The iNSiGHT DXA system is a cutting-edge in vivo Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA/DEXA) technology intended for preclinical studies. It offers a comprehensive solution for assessing a wide range of metabolic problems, including osteoporosis, arthritis, diabetes, obesity, and musculoskeletal pathologies such as bone regeneration and muscle wasting diseases.
This system has a fully shielded X-ray cabinet, making it ideal for small animal DXA applications, particularly mice, rats, and animals of similar size (up to 5 kg). It offers quick and accurate body composition measurements. The system's quick 25-second scan durations and low-dose radiation make it excellent for longitudinal research.
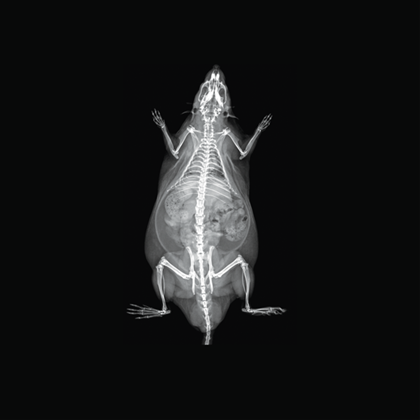
Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc
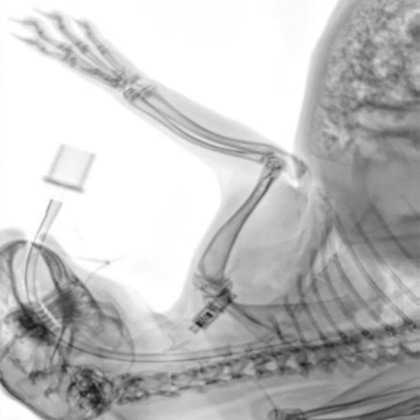
Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc
The iNSiGHT technology employs dual energy X-rays to provide highly accurate and repeatable body composition assessments. The system categorizes each pixel into one of three compartments: fat mass, non-bone/lean mass, or bone mineral content, and provides measurements such as bone mineral density, bone mineral content, bone area, tissue area, fat tissue percentage and weight, lean tissue percentage and weight, and total weight in grams.
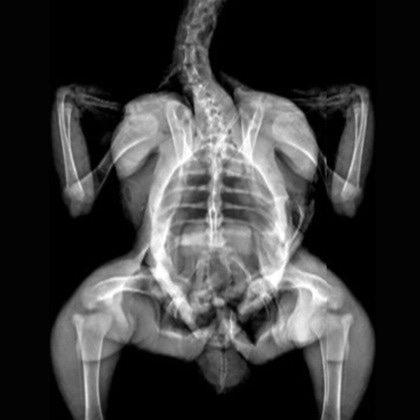
Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc
With this noninvasive, nondestructive method, no contrast, substrate injection, or animal pretreatment is necessary. The 2D X-ray image can also be used with the iNSiGHT system to determine precise bone length measurements.
Features and benefits
The iNSiGHT is a Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA/DEXA) system built especially for in vivo preclinical research purposes.
Easy data acquisition
Anesthesia is the only preparation step needed. If preferred, injectable anesthesia or the integrated anesthesia system can be used.
Using the user-friendly acquisition software, imaging can start as soon as the subject is prepared and placed on stage.
Large scan area
The iNSiGHT system can image tissue samples and animal models weighing between 10 g and 5 kg. The area scanned is 16.5×25.5 cm.
This enables users to image non-human primates, fish, rabbits, and other species besides mice and rats.
25-second scan time
With the fastest scan time available, the iNSiGHT enables high-throughput imaging.
Comprehensive set of images and parameters
The X-ray attenuated image, bone mineral density map, and color map are produced in a single scan (25 seconds).
These images are used to compute a variety of parameters, either for user-defined regions of interest (ROI) or the entire animal:
- Bone Mineral Content (BMC) (g)
- Bone Mineral Density (BMD) (g/cm2)
- Bone area (cm2)
- Tissue area (cm2)
- Fat tissue (mass and percentage) (g & %)
- Lean tissue (mass and percentage) (g & %)
- Total mass (g)
Low-dose radiation
The iNSiGHT's design reduces ionizing radiation (0.66 mGy) needed to produce data and images. This minimization makes multiple imaging time points throughout longitudinal research possible, eliminating any potential effects of the picture acquisition on the participant.
