Sponsored Content by AbcamApr 29 2019
Microtubules are cell constituents that display several astounding properties and a unique pattern of behavior during the cell cycle. Microtubules are regulated by several proteins and complexes, and it has long been the endeavor of cell biologists to delineate how tubulin works, how this protein is regulated, and the impact of these mechanisms on the function of microtubules.
Some commonly used assays include immunofluorescent imaging tests using specific antibodies, or agents which lead to alterations of several different components of microtubules. Abcam can provide the appropriate tools for the study of various different microtubular processes.
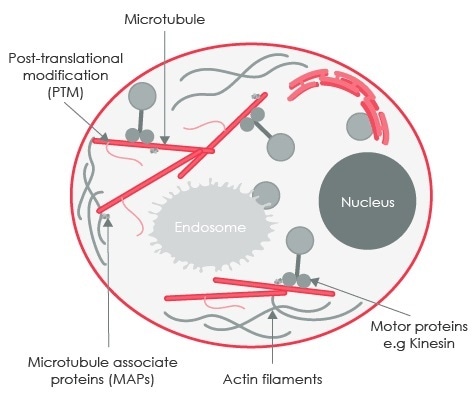
Microtubule Assembly
| Process |
Component |
Function |
Recommended Products |
| Microtubule nucleation |
γ-tubulin |
Forms part of the microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs), and facilitates tubulin dimer polymerization. |
γ-tubulin mouse monoclonal antibody [GTU-88] |
| Microtubule polymerization |
α-tubulin |
Polymerizes with β-tubulin to form microtubules. |
a-tubulin mouse monoclonal antibody [DM1A]
α-tubulin rabbit monoclonal antibody |
| β-tubulin |
Polymerizes with α-tubulin to form microtubules. |
β-tubulin rabbit monoclonal antibody
β-tubulin rabbit polyclonal antibody |
| Microtubule depolymerization |
Kinesins |
The kinesin-13 class depolymerizes microtubule by bending tubulins at microtubule ends. |
KIF2a rabbit polyclonal antibody
MCAK rabbit monoclonal antibody |
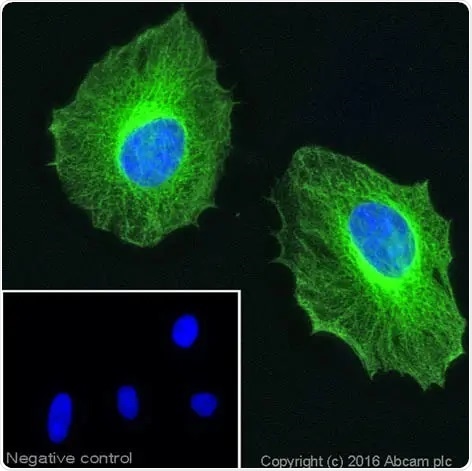
Immunocytochemistry of formaldehyde-fixed HeLa cells stained with anti-beta tubulin antibody (ab6046). The secondary antibody (green) was ab150081 Alexa Fluor® 488 goat anti-rabbit IgG. Nuclear DNA was labeled with DAPI (shown in blue). The negative control is a secondary only assay. Click here to view the full datasheet for ab6046. 10 µl trial size available.
