Sponsored Content by AbcamMay 2 2019
This article offers a summary of radial glia markers that are in widespread use.
During neurogenesis, there is a transformation of neuroepithelial (NE) cells to radial glia. Epithelial features like tight junctions are downregulated in favor of adherens junctions. Glial hallmarks start to emerge, including astrocyte markers and morphological features like glycogen granules.
Vimentin
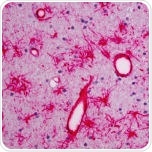
Vimentin is an intermediate filament protein whose expression is upregulated throughout the epithelial to mesenchymal transition of NE cells to radial glia and continues until astrocyte development
Rhesus monkey brain tissue sections stained with anti-vimentin (ab92547).
Vimentin inhibitor and antiangiogenic agent: Withaferin A (ab120644).
PAX 6
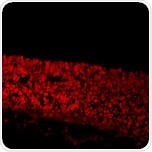
This is a transcription factor that promotes neurgenesis.
Mouse embryonic (E12.5) brain sections stained with anti-PAX6 (ab5790).
HES1 and HES5
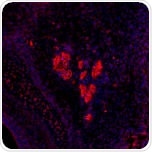
Transcription factors that regulate the maintenance of radial glia.
Mouse brain tissue sections stained with anti-HES5 (red) (ab25374).
Astrocytic Markers: GFAP, GLAST, and BLBP
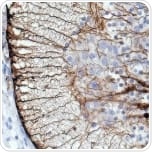
These astrocytic markers emerge as neuroepithelial cells become radial glia.
Rat embryonic (E16) spinal cord sections stained with anti-BLBP (ab32423).
Downregulator of GFAP expression: Methylprednisolone (ab142007).
Adhesion and Extracellular Matrix Molecules: TN-C and N-Cadherin
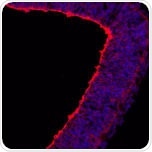
Upregulation of adhesion and extracellular matrix proteins accompanies the transformation of NE cells into radial glia.
Mouse embryonic coronal cortical section stained with anti-N -cadherin (red) (ab76011).
Nestin
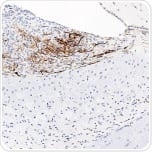
This is an intermediate filament protein in NE cells and radial glia, whose expression persists until astrocyte development.
Rat adult brain tissue sections stained with anti-nestin (ab6142).
SOX2
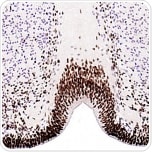
SOX2 is a transcription factor and the first marker of the neural plate. It is shown in proliferating cells and those that acquire glial fates, but downregulated in post-mitotic neurons.
Chicken embryonic (E7) brain tissue sections stained with anti-SOX2 (ab97959).
References and Further Reading
- Bargagna-Mohan, P. et al. The tumor inhibitor and antiangiogenic agent withaferin A targets the intermediate filament protein vimentin. Chem. Biol. 14, 623–34 (2007).
- Bylund, M., Andersson, E., Novitch, B. G. & Muhr, J. Vertebrate neurogenesis is counteracted by Sox1-3 activity. Nat Neurosci 6, 1162–1168 (2003).
- Heins, N. et al. Glial cells generate neurons: the role of the transcription factor Pax6. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 308–315 (2002).
- Kageyama, R., Ohtsuka, T. & Kobayashi, T. Roles of Hes genes in neural development. Development Growth and Differentiation 50, (2008).
- Kriegstein, A. & Alvarez-Buylla, A. The glial nature of embryonic and adult neural stem cells. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 32, 149–84 (2009).
- Kriegstein, A. R. & Götz, M. Radial glia diversity: A matter of cell fate. Glia 43, 37–43 (2003).
- Kriegstein, A. & Alvarez-Buylla, A. The glial nature of embryonic and adult neural stem cells. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 32, 149–84 (2009).
- Lamouille, S., Xu, J. & Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 15, 178–96 (2014).
- Liu, W.-L. et al. Methylprednisolone inhibits the expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein and chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans in reactivated astrocytes. Glia 56, 1390–400 (2008).
- Papanayotou, C. et al. A mechanism regulating the onset of Sox2 expression in the embryonic neural plate. Plos Biol 6, e2 (2008).
 About Abcam
About Abcam
Abcam is a global life sciences company providing highly validated antibodies and other binders and assays to the research and clinical communities to help advance the understanding of biology and causes of disease.
Abcam’s mission is to serve life scientists to help them achieve their mission faster by listening to their needs, continuously innovating and improving and by giving them the tools, data and experience they want. Abcam’s ambition is to become the most influential life science company for researchers worldwide.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.