Adjustable field of view and resolution
With its several magnification settings, the iNSiGHT system allows users to customize the resolution and field of vision (FOV) to meet their unique requirements. Pixel resolution in Digital Radiography Mode ranges from 100 µm to 31 µm.
Models and specifications
iNSiGHT DXA technical specifications
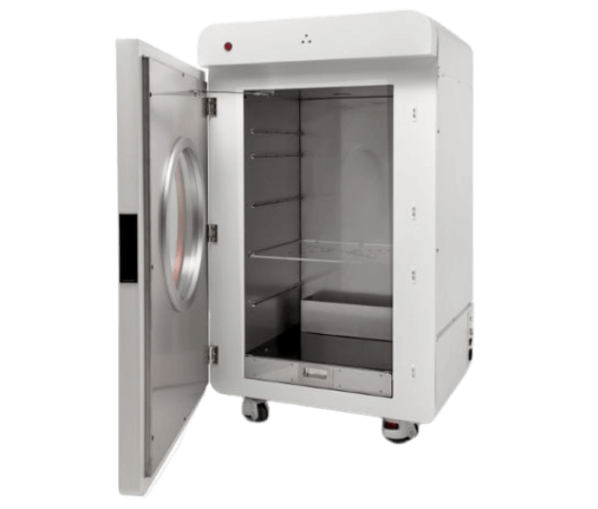

Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc
- Scan Method: Cone Beam
- Animal Size: Mice, rats, and animals of similar size (up to 5 kg)
- Image Area (maximum): 16.5×25.5 cm
- Pixel Size: 100 µm at 1.2× 31 µm at 4× with DR Mode
- Operating System: Windows 10, 64-bit
- Dimensions (WxDxH): 66×61×113 cm
- Power: 110/240 VAC, 50/60 Hz, 200 VA
- Operating Temp: 10 ~ 40 °C
Add-ons
- Digital radiography mode (acquire better quality images with a 31 µm pixel resolution)
- Offline Analysis Software
- Anesthesia Control
Applications
Metabolic disorders
Metabolic diseases occur when the body’s regular metabolic functions are interfered with, either by genetic defects or external factors.
Numerous metabolic diseases exist, but the most frequent are diabetes, metabolic syndrome, obesity, and so on. Numerous small animal models of these diseases could benefit from DXA imaging to assist in understanding the genetic, molecular, and metabolic processes that underpin them.
The iNSiGHT system measures changes in fat and lean mass over time to assess disease progression or regression and body composition assessments in response to a treatment program. The colorimetric image distinguishes visceral and subcutaneous fat using regions of interest, which could be useful in further understanding these diseases.
In this case, researchers used a diabetic mouse model to track changes in body composition. In the diabetic mouse model, fat mass, lean mass, and bone mineral content were all lower than in the control group.
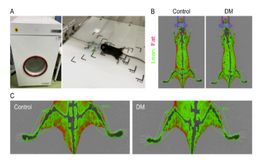
Image Credit: Kishi K, Goto M, Tsuru Y, Hori M. Noninvasive monitoring of muscle atrophy and bone metabolic disorders using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in diabetic mice. Exp Anim. 2022 Sep 15. doi: 10.1538/expanim.22-0097. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36104204.
Drug safety and toxicology
Drug safety and toxicity investigations are critical to the passage of target compounds into clinical trials. In addition to the target compound's efficacy on the desired pathology, it is critical to investigate its safety and any hazardous consequences, which can be detected by evaluating changes in the bones, fat, and lean tissues.
Small animal studies are commonly employed for medication safety and toxicology screening methods before target compounds progress to more sophisticated preclinical research in non-human primates, for example, or before entering clinical trials.
The iNSiGHT system can be used to assess changes in body composition following the delivery of a target compound at an effective dose. This can be accomplished by monitoring changes in bone mineral density and content over time, as well as assessing changes in fat and lean mass. In this case, researchers were looking at how polyphenol therapy affected a rat model of ovariectomy.
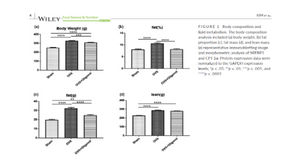
Image Credit: Kim, J. H., Lee, H., Kim, J. M., Lee, B.-J., Kim, I.-J., Pak, K., Jeon, Y. K., & Kim, K. (2022). Effect of oligonol, a lychee-derived polyphenol, on skeletal muscle in ovariectomized rats by regulating body composition, protein turnover, and mitochondrial quality signaling. Food Science & Nutrition, 10, 1184– 1194.