Regulation of Microtubule Dynamics
| Process |
Modification/Component |
Function |
Recommended Products |
| Post-translational modifications (PTMs) |
Acetylation |
Acetylation on the K40 residue contributes to microtubule stability and cell motility. Deacetylation is linked to cell cycle progression and cancer. |
Acetylated α-tubulin (acetyl K40) antibody [EPR16772]
Acetylated α-tubulin antibody [6-11B- 1]
Trichostatin A |
| Detyrosination |
Involved in cell differentiation and microtubule stabilization. |
Detyrosinated α-tubulin antibody
Human Detyrosinated α-tubulin peptide |
| Polyglutamylation |
Occurs when glutamate side chains are formed on glutamate residues. Catalyzed by tubulin tyrosine ligase like (TTLL) enzymes. |
TTLL4 rabbit polyclonal antibody
TTLL6 mouse monoclonal antibody |
| Polyamination |
Contributes to microtubule stabilization. It is irreversible and acts on free tubulin as well as microtubules. |
ZM 449829 - Potent transglutaminase inhibitor |
| Microtubule associated proteins (MAPs) |
Microtubule lattice |
Associates with microtubules and promote assembly and stabilization. |
MAP4 rabbit polyclonal antibody
Tau (phospho S396) rabbit monoclonal antibody |
| Plus-end tracking proteins (+TIPs) |
+TIP recruitment results in microtubule stabilization, continued growth, and protrusion of the plus ends (migration). |
EB3 rabbit monoclonal antibody
Dynamitin mouse monoclonal antibody
CLASP1 rabbit monoclonal antibody |
| Tubulin-binding agents |
Depolymerizing agents |
Inhibits microtubule polymerization, block mitosis and induces cell death. Most agents bind the vinca or colchicine domain. |
Vincristine sulfate
Colchicine
Nocodazole |
| Stabilizing agents |
Disrupts microtubules by promoting polymerization. This also inhibits mitosis and induces cell death. |
Paclitaxel
Docetaxel |
![Acetylation detection: Immunocytochemistry of formaldehyde-fixed HeLa cells stained with anti-alpha tubulin (acetyl K40) antibody [EPR16772] (ab179484). Positive control - Cell treatment with trichostatin A (ab120850), a potent deacetylase inhibitor. Nuclear DNA was labeled with DAPI (shown in blue). Click here to view the full datasheet for ab179484. 10 µl trial size available.](https://www.news-medical.net/image-handler/picture/2018/12/Form_611_Art4_Pic3.jpg)
Acetylation detection: Immunocytochemistry of formaldehyde-fixed HeLa cells stained with anti-alpha tubulin (acetyl K40) antibody [EPR16772] (ab179484). Positive control - Cell treatment with trichostatin A (ab120850), a potent deacetylase inhibitor. Nuclear DNA was labeled with DAPI (shown in blue). Click here to view the full datasheet for ab179484. 10 µl trial size available.
Microtubule Functions
| Process |
Component |
Function |
Recommended Products |
| Motility |
Kinesin |
Aided by ATP, they shuttle vesicular cargo away from the MTOC towards the plus-end of the microtubule. |
Kinesin 5A/B/C rabbit polyclonal antibody
Kinesin 5A rabbit polyclonal antibody
Kinesin 5C rabbit polyclonal antibody |
| Dynein |
Aided by ATP, they shuttle vesicular cargo towards the minus end of microtubules. |
Dynein mouse monoclonal antibody |
| Myosin |
Mainly associates with actin, but also interacts with tubulin for cargo exchange. |
Myosin VIIa rabbit polyclonal antibody
Non-muscle Myosin IIA rabbit monoclonal antibody |
| Mitosis |
Kinetochore |
Interacts with microtubules to maintain the integrity of chromatid spindles. |
HEC1 mouse monoclonal antibody [9G3]
Nuf2 rabbit monoclonal antibody
SPC24 rabbit monoclonal antibody
Mps1 mouse monoclonal antibody [N1] - BSA free |
| Cell migration |
Actin |
Crosstalk between actin and microtubules promotes symmetry break to polarize cells for division, shape changes, and migration. |
CytoPainter Phalloidin-iFluor 488 Reagent
Other colors available |
Actin Statin
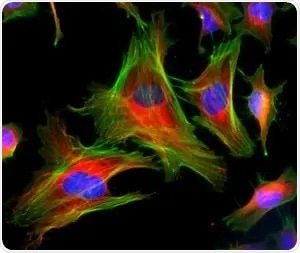
HeLa cells were stained with mouse anti-tubulin followed with a fluorescent red Goat Anti-Mouse IgG, actin filaments were stained with CytoPainter Phalloidin-iFluor 488 Reagent (ab176753), and nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342.
 About Abcam
About Abcam
Abcam is a global life sciences company providing highly validated antibodies and other binders and assays to the research and clinical communities to help advance the understanding of biology and causes of disease.
Abcam’s mission is to serve life scientists to help them achieve their mission faster by listening to their needs, continuously innovating and improving and by giving them the tools, data and experience they want. Abcam’s ambition is to become the most influential life science company for researchers worldwide.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.