Neurodegeneration is known as a neurological disorder that comes with developing atrophy and irreversible damage of neurons. Two of the most common neurodegenerative diseases are Parkinson’s (PD) and Alzheimer’s (AD).
The growth factors that are responsible for the survival, maintenance, and regeneration of specific neurons are NGF, GDNF, and BDNF. Such growth factors make them therapeutics for neurodegenerative diseases.
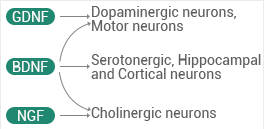
Figure 1. Neuron Specificity. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc
Clinical trials of NGF (therapeutic choice for AD), GDNF (treatment for PD), and BDNF (therapeutic target for both AD and PD) are ongoing.
Furthermore, therapies targeting neurotrophic factors and related receptors can also be a successful method for the less common neurodegenerative diseases like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Huntington’s (HD), and Rett Syndrome.
Neurotrophins and Receptors
Neurotrophins are known as growth factors crucial for neuron development, maintenance, and survival. Four neurotrophin family members are available: BDNF, NGF, neurotrophin 3, and neurotrophin 4.
They have the potential to bind to particular Trk receptors with high affinity and p75NTR with low affinity. This is done to evoke neurotrophic or pro-apoptotic signaling. NGF binds to TrkA; BDNF and neurotrophin 4 bind to TrkB; neurotrophin 3 binds to TrkC. BDNF, NGF, and all the receptors are known as targets for therapy in AD. Also, for PD, BDNF is a therapeutic choice.
NGF (Nerve growth factor)
In the neurotrophin family, NGF is known to be the first discovered member. It is crucial in the survival, growth, and maintenance of particular kinds of neurons.
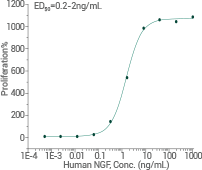
Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc
Human NGF protein
11050-HNAC
Purity: >95%
Expressed Host: CHO Stable Cells
Activity: Cell proliferation assay can be performed with the help of TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells
BDNF (Brain-derived neurotrophic factor)
BDNF aids the existence and maintenance of sensory neurons, retinal ganglia, spinal motor neurons, a few cholinergic neurons, and some dopaminergic neurons.

Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc
Mouse BDNF protein
50240-BDNF Protein
Purity: >95%
Expressed Host: HEK293 Cells
Neurotrophin 3/NT3
Human NT3 Protein
10286-HNAE
Purity: >90%
Expressed Host: E. coli
Activity: Binding ability in a functional ELISA, binds to human TrkB
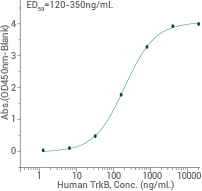
Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc
Neurotrophin 4/NT4
Human NT4 Protein
10265-HNAE
Purity: >95%
Expressed Host: HEK293 Cells
Trk receptors
Source: Sino Biological Inc
| Cat# |
Molecule |
Species |
Expressed Host |
Purity |
Tag |
Activity |
| 11073-H03H |
TrkA |
Human |
HEK293 Cells |
>98% |
C-hFc & His |
Active |
| 11073-H07E1 |
TrkA |
Human |
E. coli |
>97% |
N-His |
Active |
| 51103-M02H |
TrkA |
Mouse |
HEK293 Cells |
>90% |
C-hFc |
Active |
| 51103-M08H |
TrkA |
Mouse |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
C-His |
Active |
| 70101-D01H |
TrkA |
Canine |
HEK293 Cells |
>90% |
N-hFc |
Active |
| 70101-D07H |
TrkA |
Canine |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
N-His |
Active |
| 80404-R02H |
TrkA |
Rat |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
C-hFc |
Active |
| 80404-R08H |
TrkA |
Rat |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
C-His |
Active |
| 10047-H03H |
TrkB |
Human |
HEK293 Cells |
>90% |
C-hFc & His |
Active |
| 10047-H08H |
TrkB |
Human |
HEK293 Cells |
>97% |
C-His |
Active |
| 50132-M08H |
TrkB |
Mouse |
HEK293 Cells |
>98% |
C-His |
Active |
| 70035-D08H |
TrkB |
Canine |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
C-His |
Active |
| 80243-R08H |
TrkB |
Rat |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
C-His |
Active |
| 10048-H03H |
TrkC |
Human |
HEK293 Cells |
>98% |
C-hFc & His |
Active |
| 10048-H08H |
TrkC |
Human |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
C-His |
Active |
| 50320-M08H |
TrkC |
Mouse |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
C-His |
Active |
Low affinity common receptor to neurotrophins: p75NTR
Human p75NTR Protein
13184-H02H
Purity: >95%
Expressed Host: HEK293 Cell
Activity: Inhibit NGF-dependent proliferation of TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells, ED50 is 0.5-3 μg/mL in the presence of 4 ng/mL Recombinant Human NGF.
Mouse p75NTR Protein
50971-M02H
Purity: >90%
Expressed Host: HEK293 Cell
Activity: Inhibit NGF-dependent proliferation of TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells. ED50 is 0.5-3 μg/mL in the presence of 2 ng/mL Recombinant mouse NGF.