Musculoskeletal diseases
This broad category of pathologies encompasses the previously described metabolic bone diseases and arthritis but also other diseases that affect either the bones or the muscles. Additional diseases include bone fractures and healing, bone and/or muscle regeneration, and muscle wasting diseases.
Numerous small animal models of these diseases could benefit from DXA imaging to help understand the genetic, molecular, and metabolic processes that underpin them.
The iNSiGHT system can monitor disease development or regression in response to a treatment regimen by evaluating changes in bone mineral density and content, as well as changes in fat and lean mass over time.
In this case, low-dose lithium supplementation was investigated and found to induce adipose tissue browning and sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase uncoupling in muscle.
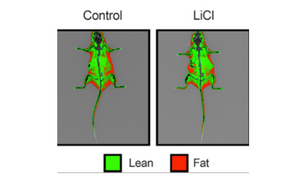
Image Credit: Geromella MS, Ryan CR, Braun JL, Finch MS, Maddalena LA, Bagshaw O, Hockey BL, Moradi F, Fenech RK, Ryoo J, Marko DM, Dhaliwal R, Sweezey-Munroe J, Hamstra SI, Gardner G, Silvera S, Vandenboom R, Roy BD, Stuart JA, MacPherson REK, Fajardo VA. Low-dose lithium supplementation promotes adipose tissue browning and sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase uncoupling in muscle. J Biol Chem. 2022 Nov;298(11):102568. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102568. Epub 2022 Oct 7. PMID: 36209826; PMCID: PMC9664358.
Metabolic bone disease & arthritis
The term “metabolic bone disease” refers to a group of diseases that all cause abnormalities or deformities in the structure of the bones. Rickets, osteoporosis, osteomalacia, osteogenesis imperfecta, and others are a few examples.
DXA imaging could benefit a variety of small animal models by helping us better understand the genetic, molecular, and metabolic processes that are essential to various disorders.
Arthritis is an inflammation of the joints that causes swelling and pain in the affected area. It is not a particular condition but a general term for joint pain or sickness. There are about 100 types of arthritis, the most prevalent being osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Numerous small animal models of these diseases could benefit from DXA imaging to help understand the genetic, molecular, and metabolic processes that underpin them.
The iNSiGHT system can determine disease progression or regression in response to a treatment regimen by detecting changes in bone mineral density and content in the affected joints. These alterations are frequently detected early in the disease course, when drugs may still be beneficial before appearing on a traditional X-ray image. Once alterations are seen on an X-ray, the disease is deemed advanced, and recovery or response to therapy is unlikely.
In this case, the iNSiGHT DXA system indicated higher cone mineral content (BMC) and bone mineral density (BMD) values in the entire body and lumbar vertebrae of C3H mice (atherosclerosis-prone mice).
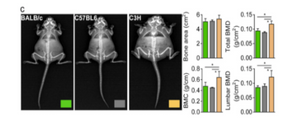
Image Credit: Kim MY, Lee K, Shin HI, Lee KJ, Jeong D. Metabolic activities affect femur and lumbar vertebrae remodeling, and anti-resorptive risedronate disturbs femoral cortical bone remodeling. Exp Mol Med. 2021 Jan;53(1):103-114. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-00548-w. Epub 2021 Jan 12. PMID: 33436949; PMCID: PMC8080628.
Hypoxia
In vivo, hypoxia is hypothesized to alter the metabolic state of the exposed animal, potentially affecting glucose metabolism and energy expenditures. Numerous small animal models are being used to study hypoxia exposure, with changes in body composition being particularly important.
The iNSiGHT system can evaluate changes in body composition parameters following hypoxia exposure. The colorimetric image allows for distinguishing visceral and subcutaneous fat using regions of interest, which may help understand the metabolic effects of such exposures. In this case, hypoxia exposure reduces the amount of fat in mice.

Image Credit: Park, Y., Hwang, D., Park, H.Y., Kim, J. and Lim, K., 2020. Hypoxic Exposure Increases Energy Expenditure by Increasing Carbohydrate Oxidation in Mice. BioMed Research International, 2020.
