Sponsored Content by AbcamMay 6 2019
Abcam provides a full array of HDAC antibodies from all the four classes of deacetylase.
Many vital cell programs such as regulation of transcription, progression of the cell cycle and other developmental occurrences depend upon the two-way acetylation-deacetylation of highly conserved lysine residues inside the N-terminal tail domains of the histones at the DNA core.
The acetylation of histones proceeds dynamically, in accordance with the level of activity of two competing sets of enzymes, the histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs).
The activity of HDACs are in many cases, though not universally, accompanied by the repression of transcription and condensation of nucleosomes.
Over a dozen HDACs have been identified. They belong to four classes overall, from I to IV.
Class I HDAC Antibodies
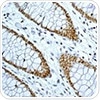
Class I HDACs are localized chiefly in the nucleus, and have a common deacetylase domain that is homologous to the extent of about 45% to 93%.
The image above depicts staining of human colonic tissue with HDAC1 using ab109411.
Class II HDAC Antibodies

Class II HDACs are markedly bigger molecules, with the molecular weight being about double that of class I enzymes. In this class, the enzymes are capable of moving fast between the cytosol and the nucleus, and thus help with active nuclear transport.
The image above shows HDAC9 staining of human colon tissue using ab109446.
Class III HDAC Antibodies
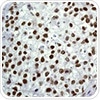
Class III HDACs are homologous to yeast strain Sir2 but they are differentiated from class I and class II, being enzymes that are activated by NADH, and are localized in both nucleus and cytoplasm.
The image above shows SIRT1 staining of human lung squamous carcinoma using ab32441.
Class IV HDAC Antibodies

Class IV HDACs consist at present of only a single enzyme, namely, HDAC11. This deacetylase requires zinc ions for activation. It has common conserved residues in the catalytic core that it shares with other HDAC classes, namely, class I and class II.
The image above shows HDAC11 western blot of Jurkat, HCT-116, MCF7 and HepG2 cell lysates using ab166907.
 About Abcam
About Abcam
Abcam is a global life sciences company providing highly validated antibodies and other binders and assays to the research and clinical communities to help advance the understanding of biology and causes of disease.
Abcam’s mission is to serve life scientists to help them achieve their mission faster by listening to their needs, continuously innovating and improving and by giving them the tools, data and experience they want. Abcam’s ambition is to become the most influential life science company for researchers worldwide.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.