks associated with these treatments include potential addiction, headaches, dizziness and drowsiness.
More than ever, there is a clear need for alternative, more effective and safer drugs for the treatment of depression and anxiety.
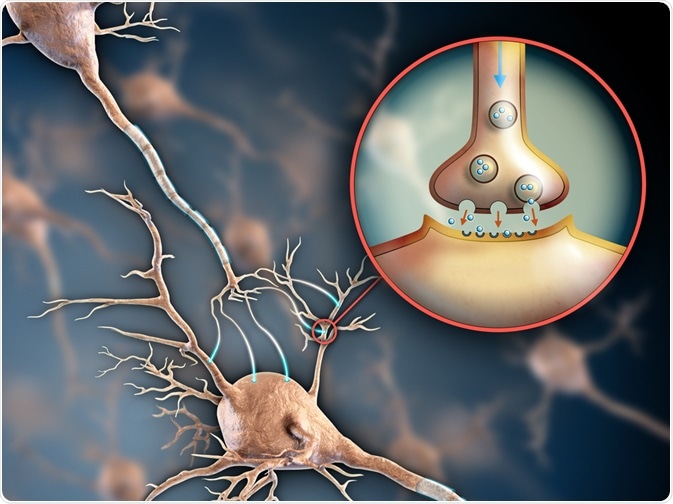
Antidepressant Medication Mechanism
Both anxiety and depression are commonly treated with antidepressants. Currently, antidepressants mainly work by enhancing the monoaminergic transmitter system, the network of neurons that use monoamine neurotransmitters to regulate emotions and some forms of memory.
This is achieved either through inhibition of the re-uptake of the neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine or norepinephrine or through inhibition of their catabolism, both of which increase the levels of these in the brain.
Halogenated Compounds
Halogenated compounds are those that contain halogen atoms such as bromine, iodine, chlorine or fluorine. Many marine organisms produce halogenated secondary metabolites, with a particularly common group being alkaloids. Bromine is abundant in the marine environment and is found in most halogenated metabolites.
The similarity in structure between endogenous indole alkaloids and amine neurotransmitters has led researchers to study the neurological activity of indole alkaloids and their potential as therapeutics for anxiety and depression.
As a result, an increasing number of marine indole alkaloids have been reported on, along with increased brominated functionality from a range of marine organisms. Certain brominated compounds have exhibited a high affinity binding for serotonin receptors.
Marine-Derived Natural Products
Several marine-derived natural products have shown potential in the treatment of neurological disorders. In a recent study by Mark Hamann and team from the University of Mississippi, the value of brominated marine natural products in targeting neurological receptors has been illustrated using high performance liquid chromatography, mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance imaging to assess mice treated with such products.
The researchers used high-performance scientific instrumentation for the study, with mass spectra recorded on Bruker’s micrOTOF and 1D and 2D NMR experiments performed using Bruker’s DRX NMR spectrometer.
Halogenated Drugs
Many currently available drugs and drug candidates are halogenated, mainly to improve membrane permeability, lower metabolic degradation and fill spaces in the binding pockets of receptors.
Halogens can improve potency and impact on target selectivity by influencing pKa and by altering the conformation, lipophilicity and hydrophobic interactions, particularly in hydrophobic pockets such as those found in the serotonin receptors 5-HT1A and 5-HT7.
In the current study by Hamann and team, derivatives of the indole alkaloid 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)-N,N-dimethylethanamine were prepared with different halogen substitutions. The team performed in vitro and in vivo assessment of the antidepressant and sedative activities of these compounds using two animal models: the forced swim test and the locomotor activity test.
They found that of the compounds prepared, six demonstrated significant antidepressant-like action and that three of those also exhibited potent sedative activity. Four of the six compounds showed nanomolar affinities to the serotonin receptors 5-HT1A and 5-HT7.
The researchers say the data they gathered indicated that the antidepressant action exerted by some of the compounds was at least partly mediated through their interaction with serotonin receptors. They also say their study points to the important role that bromine plays in providing novel chemical space and electrostatic interactions.
Hamann and colleagues suggest that further mechanistic studies be carried out so that the nature of these interactions can be delineated and the mechanism underlying the behavioural effects that the compounds had can be clarified.
References
- Hamann, M et al. Marine Inspired 2-(5-Halo-1H-indol-3-yl)-N,N-dimethylethanamines as Modulators of Serotonin Receptors: An Example Illustrating the Power of Bromine as Part of the Uniquely Marine Chemical Space. Marine Drugs 2017, 15(8), 248; doi:10.3390/md15080248
- Franḉa, P. Indole Alkaloids from Marine Sources as Potential Leads against Infectious Diseases. BioMed Research International
2014, Article ID 375423, 12 pages. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/375423
- Perry, G. Special Issue "Marine Compounds and Their Application in Neurological Disorders.” Marine Drugs. Available at: http://www.mdpi.com/journal/marinedrugs/special_issues/neurological_disorders
- Netz, N and Opatz, T. Marine Indole Alkaloids. Marine Drugs 2015, 13(8), 4814-4914; doi:10.3390/md13084814
- Royal College of Psychiatrists. Depression: key facts. Available at: http://www.rcpsych.ac.uk/healthadvice/problemsdisorders/depressionkeyfacts.aspx
- Clinical Depression.co.uk. Major depression facts. Available at: http://www.clinical-depression.co.uk/dlp/depression-information/major-depression-facts/
About Bruker BioSpin - NMR, EPR and Imaging

Bruker BioSpin offers the world's most comprehensive range of NMR and EPR spectroscopy and preclinical research tools. Bruker BioSpin develops, manufactures and supplies technology to research establishments, commercial enterprises and multi-national corporations across countless industries and fields of expertise.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.