DXA - Imaging gallery
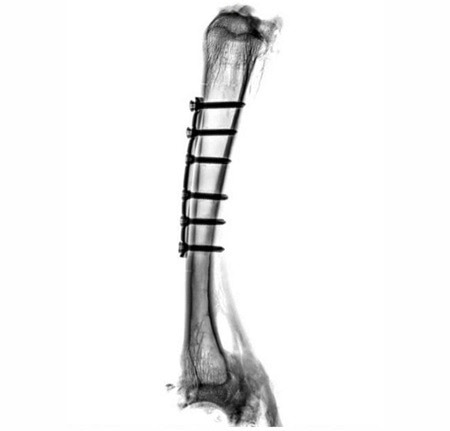
Implants on a sheep bone. The fit of the implants, the progress of healing and fissures on the screw connections are clearly visible. Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc
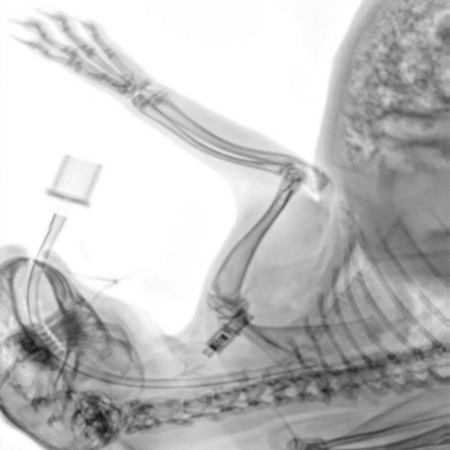
Intraoperative control image of a rabbit. The position of the intubation can be determined with great precision. Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc
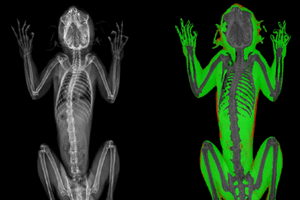
Marmosets. Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc
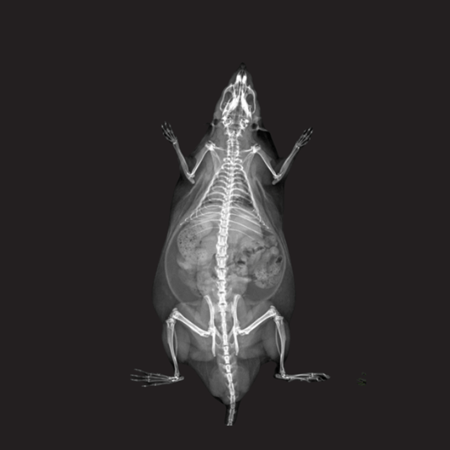
X-Ray Attenuation Image - Rat. Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc
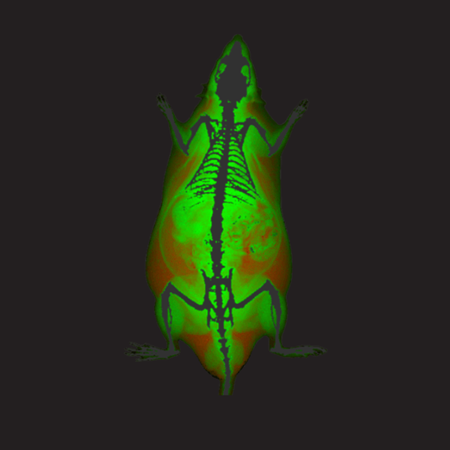
Color Image - Rat. Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc
