The complement system has more than 50 soluble and membrane-bound proteins. In innate and adaptive immunity, complement is essential for eliminating foreign pathogens and apoptotic cells. It is also linked to human pathological conditions, tumor growth, and tissue regeneration.
The approval of C1s inhibitors (sutimlimab), C3 inhibitors (pegcetacoplan), and C5 inhibitors (eculizumab, ravulizumab, pozelimab) demonstrates how complement proteins are revolutionizing immunotherapy. These agents fight against angiogenesis, blood disorders, immunosuppressive environments, and inflammation. An important turning point in complement-related therapy was the FDA's April 2024 approval of danicopan, a complement factor D inhibitor.
The broad range of recombinant complement proteins and antibodies from Sino Biological further advances the creation of cutting-edge therapies that target complement proteins and receptors, advancing the field of immunotherapy.
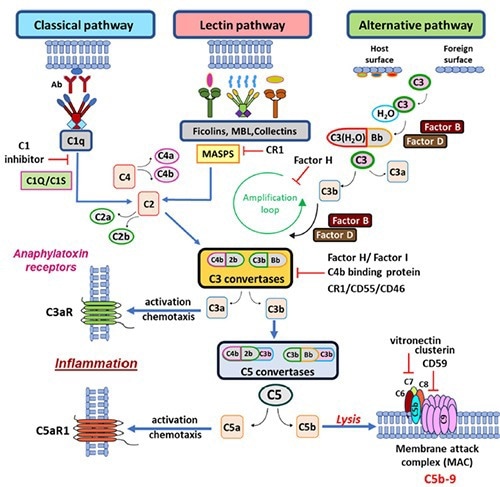
The complement cascade pathways. Image Source: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-023-02657-2.
Featured complement proteins
To help develop new treatments that target complement proteins, Sino Biological has created a wide range of recombinant complement proteins, including C1s, C2, C3, C5, C7, Factor B, D, H, and I.
- High purity
- High bioactivity
- Coverage of multiple species
- A comprehensive catalog of products
Human C5 protein (His & FLAG tag)
Validated Activity (Cat#: 13416-H18H)
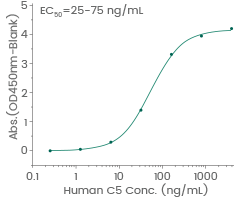
Immobilized Anti-C5 Antibody can bind Recombinant Human C5 Protein. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Human C5a protein
Cat#: 10604-HNAE
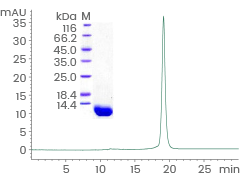
Purity: > 94 % by SDS-PAGE and ≥ 90 % by SEC-HPLC. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
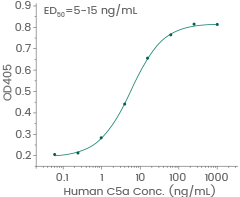
Induced N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase release from differentiated U937 human histiocytic lymphoma cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
More complement proteins and receptors
Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| Molecule |
Cat# |
Species |
Tag |
Expression Host |
Purity |
| C1D |
12432-H09E |
Human |
N-GST |
E. coli |
> 80 % |
| C1QB |
10941-H08B |
Human |
C-His |
Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
≥ 90 % |
 C1s C1s |
10220-H08H |
Human |
C-His |
HEK293 Cells |
> 90 % (SEC-HPLC) |
| C1s |
91017-C08H |
Cynomolgus |
C-His |
HEK293 Cells |
≥ 95 % (SEC-HPLC) |
| C2 |
10154-H02H |
Human |
C-hFc |
HEK293 Cells |
> 95 % |
 C2 C2 |
10154-H08H |
Human |
C-His |
HEK293 Cells |
> 97 % |
| C3 |
13182-H08H |
Human |
C-His |
HEK293 Cells |
≥ 90 % (SEC-HPLC) |
| C5 |
13416-H22H |
Human |
N-flag |
HEK293 Cells |
≥ 95 % |
| C5 |
51136-MNAE |
Mouse |
Native |
E. coli |
≥ 90 % (SEC-HPLC) |
| C5 |
90914-CNAH |
Cynomolgus |
Native |
HEK293 Cells |
> 95 % (SEC-HPLC) |
| C6 |
12426-H08H |
Human |
C-His |
HEK293 Cells |
> 90 % |
| C7 |
13848-H02H |
Human |
C-hFc |
HEK293 Cells |
> 90 % |
| C7 |
13848-H08H |
Human |
C-His |
HEK293 Cells |
> 88 % |
| CFB |
17064-H08H |
Human |
C-His |
HEK293 Cells |
> 90 % |
 CFD CFD |
10160-H08H |
Human |
C-His |
HEK293 Cells |
> 97 % |
 CFH CFH |
10714-H08H |
Human |
C-His |
HEK293 Cells |
≥ 95 % (SEC-HPLC) |
 CD21 CD21 |
10811-H08H |
Human |
C-His |
HEK293 Cells |
≥ 95 % (SEC-HPLC) |
 CD93 CD93 |
12589-H02H |
Human |
C-hFc |
HEK293 Cells |
> 85 % |
 CD93 CD93 |
12589-H08H |
Human |
C-His |
HEK293 Cells |
≥ 90 % (SEC-HPLC) |
 CD93 CD93 |
50759-M02H |
Mouse |
C-hFc |
HEK293 Cells |
≥ 95 % (SEC-HPLC) |
| C1QBP |
11874-H08E |
Human |
C-His |
E. coli |
> 96 % |
| CALR |
13539-H08H |
Human |
C-His |
HEK293 Cells |
≥ 90 % (SEC-HPLC) |
| CALR |
13539-HNAH |
Human |
Native |
HEK293 Cells |
≥ 90 % |
Featured antibodies against complement proteins and receptors
Human C1s antibody pair set: (Cat#: SEK10220)
Application: ELISA
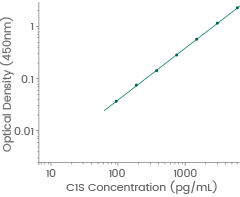
Human C1s standard curve. Linear range: 93.75-6000 pg/mL. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Anti-CR1/CD35, Rabbit pAb: (Cat#: 100464-T08)
Application: IHC-P
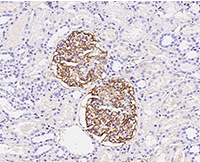
Immunochemical staining of human CD35 in human kidney. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Anti-C5a, Rabbit mAb: (Cat#: 10604-R215)
Application: IHC-P
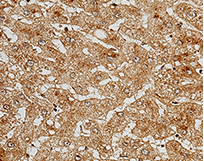
Immunochemical staining of human C5a in human cirrhosis. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Learn More About Reagents