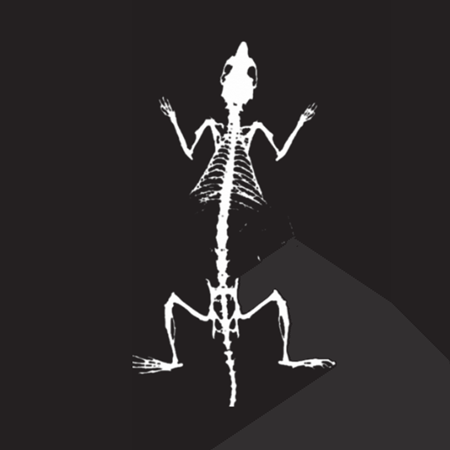

Bone Mineral Density Image - Rat. Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc
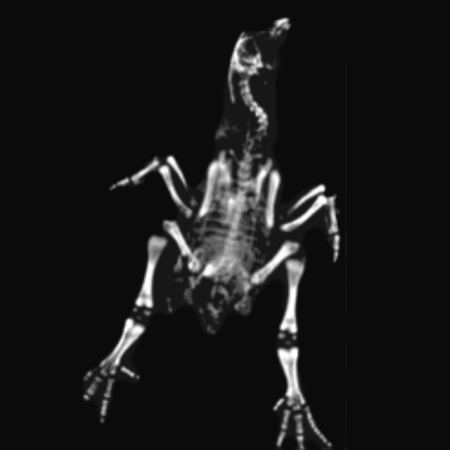
Chicken Bone Mineral Density. Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc
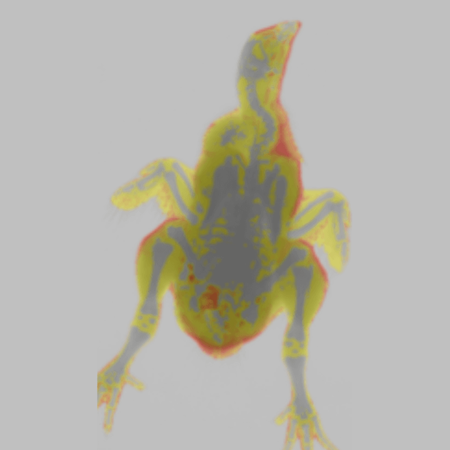
Chicken Color Image. Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc
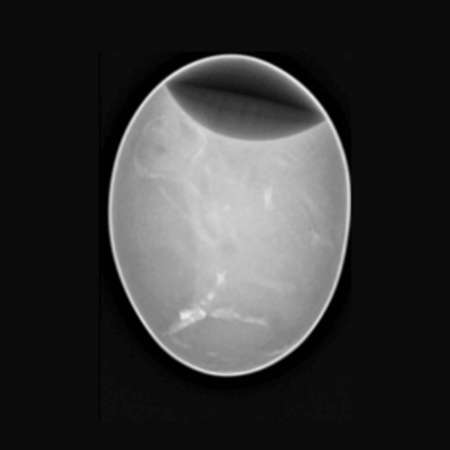
Chicken Egg. Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc
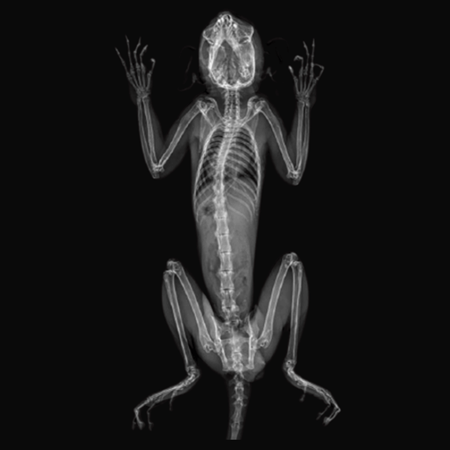
Marmosets. Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc
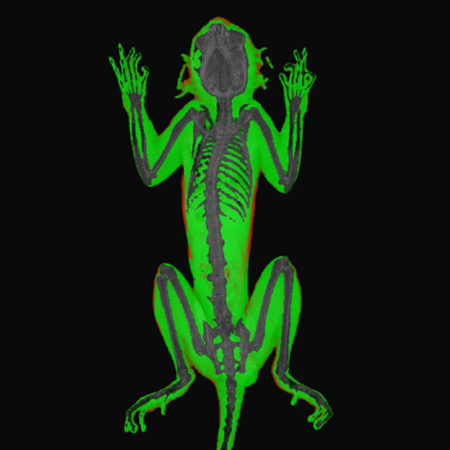

Marmosets. Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc
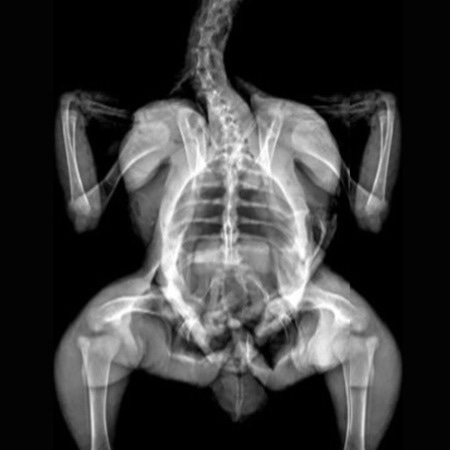
Chicken X-Ray. Image Credit: Scintica Instrumentation Inc